Maximum Average Sub-array of K length in C
Maximum Average Sub-array of K length
On this page we will discuss about maxium average sub-array of K length in C language . we are given with a sequence of N integers, a[1], a[2], , , , a[N] of N length and a integer K integer.
We have to Find out the maximum possible average value of sub-array of K length.

Maximum Average Sub-array of K length in C
The maximum average subarray of length k refers to a contiguous subarray of length k within a given array of numbers, whose average is maximum among all possible subarrays of length k in that array. In other words, it is the subarray of k consecutive elements whose sum is the largest possible among all subarrays of k consecutive elements in the array.
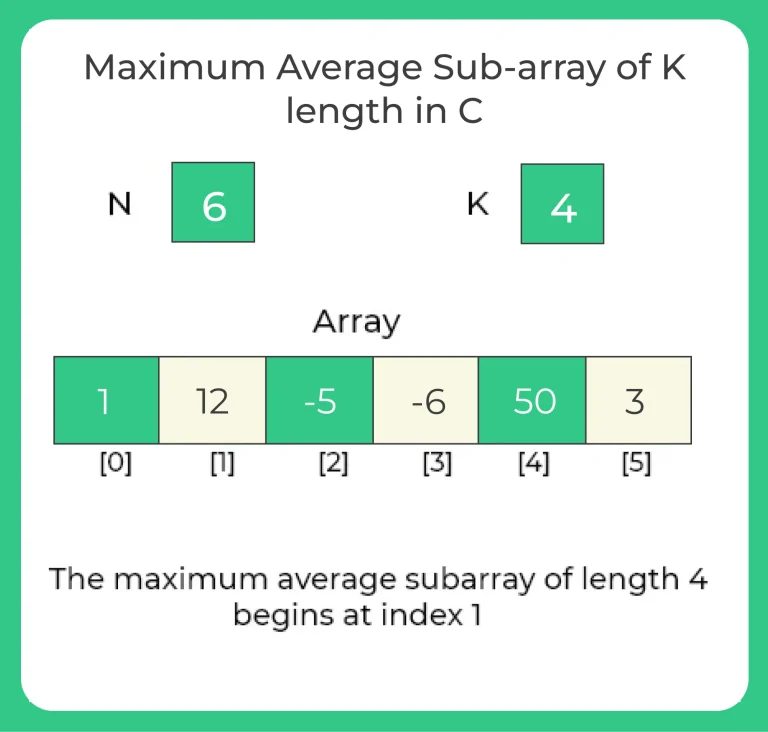
For example,consider the array
[1, 12, -5, -6, 50, 3] and k=4.
The subarrays of length 4 are [1, 12, -5, -6], [12, -5, -6, 50], [-5, -6, 50, 3], and their averages are 0.5, 12.75, and 10.5 respectively. The maximum average subarray of length 4 in this case is [12, -5, -6, 50], whose average is 12.75.
Algorithm:
Create an auxiliary array of size n.
Store cumulative sum of elements in this array.
Let’s the array be csum[]. csum[i] stores sum of elements from arr[0] to arr[i].
Once we have csum[] array with us, we can compute sum between two indexes.
C code for maximum average sub-array of k length
#include<stdio.h>
int findMaxAverage (int arr[], int n, int k)
{
if (k > n)
return -1;
int *csum = arr;
csum[0] = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
csum[i] = csum[i - 1] + arr[i];
int max_sum = csum[k - 1], max_end = k - 1;
for (int i = k; i < n; i++)
{
int curr_sum = csum[i] - csum[i - k];
if (curr_sum > max_sum)
{
max_sum = curr_sum;
max_end = i;
}
}
return max_end - k + 1;
}
int main ()
{
int arr[] = { -1, 10, -15, -6, 50, 3 };
int k = 4;
int n = sizeof (arr) / sizeof (arr[0]);
printf ("The maximum average subarray of length %d begins at index %d", k,
findMaxAverage (arr, n, k));
return 0;
}
Output
The maximum average subarray of length 4 begins at index 1



Login/Signup to comment