Find the Union and Intersection of the two sorted arrays in C
Union and Interaction of the two sorted arrays in C
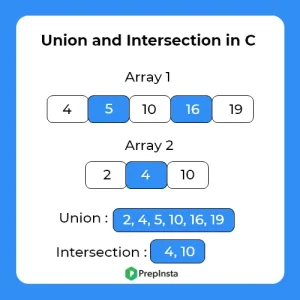
Here, in this page we will discuss the program to find the union and interaction of two sorted arrays in C . We are given with two sorted arrays and we have to find the union and interaction of the given two arrays.
Example : Input : arr1[4] = {1, 6, 9 ,10} arr2[3] = {10, 11, 90}
Output : Union = 1 6 9 11 90
Interaction = 10

Algorithm to find Union :
- Use two index variables i and j, initial values i = 0, j = 0
- If arr1[i] is smaller than arr2[j] then print arr1[i] and increment i.
- If arr1[i] is greater than arr2[j] then print arr2[j] and increment j.
- If both are same then print any of them and increment both i and j.
- Print remaining elements of the larger array.
Algorithm to find Interaction :
- Use two index variables i and j, initial values i = 0, j = 0.
- If arr1[i] is smaller than arr2[j] then increment i.
- If arr1[i] is greater than arr2[j] then increment j.
- If both are same then print any of them and increment both i and j.
Code to find Union and Interaction of the two sorted arrays in C
#include <stdio.h>
void printUnion(int arr1[], int arr2[], int m, int n)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < m && j < n) {
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
printf("%d ",arr1[i++]);
else if (arr2[j] < arr1[i])
printf("%d ",arr2[j++]);
else {
printf("%d ",arr2[j++]);
i++;
}
}
/* Print remaining elements of the larger array */
while (i < m)
printf("%d ",arr1[i++]);
while (j < n)
printf("%d ",arr2[j++]);
}
void printIntersection(int arr1[], int arr2[], int m, int n)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < m && j < n) {
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
i++;
else if (arr2[j] < arr1[i])
j++;
else /* if arr1[i] == arr2[j] */
{
printf("%d ",arr2[j]);
i++;
j++;
}
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main()
{
int m, n;
scanf("%d", &m);
int arr1[m];
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) scanf("%d", &arr1[i]);
scanf("%d", &n);
int arr2[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) scanf("%d", &arr2[i]);
// Function calling
printf("Union : ");
printUnion(arr1, arr2, m, n);
printf("\nIntersection ");
printIntersection(arr1, arr2, m, n);
return 0;
}
Output :
5
1 2 3 4 5
4
1 2 3 4
Union : 1 2 3 4 5
Intersection : 1 2 3 4
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription



Login/Signup to comment