Largest Sum Contigous SubArray in C
Largest Sum Contiguous Sub-Array
Here, in this page we will discuss the C program to find the largest sum contiguous Sub-array . We use Kadane’s algorithm, which runs in O(n) time.
The idea is to keep scanning through the array and calculating the maximum sub-array that ends at every position.

Largest Sum Contiguous Sub-Array in C
The Largest Sum Contiguous Subarray is a problem in computer science where we need to find the subarray in a given array that has the maximum sum of its elements. In other words, we are looking for a contiguous subarray in the given array whose sum is maximum.
For example, consider the following array:
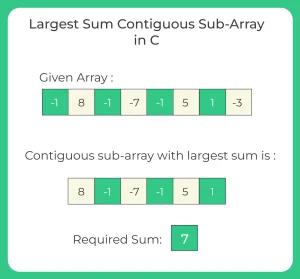
arr = [-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3]
The largest sum contiguous subarray in this array is [4, -1, -2, 1, 5], which has a sum of 7.
The problem of finding the largest sum contiguous subarray has a well-known algorithm called Kadane’s algorithm. The algorithm has a time complexity of O(n) and can be easily implemented in C.
Algorithm:
Create two intermediate variables max_ending_here and max_so_far.
Initialized these two intermediate variables using the 0.
Traverse the array from 0 to N-1 and calculate the max_ending_here and max_so_far.
- Now we will keep max_so_far which indicates the maximum sum found so far.
C code for largest sum contiguous sub-array
#include <stdio.h>
#define ARRAY_SIZE(a) sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0])
int maxSubArraySum (int arr[], int n)
{
int i = 0;
int max_so_far = 0;
int max_ending_here = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
max_ending_here = max_ending_here + arr[i];
if (max_ending_here < 0)
{
max_ending_here = 0;
}
if (max_so_far < max_ending_here)
{
max_so_far = max_ending_here;
}
}
return max_so_far;
}
int main ()
{
int arr[] = { -2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4 };
int arr_size = ARRAY_SIZE (arr);
const int maxSum = maxSubArraySum (arr, arr_size);
printf ("Largest Sum Contiguous Sub-Array : %d ", maxSum);
return 0;
}
Output
Largest Sum Contiguous Sub-Array : 6



Login/Signup to comment