Introduction to Doubly Linked List
What are Doubly Linked Lists?
Doubly linked lists are an extension to singly linked lists and provide a little more additional features and security to singly-linked lists. Let us see what these linked lists are –
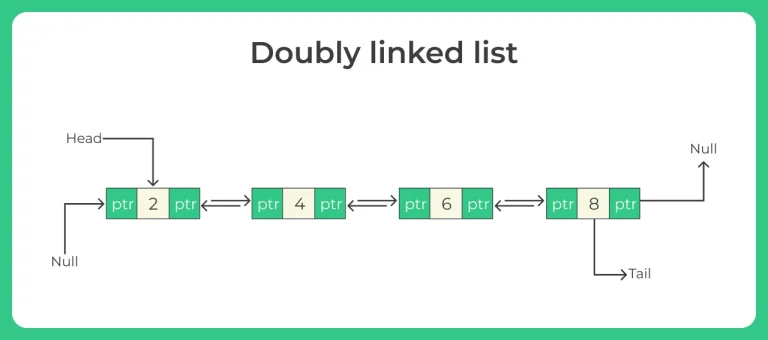
Doubly Linked list
Doubly linked lists have the following –
- Data: Like Singly-linked lists, it also contains data that is stored.
- Pointer (next) – Contains the address of the next node in the doubly linked list
- Pointer (previous) – Contains the address of the previous node in the doubly linked list
Apart from these basic terminologies are same – Node, Head, Tail
Structure of doubly linked list
Using the following statements in our program we can create a doubly linked list. This set of code will construct a doubly linked list that will store integer type of data.
struct Node { int Data; Struct Node* next; Struct Node* prev; };
Advantages
- It is better as unlike singly linked list, in a doubly-linked list we can traverse in both directions. Thus, if in case any pointer is lost we can still traverse.
- Thus, in Doubly Linked List we can traverse from Head to Tail as well as Tail to Head.
- Delete operation is quicker if the pointer to the node to be deleted is given to us already.
- Insertion is quicker in doubly-linked lists.
Disadvantages
- Extra space is required for the previous pointer for doubly-linked lists(DLL)
- All operations require an additional modification of the previous pointer as well along with next pointer.
C++ programming code for creating a doubly linked list
Run
#include <iostream> using namespace std; struct Node { int data; struct Node *prev; struct Node *next; }; struct Node* head = NULL; void insert(int newdata) { struct Node* newnode = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); newnode->data = newdata; newnode->prev = NULL; newnode->next = head; if(head != NULL) head->prev = newnode ; head = newnode; } void display() { struct Node* ptr; ptr = head; while(ptr != NULL) { cout<< ptr->data <<" "; ptr = ptr->next; } } int main() { insert(3); insert(1); insert(7); insert(2); insert(9); cout<<"The doubly linked list is: "; display(); return 0; }
Output: The doubly linked list is: 9 2 7 1 3



Login/Signup to comment