Circular Queue using Linked List in C++
Circular Queue in C++
Circular Queue is a category of Queue data structure. If we equal the linear queue with the linear single linked list, the Circular queue can be equaled by the circular linked list. Here is an article about how to create a circular queue using a circular linked list in C++. Here the circular linked list will be implemented using class.

Circular Queue using Linked List in C++
Circular Queue using Linked List in C++ is a dynamic implementation where the last node connects back to the first, forming a circular structure. It efficiently manages memory as nodes are created and deleted during runtime. This approach helps avoid overflow issues that typically occur in array based circular queues.
- Uses linked list nodes, allowing flexible size without fixed capacity limits.
- Rear pointer links back to front, ensuring continuous circular traversal and efficient enqueue/dequeue operations.
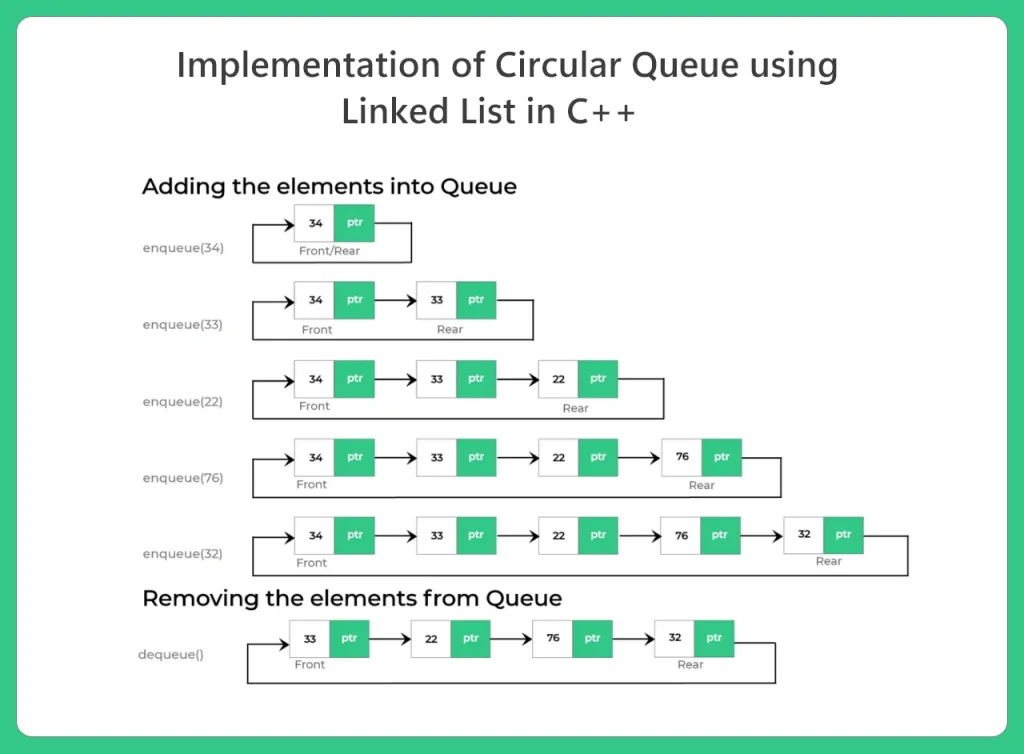
Algorithm to Create Circular Queue (using a Linked List Class)
In the circular queue, the back (Where elements will be pushed) will be pointing the front (From where elements are to be popped out). That is the main logic behind circular queues, like circular linked lists. Here is the algorithm to implement it in C++.
- A class is made with the name Node, that represents the nodes in the queue. In our code, the nodes are actually holding an integer value, and a pointer of the same type as the node class.
- A class is made with the named Queue or Circular_Queue. It is actually a class that will make an array of the Node type.
- In the default constructor, the front and back will be NULL pointer, to show the queue is empty.
- The enqueue function (Pushing a node into the queue) will be getting a value or a node value in the argument, and it will be pushing the element in the circular queue using the back pointer. And the new back pointer will be pointing to the front.
- The Dequeue function will be deleting the node in the front position. And then the back pointer will be pointing to the new front. If the queue becomes null, the front and back both will point to null.
- The show function will be showing the total circular queue starting from the back to the front.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
C++ Program for the implementation of circular queue using Linked Lists
A C++ program for implementing a circular queue using linked lists creates a dynamic structure where each node points to the next, and the last node loops back to the front. This method eliminates fixed-size limitations and efficiently supports enqueue and dequeue operations. It is commonly used when continuous memory blocks are not ideal.
- No overflow unless memory is full, as nodes are created dynamically during runtime.
- Rear node always links back to the front node, maintaining the circular behavior of the queue.
//Circular queue C++ program
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
class CircularQueue
{
private:
Node * front;
Node *rear;
public:
CircularQueue ()
{
front = rear = nullptr;
}
void enqueue (int data)
{
Node *newNode = new Node ();
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = nullptr;
if (front == nullptr)
{
front = rear = newNode;
rear->next = front;
}
else
{
rear->next = newNode;
rear = newNode;
rear->next = front;
}
cout << data << " has been enqueued." << endl;
}
void dequeue ()
{
if (front == nullptr)
{
cout << "Queue is empty." << endl; } else if (front == rear) { Node *temp = front; front = rear = nullptr; delete temp; } else { Node *temp = front; front = front->next;
rear->next = front;
delete temp;
}
}
void display ()
{
if (front == nullptr)
{
cout << "Queue is empty." << endl;
}
else
{
Node *temp = front;
cout << "Circular Queue: ";
do
{
cout << temp->data << " "; temp = temp->next;
}
while (temp != front);
cout << endl;
}
}
};
int main ()
{
CircularQueue q;
q.enqueue (10);
q.enqueue (20);
q.enqueue (30);
q.enqueue (40);
q.display ();
q.dequeue ();
q.dequeue ();
q.display ();
q.enqueue (50);
q.enqueue (60);
q.display ();
return 0;
}
Output:
10 has been enqueued. 20 has been enqueued. 30 has been enqueued. 40 has been enqueued. Circular Queue: 10 20 30 40 Circular Queue: 30 40 50 has been enqueued. 60 has been enqueued. Circular Queue: 30 40 50 60
Explanation:
- The queue uses a circular linked list, where rear->next always points back to front, ensuring circular behavior and efficient traversal.
- In enqueue(), if the queue is empty, both front and rear are set to the new node; otherwise, the new node is added at the end and the circular link is reconnected.
- The dequeue() function handles three cases: empty queue, single-node queue, and multi-node queue, ensuring proper memory deletion and pointer updates.
- The display() function uses a do-while loop to traverse the circular queue, stopping when the traversal reaches front again.
- Dynamic memory allocation (new Node) is used for each insertion, making the queue scalable without size limits like array-based implementations.
Time & space complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Enqueue | O(1) | O(1) |
| Dequeue | O(1) | O(1) |
| Display / Traversal | O(n) | O(1) |
| Overall Space Usage | O(n) | — |
To wrap it up:
The article on implementing a circular queue using a linked list in C++ clearly demonstrates how linking the rear node back to the front node enables continuous enqueuing and dequeuing without wasted space unlike a linear queue structure.
By defining a Node class and a Circular Queue class with enqueue, dequeue, and display methods, it shows both the logic and the complete code example, making it easy to understand and implement in practice.
FAQs
A circular queue eliminates wasted space by reusing freed positions. It ensures efficient memory use and supports continuous enqueue and dequeue operations.
The rear pointer always points to the last inserted node. Its next pointer connects to the front node to maintain the circular structure.
When the queue is empty, both front and rear are set to the new node. The node then points to itself, forming the circular link.
Overflow occurs only when system memory is full. Otherwise, linked list–based queues expand dynamically.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment