Run
#include<stdio.h>
void countFrequency(int *arr, int size){
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++){
int flag = 0;
int count = 0;
// Counting of any element has to be delayed to its last occurrence
for (int j = i+1; j < size; j++){
if (arr[i] == arr[j]){
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
// The continue keyword is used to end the current iteration
// in a for loop (or a while loop), and continues to the next iteration
if (flag == 1)
continue;
for(int j = 0;j<=i;j++){
if(arr[i]==arr[j])
count +=1;
}
printf("%d : %d\n", arr[i], count);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {5, 8, 5, 7, 8, 10};
int size = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
countFrequency(arr, size);
return 0;
}






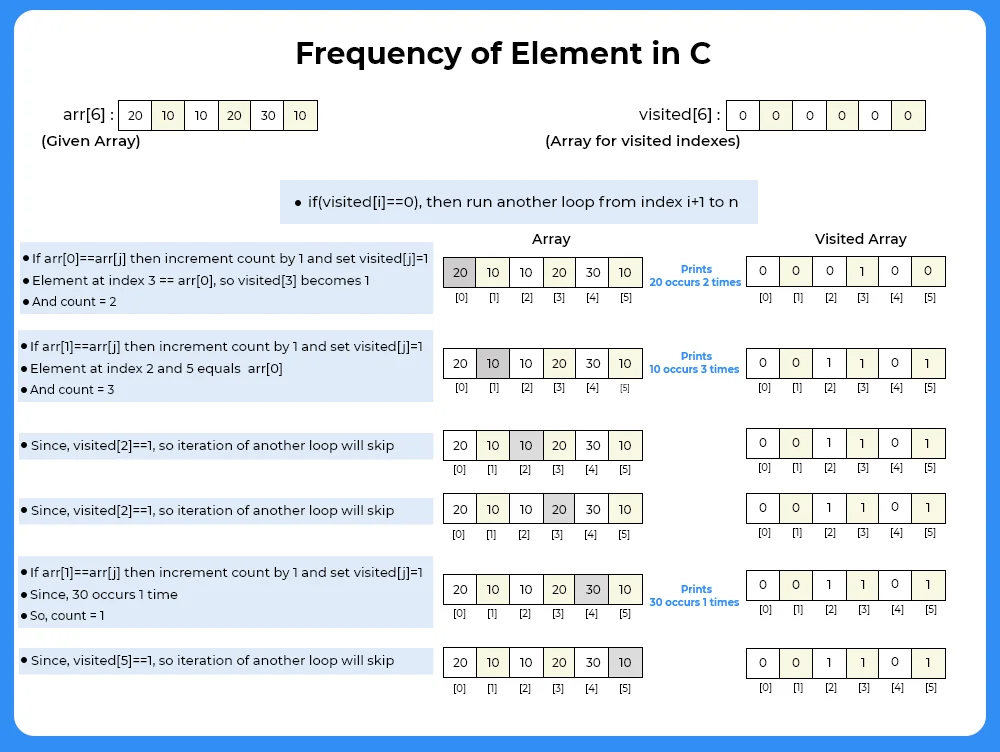

import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
int[] arr= {10,20,30,20,50,50,40};
// Hashamap(arr);
// boolean_array(arr);
}
public static void boolean_array(int[] arr){
boolean[] bool=new boolean[arr.length];
Arrays.fill(bool,false);
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
int count=1;
if(bool[i]!=true){
bool[i]=true;
for(int j=i+1;j<arr.length;j++){
if(arr[i]==arr[j]){
count++;
bool[j]=true;
}
}
System.out.println(arr[i]+" "+count);
}
// System.out.println(arr[i]+" "+count);
}
}
public static void Hashamap(int arr[]){
HashMap map=new HashMap();
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(map.containsKey(arr[i])){
map.put(arr[i],map.get(arr[i])+1);
}
else{
map.put(arr[i],1);
}
}
for(Map.Entry entry:map.entrySet()){
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+” “+entry.getValue());
}
}
}
In method 1, when I am giving (10,20,30,20,50,50,40) The output is :
20 occurs 2 times
50 occurs 2 times
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
int[] arr= {10,20,30,20,50,50,40};
HashMap map=new HashMap();
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(map.containsKey(arr[i])){
map.put(arr[i],map.get(arr[i])+1);
}
else{
map.put(arr[i],1);
}
}
for(Map.Entry entry:map.entrySet()){
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+” “+entry.getValue());
}
}
}