Functions in Python
Functions in Python
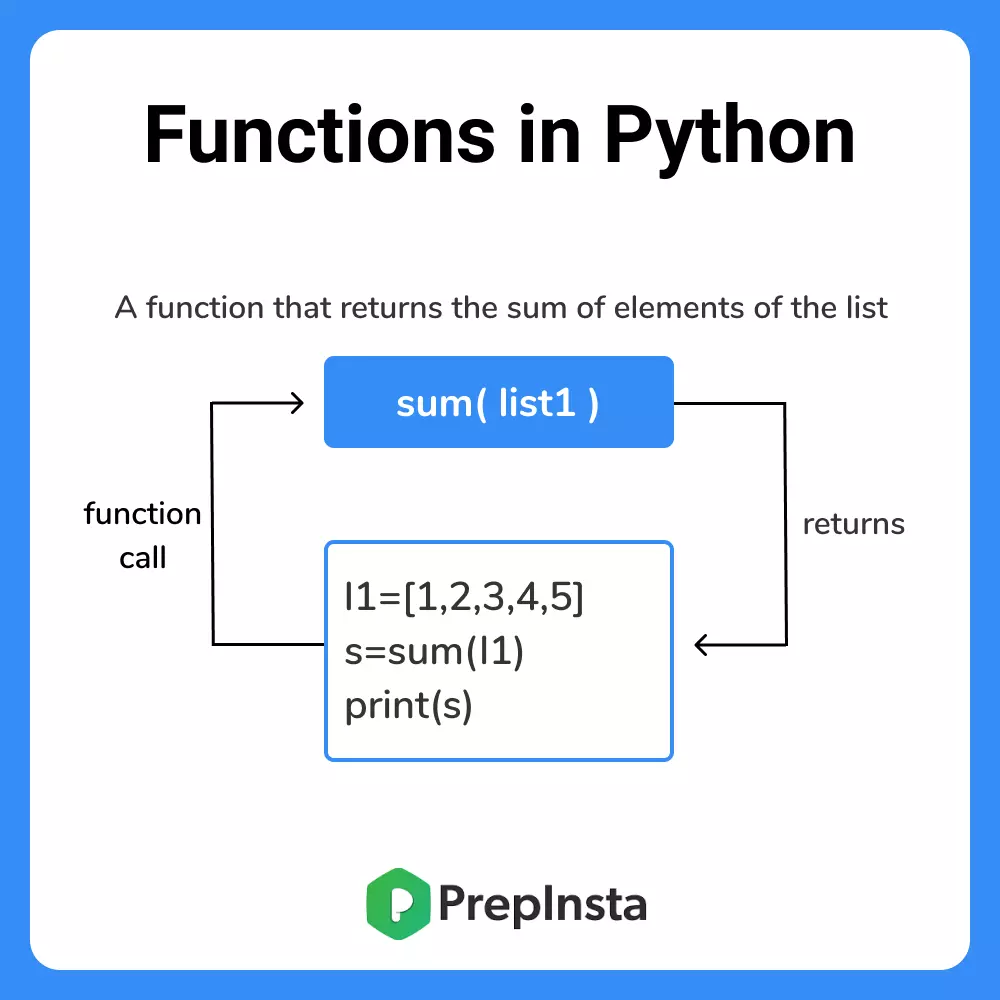
The function is a block of related statements that performs a specific task when it is called.
Functions helps in breaking our program into smaller and modular chunks which makes our program more organized and manageable. Also, it avoids repetition and makes the code reusable.
Types of Function
Functions in python can be divided into two types
- Built-in Functions : Functions that are built into Python.
- User-defined Functions : Functions defined by the users themselves.
Output : 4 9 16
The pass Statement
The pass statement is used to avoid getting an error in empty functions as function definitions can not be empty in python.
Docstring
The first string after the function header is called the docstring and is short for documentation string.
Output : This is a docstring of the function docString()
Default Parameters
If we call the function without argument, it uses the default value.
Output : Sum of a = 10 and b = 20 is 30 Sum of a = 30 and b = 20 is 50 Sum of a = 10 and b = 50 is 60 Sum of a = 100 and b = 200 is 300
Keyword Parameters
To allow the caller to specify the argument name with values so that caller does not need to remember the order of parameters.
Output : Hello Muskan Salampuria . Your score is 100 Hello Vaibhav Kumar . Your score is 99 Hello abc xyz . Your score is 10
Arbitrary Parameters
If we are not sure with number of arguments that will be passed in our function, we can use * before the parameter name so that the function will receive a tuple of arguments, and we can access the items accordingly.
Output : Total number of names are : 6 Welcome Saz Welcome Joe Welcome Hena Welcome Justin Welcome Karx Welcome Max Total number of names are : 3 Welcome Sufi Welcome Sana Welcome Muskan



Login/Signup to comment