Loop-Types in C++
Loops in C++
Here, in this section, we will discuss loops in C++. Loops help us automate repetitive work that we may have to do over and over again.

Loops discussed
- While loop
- For loop
- Do while
- Nested loops
We will also learn more about the following as these are used in conjunction with loops
- Switch statements
- Jump Statements:
- break
- continue
While Loop
Imagine we had to print “Hello World” 100 times or n-number of times. Would it be wise to write cout << “Hello World\n” 100 times. While loops help us automate this.
Syntax
while(condition(s)){
// execute statement(s)
}Sometimes, the loop also uses an external initialization and incrementation logic to control how many times the loop may run
initialization;
while(condition(s)){
// execute statement(s)
incrementation;
} 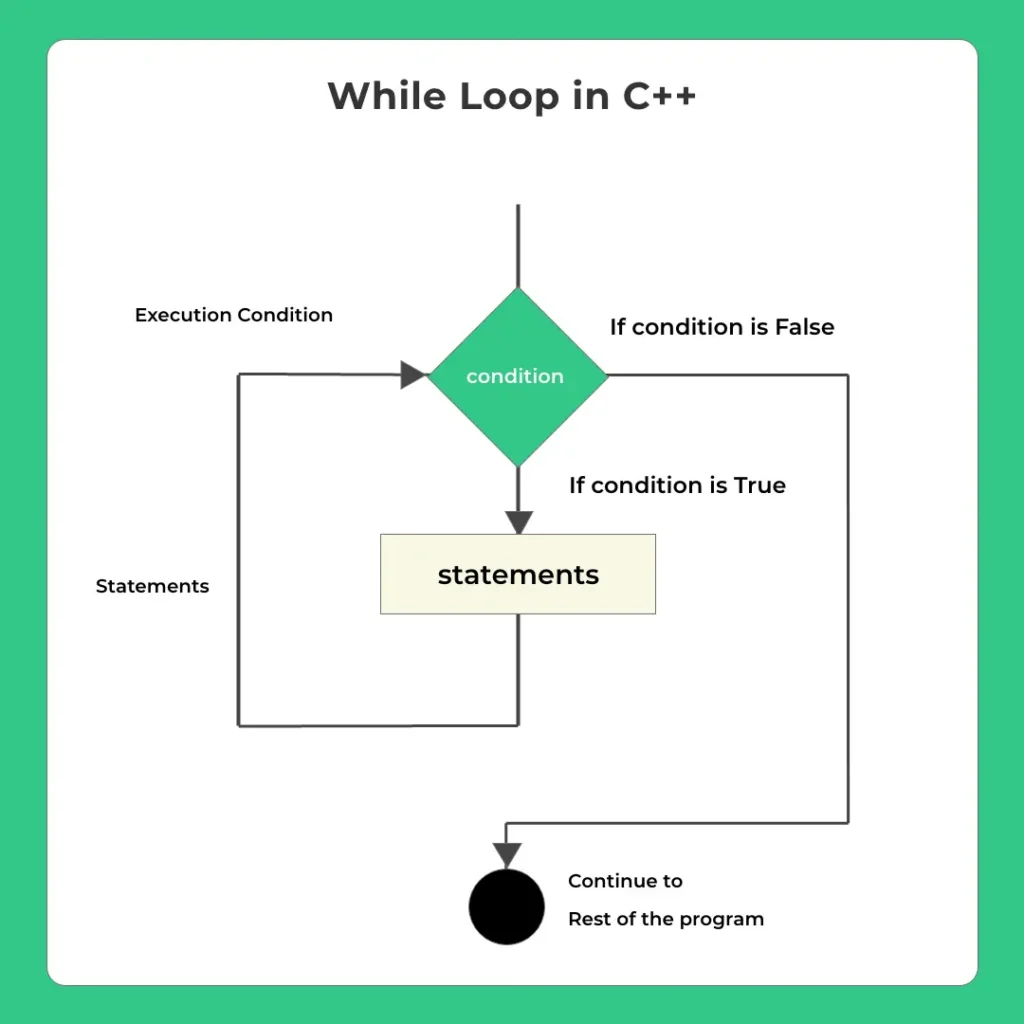
What we basically mean by it is that decision to run the loop again that is called as condition checking.
