Circular Queue using Array in C++
Circular Queue in C++
A basic linear data structure is Linear queue, where you can get First in First out feature for nodes. Circular Queue is a implementation of that very linear queue in which you can overcome the problems regarding linear fixed length queues. Here is an article on how to implement a Circular Queue using array in C++.

Queue VS Circular Queue?
Let’s say, the queue is implemented using an array. So everytime you pop out one element, the front pointer in the array will be increasing by one. After popping out many products, the queue may be impossible to access for storage reasons, even if you don’t have any element in it.
That’s why at first the concept of Circular queue came in. In Circular queue, even if you change the front, after some time if the last pointer is accessed with the front pointer, after popping out again, the front pointer will again reach the first position.
Members of Circular Queue:
- Front : From where nodes are to be popped out.
- Back : Back or Rear, where nodes are pushed into.
- Enqueue : Pushing a new node at the back.
- Dequeue : Popping out nodes from front, if any.
- Overflow : If the Circular Queue has predefined storage and is full.
- Underflow : If the Circular Queue is empty.
- Size : Number of nodes present.
If we create a queue using an array, where enqueuing and dequeuing takes O(1) time and space complexity each, one the queue is full, you cannot insert new elements, also sometimes when you delete elements, the queue may be totally empty but still the front will be in the back most position, so you can’t insert any value over there.
In this meantime, a circular queue comes into the picture. In Circular queue, the front and back only overlap when the queue is empty, but there is no problem when you want to delete elements and insert them again. The front pointer wanders around the queue in the circular path.
Also : Circular Queue using Array
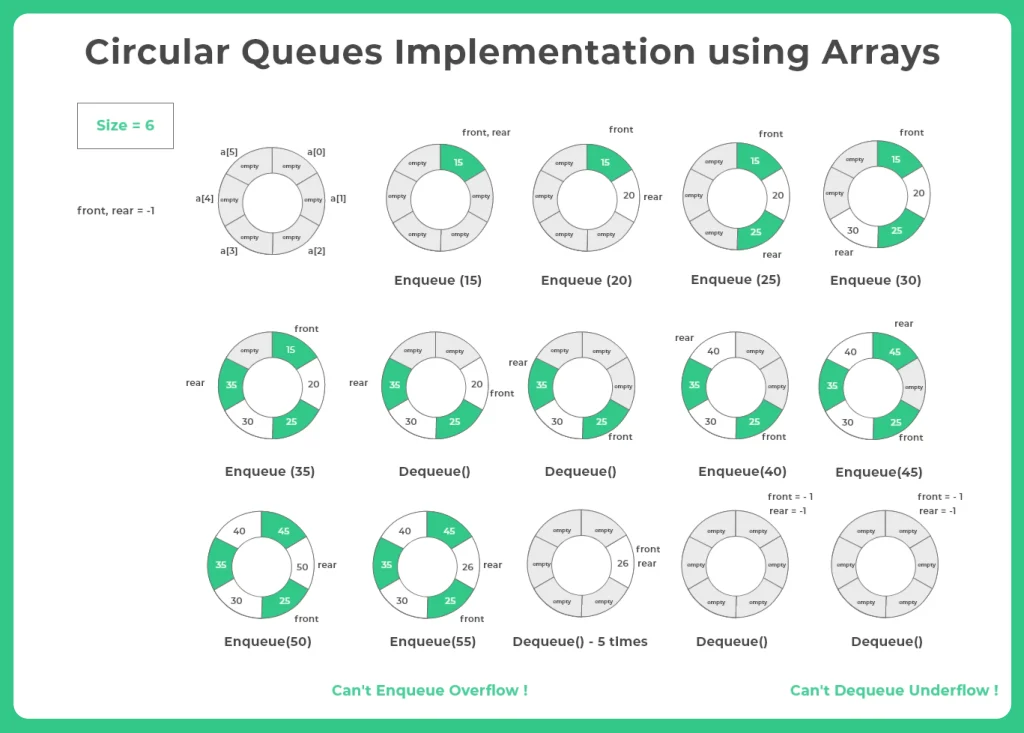
C++ Program for the implementation of circular queue using Array
A C++ program for implementing a circular queue using an array helps efficiently manage elements in a fixed-size buffer by utilizing memory in a circular manner. It ensures fast insertion and deletion while avoiding the wastage of unused space.
