C Program to delete alternate nodes of a Linked List
Delete alternate nodes of a Linked List
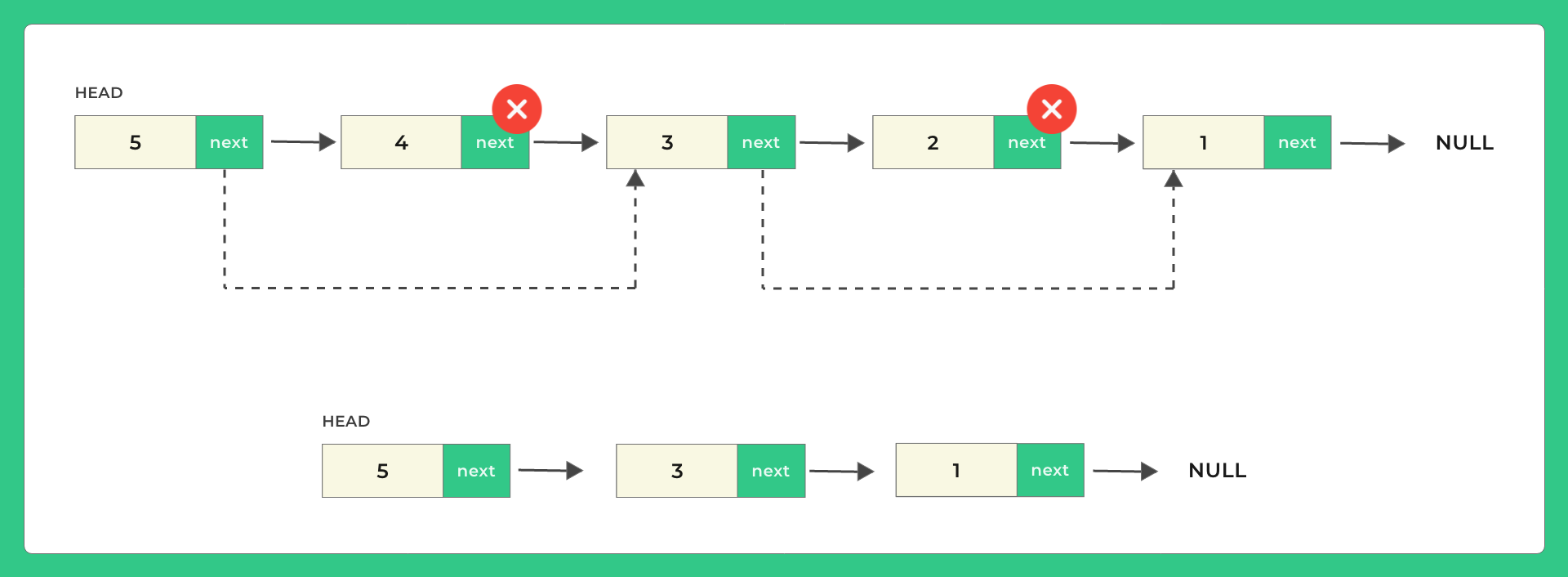
C Program to delete alternate nodes of a Linked List. In this program, we want to remove alternate nodes from the singly linked list which is start from the second node of the linked list and remove all the alternate nodes of it.
For Example,
- Input: 1 -> 3 -> 5 -> 7 -> 9
- Output: 1 -> 5 -> 9

Working for deleting alternate nodes of a Singly Linked List:-
- Take linked list input
- Initialize prev and curr, assign prev = head & curr = head->next
- Change next pointer of previous to curr->next, so link between prev & curr is broken
- Now, curr is unreachable, free its memory
- Move prev to next node in linked list
- Move curr to next node.
- Keep doing all above steps until you reach end of the node
Structure of creating a node of the singly linked list:-
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
}; 
C Program to delete alternate nodes of a Linked List
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//Structure of node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
//display the nodes
void display (struct Node *node)
{
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n");
}
// function to delete alternate nodes
void delete_Alt (struct Node *head)
{
if (head == NULL)
return;
// prev req so its next node can be changed
struct Node *prev = head;
struct Node *curr = head->next;
while (prev != NULL && curr != NULL)
{
// changing next of previous node
prev->next = curr->next;
// free the memory
free (curr);
// Update prev and curr
prev = prev->next;
if (prev != NULL)
curr = prev->next;
}
}
int main ()
{
//creating 4 pointers of type struct Node
//So these can point to address of struct type variable
struct Node *head = NULL;
struct Node *node2 = NULL;
struct Node *node3 = NULL;
struct Node *node4 = NULL;
struct Node *node5 = NULL;
// allocate 4 nodes in the heap
head = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node2 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node3 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node4 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node5 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
head->data = 5; // data set for head node
head->next = node2; // next pointer assigned to address of node2
node2->data = 4;
node2->next = node3;
node3->data = 3;
node3->next = node4;
node4->data = 2;
node4->next = node5;
node5->data = 1;
node5->next = NULL;
printf ("Before deletion: ");
display (head);
delete_Alt (head);
printf ("After deletion: ");
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
Before deletion: 5 4 3 2 1 After deletion: 5 3 1
Above has a time complexity of O(N)
Now let us look at the recursive approach for the same.
Now let us look at the recursive approach for the same.
Method 2 (using Recursion)
Below also has O(N) time complexity due to n order recursive calls.
Run
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//Structure of node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
//display the nodes
void display (struct Node *node)
{
//as linked list will end when Node is Null
while (node != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
printf ("\n");
}
// function to delete alternate nodes
void delete_Alt (struct Node *curr)
{
if (curr == NULL)
return;
// assigning node to current node's next
struct Node *del_node = curr->next;
if (del_node == NULL)
return;
// changing next node of curr to alternative node
// del_node is no more part of Linked List
curr->next = del_node->next;
// memory for del_node also freed
free (del_node);
// Recursively call for the new next of curr
delete_Alt (curr->next);
}
int main ()
{
//creating 4 pointers of type struct Node
//So these can point to address of struct type variable
struct Node *head = NULL;
struct Node *node2 = NULL;
struct Node *node3 = NULL;
struct Node *node4 = NULL;
struct Node *node5 = NULL;
// allocate 4 nodes in the heap
head = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node2 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node3 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node4 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
node5 = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
head->data = 5; // data set for head node
head->next = node2; // next pointer assigned to address of node2
node2->data = 4;
node2->next = node3;
node3->data = 3;
node3->next = node4;
node4->data = 2;
node4->next = node5;
node5->data = 1;
node5->next = NULL;
printf ("Before deletion: ");
display (head);
delete_Alt (head);
printf ("After deletion: ");
display (head);
return 0;
}
Output
Before deletion: 5 4 3 2 1 After deletion: 5 3 1



Login/Signup to comment