1. Happens before entry inside loop in while and for loop.
2. In case of Do While this decision to run loop again or not happens when exiting the loop
Example
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i = 1;
while(i <= 10)
{
cout << "Hello World, i:" << i << endl;
i++;
}
return 0;
}
Output
Hello World, i:1 Hello World, i:2 Hello World, i:3 Hello World, i:4 Hello World, i:5 Hello World, i:6 Hello World, i:7 Hello World, i:8 Hello World, i:9 Hello World, i:10
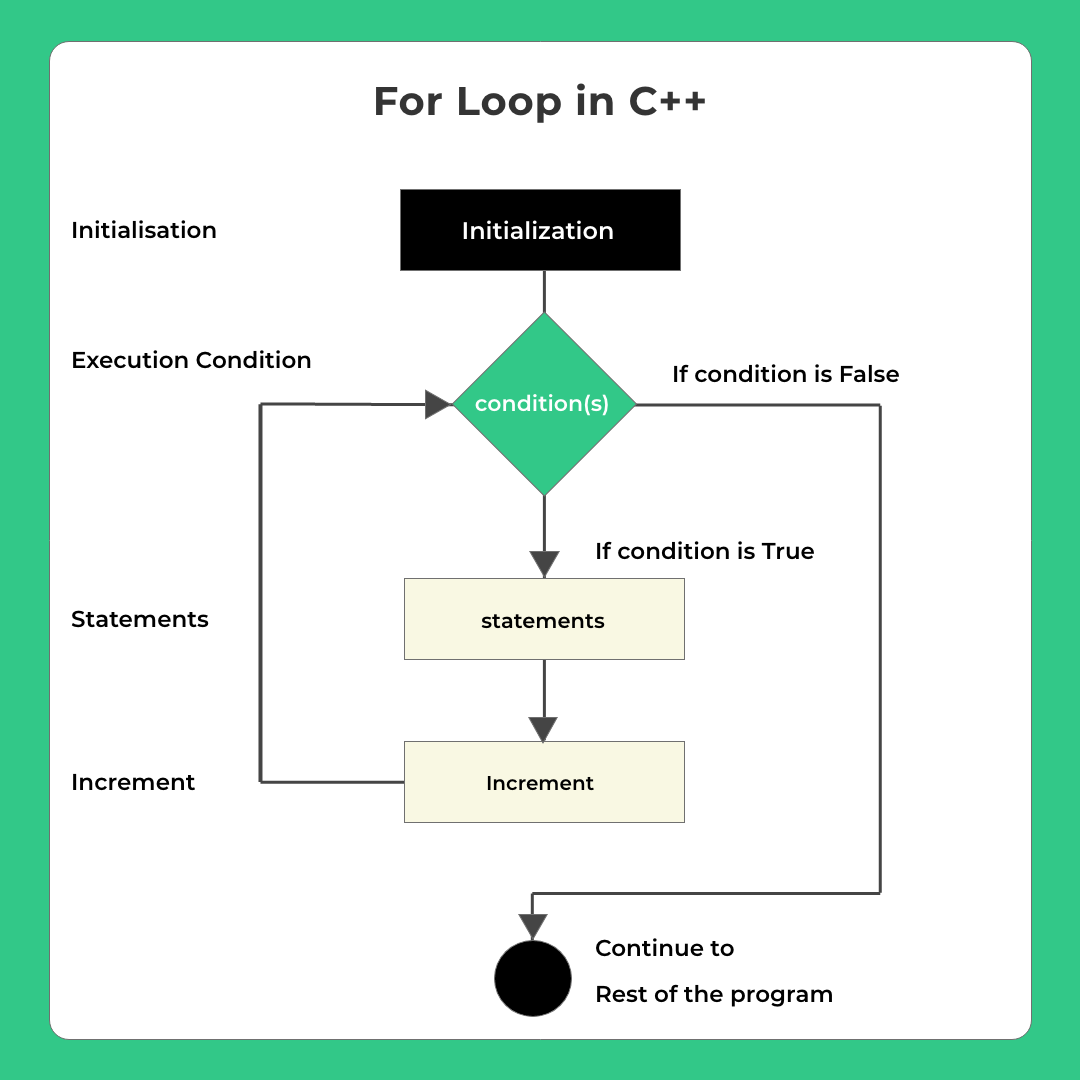
For Loop
While loop uses an external variable to control the execution. A for loop takes into account the
- Initialization
- Condition checking
- Incrementation
In its syntax itself. The syntax is shown below-
// initialization happens once before 1st iteration of loop
// condition checking happens everytime before new iteration
for(intialization ; condition(s); incrementation)
{
// execution statements(s)
// increment happens everytime as soon as current iteration completed
} 
Example
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num = 5;
// i = 1 is set once, before first running iteration