- It uses front and rear pointers to track the queue’s current state.
- The modulo operator is used to wrap around the array, enabling circular movement.
//Circular queue C++ program
#include<iostream>
#define MAX_SIZE 100 // Maximum size of the queue
using namespace std;
class CircularQueue
{
private:
int front, rear;
int arr[MAX_SIZE];
public:
CircularQueue ()
{
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
// Function to check if the queue is full
bool isFull ()
{
if ((front == 0 && rear == MAX_SIZE - 1)
|| (rear == (front - 1) % (MAX_SIZE - 1)))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Function to check if the queue is empty
bool isEmpty ()
{
if (front == -1)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Function to add an element to the queue
void enQueue (int value)
{
if (isFull ())
{
cout << "Queue is full." << endl;
}
else
{
if (front == -1)
{
front = 0;
}
rear = (rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
arr[rear] = value;
cout << "Enqueued element: " << value << endl;
}
}
// Function to remove an element from the queue
int deQueue ()
{
int element;
if (isEmpty ())
{
cout << "Queue is empty." << endl;
return -1;
}
else
{
element = arr[front];
if (front == rear)
{
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
else
{
front = (front + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
}
cout << "Dequeued element: " << element << endl;
return element;
}
}
// Function to display the elements in the queue
void display ()
{
if (isEmpty ())
{
cout << "Queue is empty." << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Elements in the queue: ";
int i;
for (i = front; i != rear; i = (i + 1) % MAX_SIZE)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}
}
};
int main ()
{
CircularQueue q;
q.enQueue (10);
q.enQueue (20);
q.enQueue (30);
q.enQueue (40);
q.display ();
q.deQueue ();
q.deQueue ();
q.display ();
q.enQueue (50);
q.enQueue (60);
q.display ();
return 0;
}
Output:
Enqueued element: 10 Enqueued element: 20 Enqueued element: 30 Enqueued element: 40 Elements in the queue: 10 20 30 40 Dequeued element: 10 Dequeued element: 20 Elements in the queue: 30 40 Enqueued element: 50 Enqueued element: 60 Elements in the queue: 30 40 50 60
Explanation:
- The class initializes front and rear to -1, which indicates the circular queue is empty at the beginning.
- The isFull() function uses circular conditions to detect when the queue has wrapped around and reached maximum capacity.
- The enQueue() function inserts elements by moving rear circularly using (rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE, ensuring the queue behaves like a ring buffer.
- The deQueue() function removes elements from front and resets both pointers to -1 when the last element is removed.
- The display() function loops from front to rear using modular arithmetic to correctly print the circular queue elements in order.
Time & Space Complexity:
| Operation | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| isFull() | O(1) | O(1) |
| isEmpty() | O(1) | O(1) |
| enQueue() | O(1) | O(1) |
| deQueue() | O(1) | O(1) |
| display() | O(n) | O(1) |
| Total Space Used | – | O(MAX_SIZE) = O(n) |
To wrap it up:
The circular queue implemented using an array provides an efficient way to reuse available space by wrapping around when the end of the array is reached, thereby eliminating wasted slots that occur in a linear queue.
With constant-time operations for enqueue and dequeue and a fixed amount of additional memory, this implementation is both performant and predictable, making it a solid choice for queue operations where maximum size is known in advance.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
FAQs
When front and rear are equal after a dequeue, it means the queue becomes empty. Both pointers are reset to -1 to indicate no elements remain.
The circular behavior is maintained using the modulo operator (index % size). This ensures the pointer wraps back to the start when it reaches the end.
Yes, overflow can occur if rear is just behind front in circular order. This condition prevents overwriting valid data even if the array has unused gaps.
Using an array makes indexing extremely fast and predictable. It offers constant-time access without needing dynamic memory allocation.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment