Arrays in Python
Arrays
In this tutorial, you’ll learn about the Python Arrays module, the difference between arrays and lists, and how and when to use them with the help of examples.
In this tutorial, we will focus on a module named Array. The Array module allows us to store a collection of numeric values.
To learn the Implementation of Array using List visit our Python List Tutorial.

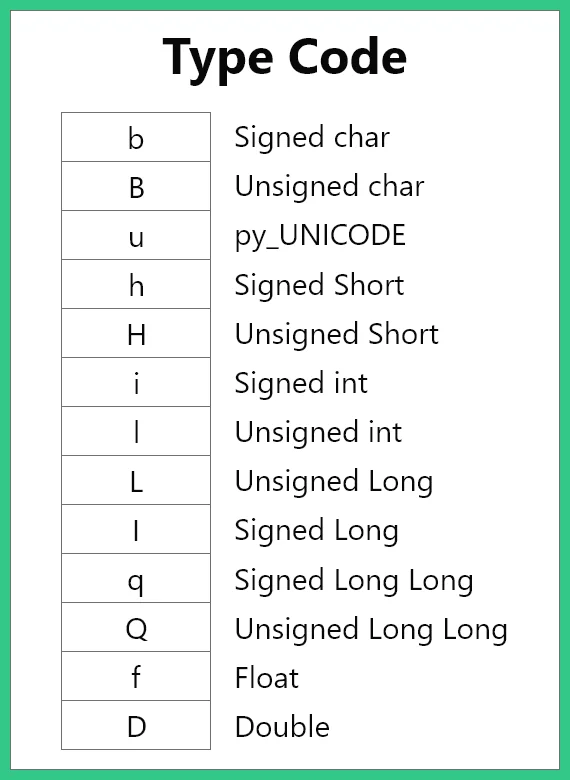
Type Code
Type codes are characters assigned to different types of data types. This is not much used in Python Programming Language as the interpreter automatically understands the data type and dynamically increases the size but in the case of an array in python, we use type code to constrain the type of elements to be stored in the array.
Different types of Type codes are :-
Creating Array
In python, a module named array needs to be imported for the implementation of the array and to use inbuilt functions for the Arrays.
import array
Afterward, we need to assign a name and create an array by passing type code ( data type code which we want to store ) and a list storing the values to be stored in an array. The type Code of float values is d.
a = array.array('d', [1.5, 2.5, 3.5]Syntax:
import module_name variable_name = module_name.array( type_code, list_of_values)
Accessing Array Elements
We use indices to access elements of an array:
import array as arr
a = arr.array('i', [2, 4, 6, 8])
print("First element:", a[0])
print("Second element:", a[1])
print("Last element:", a[-1])Slicing Python Arrays
We can access a range of items in an array by using the slicing operator :import array as arr
numbers_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
numbers_array = arr.array('i', numbers_list)
print(numbers_array[1:4]) # 2rd to 4th
print(numbers_array[:3]) # beginning to 4th
print(numbers_array[5:]) # 6th to end
print(numbers_array[:]) # beginning to end
Changing and Adding Elements
Arrays are mutable, their elements can be changed similarly to lists.import array as arr
numbers = arr.array('i', [1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10])
# changing first element
numbers[0] = 0
print(numbers) # Output: array('i', [0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10])
# changing 3rd to 5th element
numbers[2:5] = arr.array('i', [4, 6, 8])
print(numbers) # Output: array('i', [0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10])
import array as arr
numbers = arr.array('i', [1, 2, 3])
numbers.append(4)
print(numbers) # Output: array('i', [1, 2, 3, 4])
# extend() appends iterable to the end of the array
numbers.extend([5, 6, 7])
print(numbers) # Output: array('i', [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
import array as arr
odd = arr.array('i', [1, 3, 5])
even = arr.array('i', [2, 4, 6])
numbers = arr.array('i') # creating empty array of integer
numbers = odd + even
print(numbers)
Removing Python Array Elements
We can delete one or more items from an array using Python’s del statement.import array as arr
number = arr.array('i', [1, 2, 3, 3, 4])
del number[2] # removing third element
print(number) # Output: array('i', [1, 2, 3, 4])
del number # deleting entire array
print(number) # Error: array is not defined
import array as arr
numbers = arr.array('i', [10, 11, 12, 12, 13])
numbers.remove(12)
print(numbers) # Output: array('i', [10, 11, 12, 13])
print(numbers.pop(2)) # Output: 12
print(numbers) # Output: array('i', [10, 11, 13])
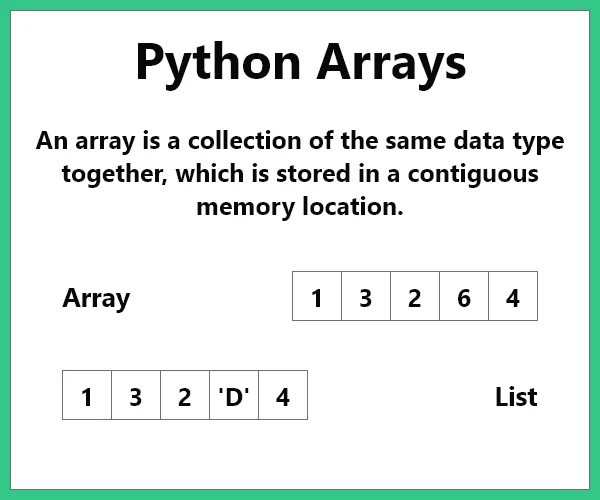
Lists Vs Arrays
Array
If you create arrays using the array module, all elements of the array must be of the same type.import array as arr
# Error
a = arr.array('d', [1, 1.5, 'A', "Prep"])
List
In Python, we can treat lists as arrays. However, we cannot constrain the type of elements stored in a list. For example:
# elements of different types a = [1, 1.5, 'A', "Prep"]






Login/Signup to comment