// i <= 10 condition is checked before every new running iteration
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
cout << num << " * " << i << " = " << (num * i) << endl;
// i++ i.e. value of i is incremented before each iteration completes
}
return 0;
}
Output
5 * 1 = 5 5 * 2 = 10 5 * 3 = 15 5 * 4 = 20 5 * 5 = 25 5 * 6 = 30 5 * 7 = 35 5 * 8 = 40 5 * 9 = 45 5 * 10 = 50
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Do While Loop
- Do while is very similar to while loop with one difference that it is exit control loop.
- That is the decision to run the loop again or not happens at the time of exit of the current loop.
- While in the while loop it happens before entry in the loop.
Syntax
do{
// execute statement(s)
}
while(condition(s))Sometimes when loop uses an external initialization and incrementation logic the syntax may look like –
initialization;
do{
// execute statement(s)
incrementation;
}while(condition(s)) 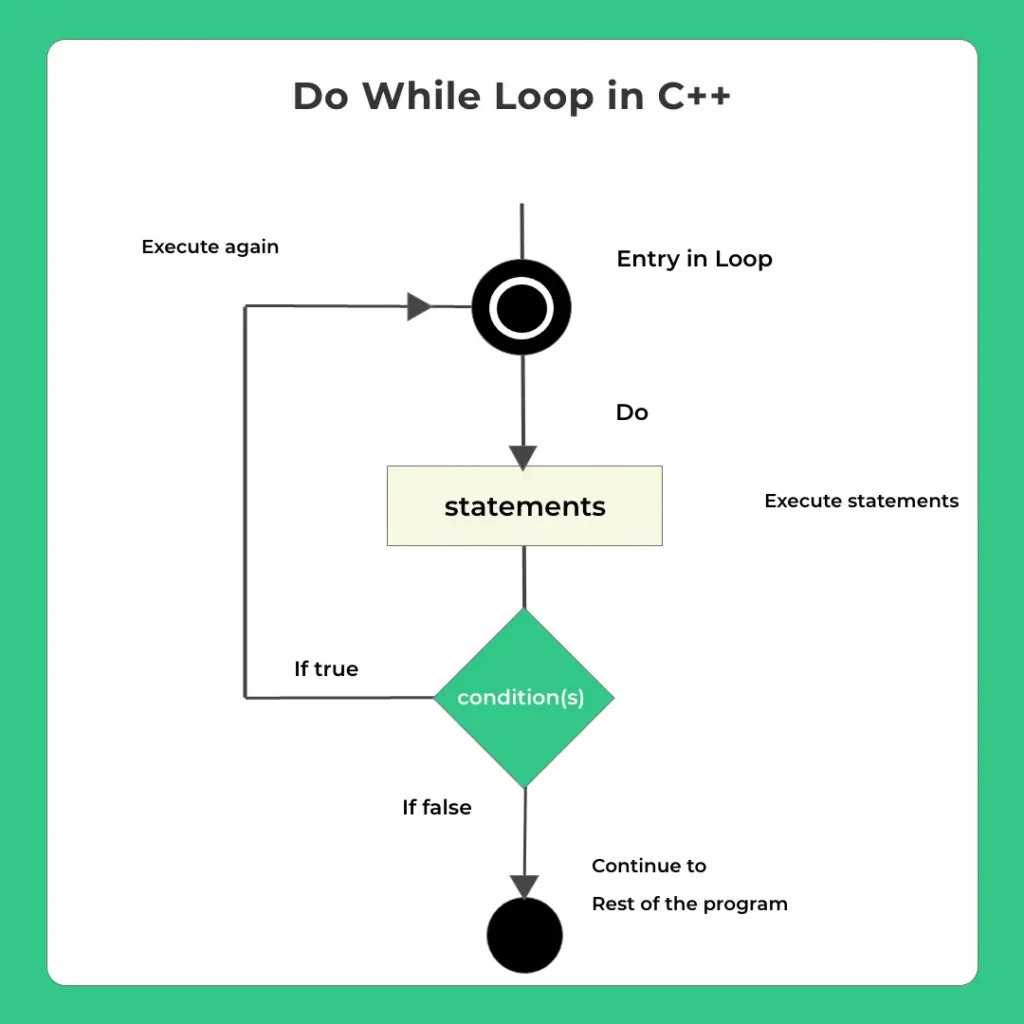
Example
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i = 1;
do
{
cout << "Hello World, i:" << i << endl;
i++;
}while(i <= 10);
return 0;
