Find kth node from end of the linked list in C
To find kth node from end of the linked list in C
Find kth Node from end of the linked list in C ,We know that in singly linked list traversal is done through front only. so we will count the element from front to end of the linked list and we will find the position from front to last. when we find the position of the element then we get the node.
We can solve this problem in one traversal only.The idea is start from the head node to move a pointer K nodes ahead in given list.
Working for finding the kth node:-
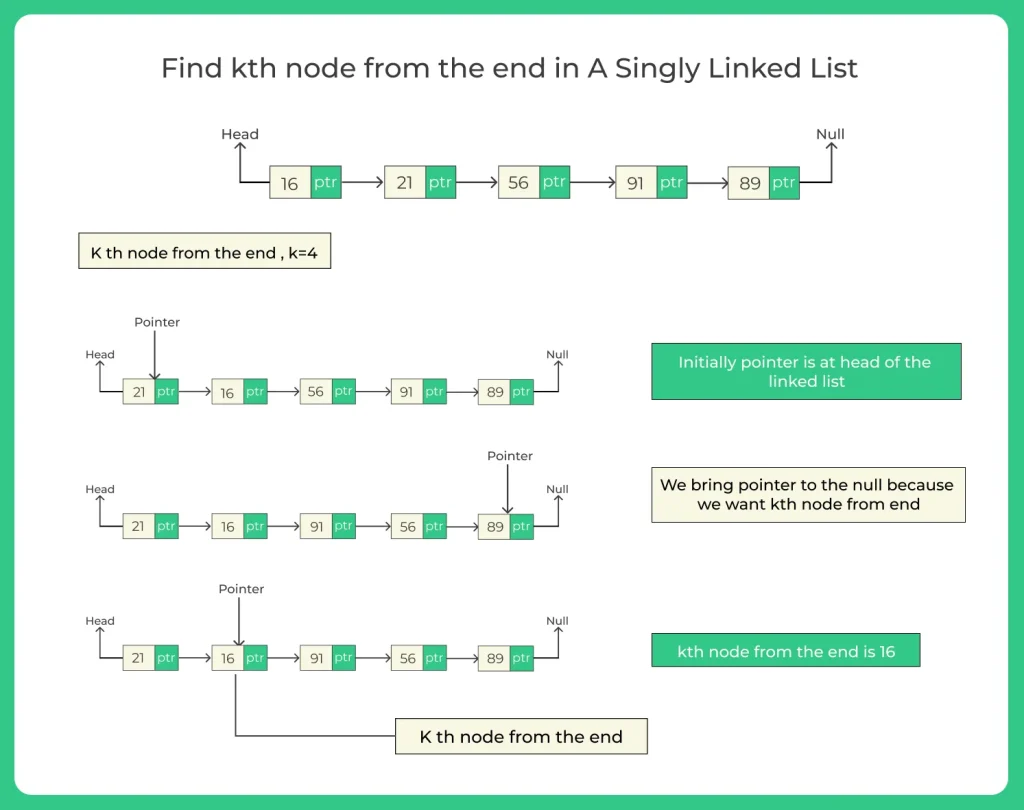
- First take the input in the list.
- Initially PTR -> HEAD (pointer is the head of the linked list).
- Then PTR=NULL (we need to find kth from the end of the linked list).
- When k=3 means the last third element of the linked list.
- After that print it.

Structure of the node in the Singly Linked List:-
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
Find kth Node from end of the linked list in C:-
#include<stdio.h> //header files
#include<stdlib.h> //library files
// Data Structure to store a linked list node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
// Iterative function to return K'th node from the end in a linked list
struct Node *getKthFromtheEnd (struct Node *head, int k)
{
struct Node *temp = head;
int n = 0;
// Count number of nodes in the linked list
while (temp)
{
temp = temp->next;
n++;
}
// if number of nodes is more than or equal to K
if (n >= k)
{
// return (n-k+1)th node from the beginning
temp = head;
for (int i = 0; i < n - k; i++) temp = temp->next;
}
return temp;
}
// function for create a new Node with the given data and
// pushes it onto the front of the list
void push (struct Node **head, int data)
{
// create a new linked list node from heap
struct Node *newNode = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = *head;
*head = newNode;
}
// main method
int main (void)
{
// given input keys
int keys[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int n = sizeof (keys) / sizeof (keys[0]);
struct Node *head = NULL;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
push (&head, keys[i]);
int k = 3;
struct Node *node = getKthFromtheEnd (head, k);
if (node)
printf ("K'th node from the end is %d", node->data);
return 0;
}Output:- K'th node from the end is 3
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Complexity Table of kth node from the end of a singly linked list in C
| Scenario | Time Complexity | Space Complexity | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best Case | O(n) | O(1) | Even if k is 1 or invalid, you must still count all nodes. |
| Average Case | O(n) | O(1) | Count all nodes (O(n)), then access (n – k)th node (O(n)) overall. |
| Worst Case | O(n) | O(1) | Always two full traversals in worst case (k = 1). Still linear. |
Applications of "Find kth Node from End" in C
- Because it tests:
- Pointer handling
- Understanding of linked lists
- Space and time optimization
To Summarize
This program finds the K’th node from the end of a singly linked list using a simple two step approach counting nodes and accessing the required one. It’s an effective way to practice pointer handling in C.
Such problems are common in interviews and help build strong fundamentals in linked lists and memory management.
FAQs
Using two pointers move one pointer K steps ahead, then move both until the first reaches the end. The second pointer points to the K’th node from the end.
It runs in O(n) time due to a full traversal to count nodes, followed by another to reach the target node.
Yes, by using the two-pointer technique, you can find the K’th node from the end in a single pass.
The function should return NULL or indicate invalid input, as the K’th node doesn’t exist.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others




Login/Signup to comment