Smallest Sub-array with sum greater than a given value in C++
Smallest Sub-array with sum greater than a given value in C++
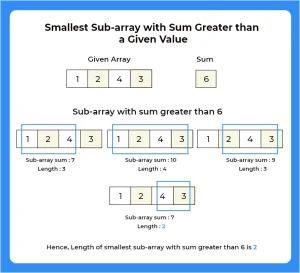
Here, in this page we will discuss the program to find smallest sub-array with sum greater than a given value in C++ programming language. We are given with an unsorted array contain non-negative integers we need to find a continuous sub-array of minimum length whose sum is greater than the given sum
Example :
- Input : arr[] : {1, 4, 0, 0, 2, 6, 3} and sum = 6
- Output : Sub-array with greater than given sum found from index 4 to 5.
- Explanation : In the given array sub-array from index 4 to 5 will give sum 8 as(2+6=8) which is greater than value 6 , is the smallest sub-array with sum greater than the given sum.

Method 1 (Brute force approach) :
- Take the variable named n to store the size of the array, input by the user.
- Declare an array of size n and take n elements of the array from the user.
- Now, declare another variable say sum, that store the value of the sum, input by the user.
- Call the function that will return the length.
- Inside the function, declare a variable min_length with value INT_MAX
- Run a loop from 0 to n and declare a variable curr_sum with value of i-th element.
- Chech if curr_sum > sum, if so then return 1.
- Otherwise, run another loop inside it, that will traverse from i+1 to n index, and add the value of j-th element to curr_sum.
- If curr_sum > sum and (j-i+1 < min_length), then update min_length to (j-i+1)
- After coming out from the nested loop return min_length.
- Now, in main function check if the return value from the function == INT_MAX then print “No such array found”
- Else print the return value from the function
Time and Space Complexity
- Time-Complexity : O(n*2)
- Space-Complexity : O(1)
Code for smallest sub-array with sum greater than a given value in C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int fun(int a[], int n, int sum){
int min_length=INT_MAX;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int curr_sum = a[i];
if(curr_sum>sum) return 1;
for(int j=i+1; j<n; j++){
curr_sum += a[j];
if(curr_sum>sum and min_length>(j-i+1))
min_length = (j-i+1);
}
}
return min_length;
}
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
int a[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>a[i];
int sum;
cin>>sum;
if(fun(a, n, sum)==INT_MAX)
cout<<"No such subarray found";
else cout<<fun(a, n, sum);
}
Input :
5
1 2 3 4 5
5
Output :
1
Method 2 (Efficient approach) :
- Take the variable named n to store the size of the array, input by the user.
- Declare an array of size n and take n elements of the array from the user.
- Now, declare another variable say sum, that store the value of the sum, input by the user.
- Call the function that will return the length.
- Inside the function, declare a variable min_length with value INT_MAX and a variable curr_sum = 0.
- Declare two variables say i and j initialized with 0.
- Run a while loop that terminate when, j >= n.
- Inside that while loop run
while (curr_sum <= sum && j < n)
curr_sum += a[j++]; Now, run another while loop as,
while (curr_sum > x && start < n) {
// Update minimum length if needed
if (j - i < min_length)
min_length = j - i
curr_sum -= a[i++];
}- After termination of loop return min_length.
- After coming out from the nested loop return min_length.
- Now, in main function check if the return value from the function == INT_MAX then print “No such array found”
- Else print the return value from the function
Time and Space Complexity
- Time-Complexity : O(n)
- Space-Complexity : O(1)
Code for smallest sub-array with sum greater than a given value in C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int fun(int a[], int n, int sum){
int curr_sum = 0, min_length = INT_MAX;
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (j < n) {
while (curr_sum <= sum && j < n)
curr_sum += a[j++];
while (curr_sum > sum && i < n) {
if (j - i < min_length)
min_length = j - i;
curr_sum -= a[i++];
}
}
return min_length;
}
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
int a[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
cin>>a[i];
int sum;
cin>>sum;
if(fun(a, n, sum)==INT_MAX)
cout<<"No such subarray found";
else cout<<fun(a, n, sum);
}
Input :
5
1 2 3 4 5
5
Output :
1
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription




Login/Signup to comment