}
Output
Hello World, i:1 Hello World, i:2 Hello World, i:3 Hello World, i:4 Hello World, i:5 Hello World, i:6 Hello World, i:7 Hello World, i:8 Hello World, i:9 Hello World, i:10
Major difference between while and do-while
- do-while loop run atleast once Since condition are checked later
Following do-while loop runs once and prints hello world once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i = 100;
// do while runs atleast once
do
{
cout << "Hello World, i:" << i << endl;
i++;
}while(i <= 10);
return 0;
}Output
Hello World, i:100
However, the following while loop doesn’t even run once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i = 100;
// wont even run once as while is entry controlled
while(i <= 10)
{
cout << "Hello World, i:" << i << endl;
i++;
}
return 0;
}Output
**Nothing is printed
Jump Statements
Now we will discuss jump statements which are
- Jump Statements:
- break
- continue
Break Statement
Whenever a break statement is encountered inside a loop (for or While or Do-while), the loop is immediately terminated and program control resumes at the next statement following the loop
for(init;conditions;increments){
if(some condition(s)){
// For loop immediately terminates
// no matter if there are pending iterations
break;
}
}
// program flow will come here immediately 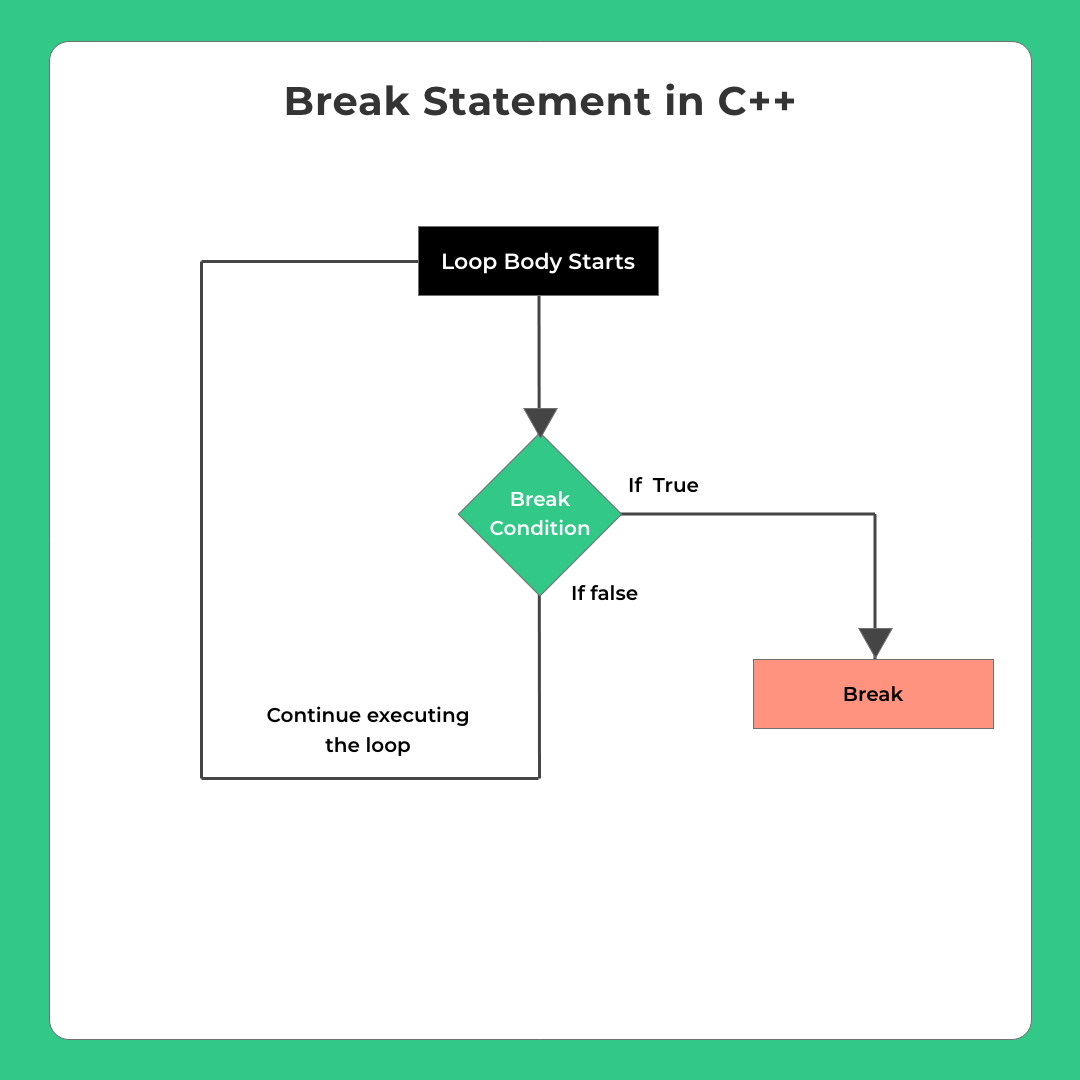
Example
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// ideally should run 10 times b/w [1,10]
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){
// whole loop terminates when i becomes divisible by 5
if(i % 5 == 0)
break;
cout << "i: " << i << endl;
}
}Output
i: 1 i: 2 i: 3 i: 4
Continue Statement
Whenever a continue statement is encountered inside a loop, the current iteration of the loop is skipped and the loop executes from the next iteration
for(init;conditions;increments){
if(some condition(s)){
// Current iteration of loop is skipped
// Starts from next iteration
break;
}
}
// program flow will come here after loop completion 
Example
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// ideally should run 10 times b/w [1,10]
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){
// Even iterations are skipped
// it true then continue statement forces
