Check If binary tree is Foldable or not in C
Tree is Foldable or Not?
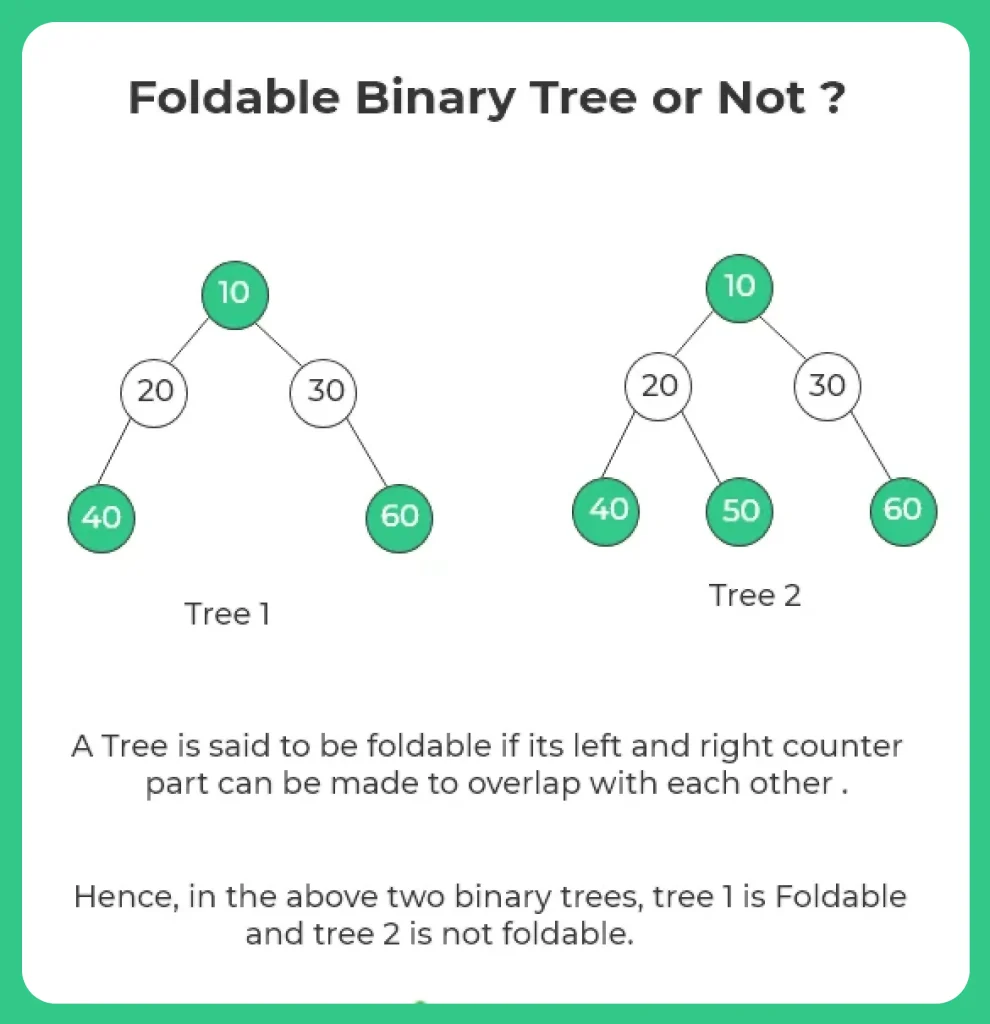
Here, in this page we will write a C program to check whether the given binary tree is foldable or not. A Tree is said to be foldable if its left and right counter part can be made to overlap with each other .
Check If binary tree is Foldable or not in C Language
Algorithm :
- If tree is empty, then return true.
- Convert the left subtree to its mirror image mirror(root->left);
- Check if the structure of left subtree and right subtree is same and store the result. res = isStructSame(root->left, root->right);
- isStructSame() recursively compares structures of two subtrees and returns true if structures are same
- Revert the changes made in step 2 to get the original tree. mirror(root->left);
- Return result res stored in step 2.
Code in C based on above approach
Run
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define bool int
#define true 1
#define false 0
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *left;
struct node *right;
};
void mirror (struct node *node);
bool isStructSame (struct node *a, struct node *b);
bool isFoldable (struct node *root)
{
bool res;
if (root == NULL)
return true;
mirror (root->left);
res = isStructSame (root->left, root->right);
mirror (root->left);
return res;
}
bool isStructSame (struct node * a, struct node * b)
{
if (a == NULL && b == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if (a != NULL && b != NULL && isStructSame (a->left, b->left)
&& isStructSame (a->right, b->right))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
void mirror (struct node *node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
else
{
struct node *temp;
mirror (node->left);
mirror (node->right);
temp = node->left;
node->left = node->right;
node->right = temp;
}
}
struct node *newNode (int data)
{
struct node *node = (struct node *) malloc (sizeof (struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
int main (void)
{
struct node *root = newNode (10);
root->left = newNode (20);
root->right = newNode (30);
root->right->left = newNode (40);
root->left->right = newNode (50);
if (isFoldable (root) == 1)
{
printf ("Tree is foldable");
}
else
{
printf ("Tree is not foldable");
}
return 0;
}
Output:
Tree is foldable



Login/Signup to comment