Double Data Type in C
C-Double Data Type
On this page we will discuss about Double Data Type which is used in C.The Double data type is used to store floating point numbers that have a large range or require a high degree of precision(upto 15-17 digits).

Representation of Double Data Type in C
In C programming , the double data type is used to represent the various types of data in form of decimal numbers, negative values, real numbers etc.
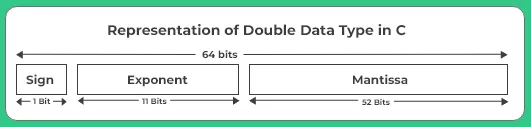
The double data type is represented by 64 bits(0-63) in following manner:
- 1 Bit is used for sign representation.
- 11 Bits are used for the exponent.
- 52 Bits are used for the fractional part(mantissa).
| Double Data Type | Information |
|---|---|
| Range | 1.7E-308 to 1.7E+308 |
| Storage size | 8 bytes |
| Format Specifier | %lf |
Declaration of Double type variable
double variable_name;
Initialization of Double type variable
A double variable can be initialized in two ways as follows:
1. By assigning value to a variable using assignment operator.
cost = 13.31;
2. By assigning value to a variable during declaration only using assignment operator.
double cost = 13.31;
Program to Demonstrate the use of Double Data Type
Example 1:
Run
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// Initialization of temporary double type variables
double x = 456456456.00;
double y = 14.319246;
double z = 6786543210.321321;
printf("Value of variable x is %lf\n", x);
printf("Value of variable y is %lf\n", y);
printf("Value of variable z is %lf", z);
return 0;
}
Output:
Value of variable x is 456456456.000000 Value of variable y is 14.319246 Value of variable z is 6786543210.321321
Example 2:
Run
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// declaration of the double variables
double p, q, sum;
printf (" Enter two double numbers\n ");
// take two double variable from user
scanf(" %lf %lf", &p, &q);
// Assign sum of double variables to sum variable.
sum = p + q;
printf (" The result of sum of two double numbers is: %lf", sum);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter two double numbers 13.50 33.46 The result of sum of two double numbers is: 46.960000
Note:
The 'double' data type is not suitable for storing exact values, as it is subject to rounding errors due to the way it is represented in memory. If you need to store exact values, you may want to consider using the 'long double' data type, which is typically represented in memory using 80 bits and has a greater range and precision than 'double' data type.
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others






Login/Signup to comment