// loop to be started from next iteration
if(i % 2 == 0)
continue;
// statements skipped if continue statement executes
cout << "i: " << i << endl;
}
}
Output
i: 1 i: 3 i: 5 i: 7 i: 9
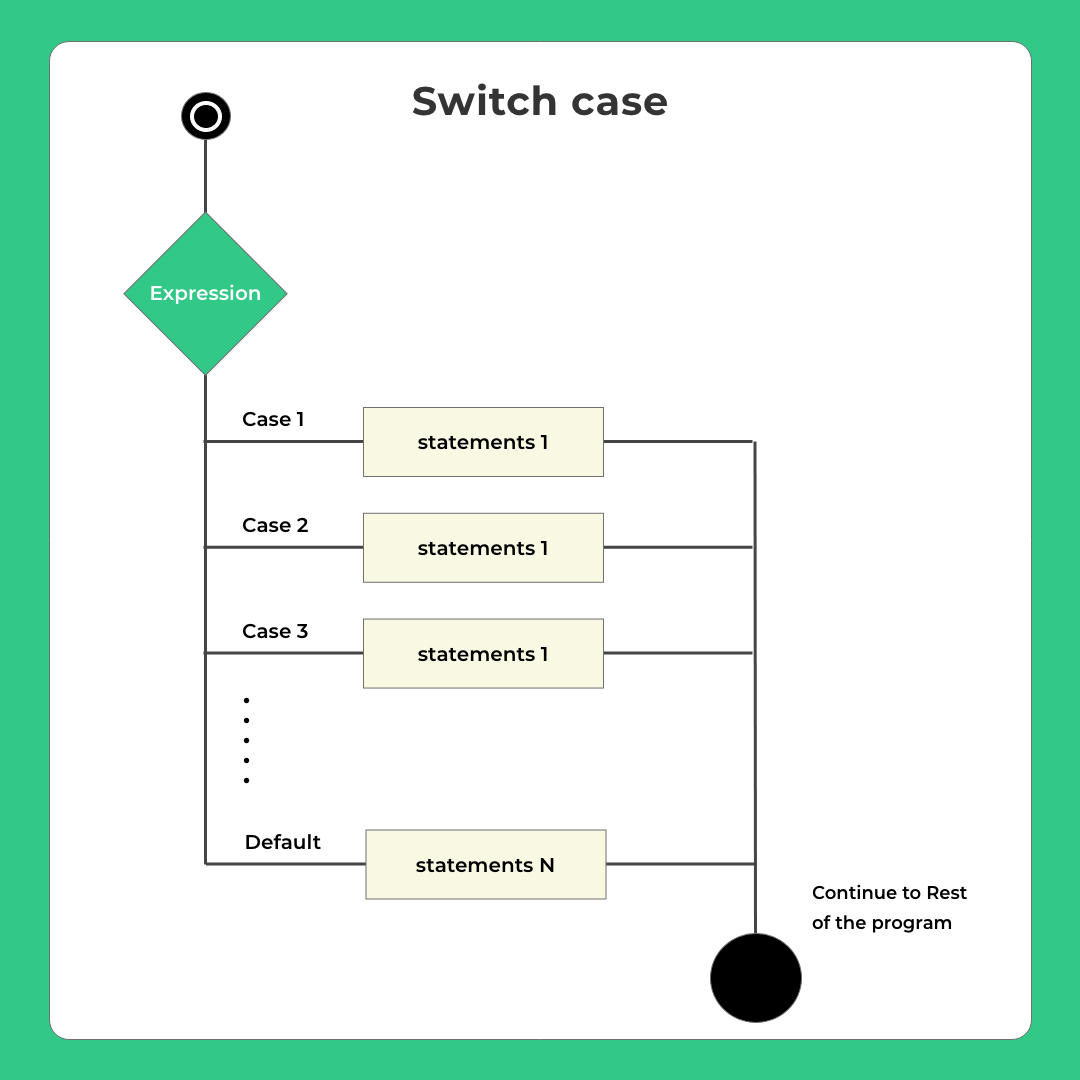
Switch Case
It is ideal for whenever we can to merge a lot of if – else loops into multiple cases checking and executing unique statements if one of them is true.
switch(expression)
{
case constant-expression1:
// statement(s);
break;
case constant-expression2:
// statement(s);
break;
// you can have any number of case statements
default: // Optional but ideal
// statement(s);
} 
Example
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char op;
int num1 = 20, num2 = 5;
cout << "Enter operator either + or - or * or /: "; cin >> op;
switch(op)
{
case '+':
cout << num1+num2;
break;
case '-':
cout << num1-num2;
break;
case '*':
cout << num1*num2;
break;
case '/':
cout << num1/num2;
break;
//if case label not available example op = %
default:
cout << "Select valid choice";
break;
}
}
Output
Enter operator either + or - or * or /: * 100
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment