C Program to search an element in a linked list
To find an element in a linked list
C Program to search an element in a linked list. In this article, we will find an element just like we find an element in an array which is the most common operation performed on any data structure.
For Example:-
- Input: 5 -> 6 -> 9 -> 3 -> 47
- Search Item: 9
- Output: Element found position 3

Methods Discussed
We will discuss two methods in this post –
- Method 1: Iterative
- Method 2: Recursive
Structure for creating node in the linked list as follows:-
struct node
{
int data; // Data
struct node *next; // For address of next node
}; Implementation for C Program to search an element in a linked list:-
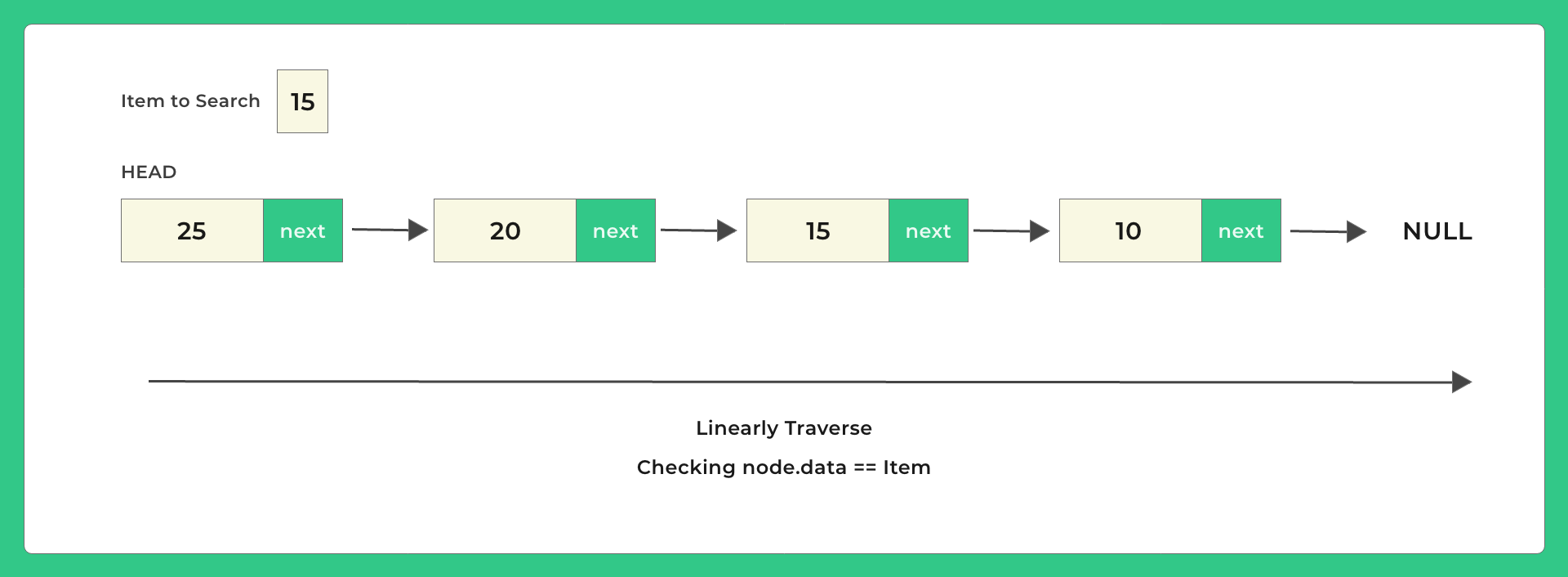
- Initialize head = Null
- Add a few items to the Linked List
- Take input from the user for the item he wants to search
- Linearly traverse the Linked List from head to the end until you hit the null node
- For each node check if its data value == item user wants to search
- Return index of node where data was found else return -1
Method 1 (Iterative)
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void display (struct Node *node)
{
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n");
}
int searchElement (struct Node *head, int item)
{
struct Node *current = head; // Initialize current
int index = 0;
// traverse till then end of the linked list
while (current != NULL)
{
if (current->data == item)
{
return index;
}
current = current->next;
index++;
}
return -1;
}
int main ()
{
int item;
//creating 4 pointers of type struct Node
//So these can point to address of struct type variable
struct Node *head = NULL;
struct Node *node2 = NULL;
struct Node *node3 = NULL;
struct Node *node4 = NULL;
// allocate 3 nodes in the heap
head = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node2 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node3 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node4 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
head->data = 10; // data set for head node
head->next = node2; // next pointer assigned to address of node2
node2->data = 15;
node2->next = node3;
node3->data = 20;
node3->next = node4;
node4->data = 25;
node4->next = NULL;
printf ("Linked List: ");
display (head);
printf ("Enter element to search: ");
scanf ("%d", &item);
int index = searchElement (head, item);
if (index == -1)
printf ("Item not found");
else
printf ("Item found at position: %d", index + 1);
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List: 10 15 20 25 Enter element to search: 20 Item found at position: 3
Method 2 (Recursive)
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void display (struct Node *node)
{
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n");
}
int searchElement (struct Node *head, int item, int index)
{
// Base case
if (head == NULL)
return -1;
// If data is present in current node, return true
if (head->data == item)
return index;
// not present here will check for next position
// in next recursive iteration
index++;
// Recur for remaining list
return searchElement (head->next, item, index);
}
int main ()
{
int item;
//creating 4 pointers of type struct Node
//So these can point to address of struct type variable
struct Node *head = NULL;
struct Node *node2 = NULL;
struct Node *node3 = NULL;
struct Node *node4 = NULL;
// allocate 3 nodes in the heap
head = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node2 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node3 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node4 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
head->data = 10; // data set for head node
head->next = node2; // next pointer assigned to address of node2
node2->data = 15;
node2->next = node3;
node3->data = 20;
node3->next = node4;
node4->data = 25;
node4->next = NULL;
printf ("Linked List: ");
display (head);
printf ("Enter element to search: ");
scanf ("%d", &item);
int index = searchElement (head, item, 0);
if (index == -1)
printf ("Item not found");
else
printf ("Item found at position: %d", index + 1);
return 0;
}
Output
Linked List: 10 15 20 25 Enter element to search: 10 Item found at position: 1



Login/Signup to comment