Print Elements in Sorted Order using Row-Column Wise Sorted Matrix in C++
Print Elements in Sorted Order using row-column wise sorted matrix in C++
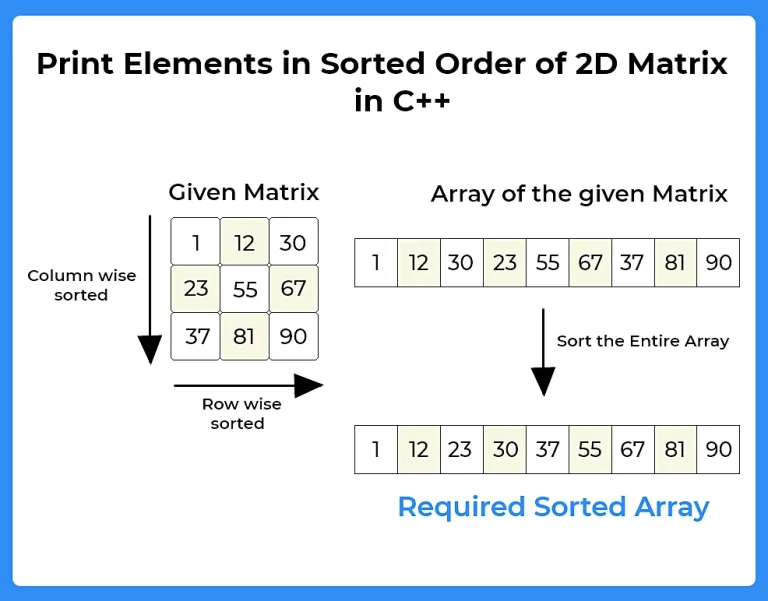
Here, in this page we will discuss the program to print elements in sorted order using row-column wise sorted matrix in C++ programming language. We are given with a matrix in which each row and column are sorted in non-decreasing manner.
Example :
- Input : mat[][] = { {10, 20, 30, 40}, {15, 25, 35, 45}, {27, 29, 37, 48}, {32, 33, 39, 50}, }
- Output : 10 15 20 25 27 29 30 32 33 35 37 39 40 45 48 50
Method 1 :
- Let’s say the number of rows be n and number of columns be m.
- Now, create an array of size (n*m).
- Insert all the elements of the matrix in the declared array.
- Using sort() function sort the entire array.
- Print the array.
Time and Space Complexity :
- Time-Complexity : O(n*m*log(n*m))
- Space-Complexity : O(n*m)
Code to Print Elements in Sorted Order in C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n=4, m=4;
int mat[n][m]= { { 1, 20, 43, 14 },{ 50, 69, 17, 81 },{ 99, 10, 11, 22 },{ 13, 54, 95, 16 } };
int arr[n*m], x=0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
for(int j=0; j<m; j++){
arr[x++]=mat[i][j];
}
}
int size = n*m;
sort(arr, arr+size);
for(int i=0; i<size; i++)
cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
}
Output
1 10 11 13 14 16 17 20 22 43 50 54 69 81 95 99
Method 2 :
- Let’s say the number of rows be n and number of columns be m.
- Now, create a recursive function which takes n arrays and returns the output array.
- In the recursive function, if the value of n is 1 then return the array else if the value of n is 2 then merge the two arrays in linear time and return the array.
- If the value of n is greater than 2 then divide the group of n elements into two equal halves and recursively call the function, i.e 0 to n/2 array in one recursive function and n/2 to n array in another recursive function.
- Print the array.
Time and Space Complexity :
- Time-Complexity : O(n*m*log(m))
- Space-Complexity : O(n*m*log(m))
Code to Print Elements in Sorted Order in C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define n 4
void mergeArrays(int arr1[], int arr2[], int n1, int n2, int arr3[])
{
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
while (i<n1 && j <n2){
if (arr1[i] < arr2[j])
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
else
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
while (i < n1)
arr3[k++] = arr1[i++];
while (j < n2)
arr3[k++] = arr2[j++];
}
void mergeKArrays(int arr[][n], int i, int j, int output[])
{
if(i==j)
{
for(int p=0; p < n; p++)
output[p]=arr[i][p];
return;
}
if(j-i==1)
{
mergeArrays(arr[i],arr[j],n,n,output);
return;
}
int out1[n*(((i+j)/2)-i+1)],out2[n*(j-((i+j)/2))];
mergeKArrays(arr,i,(i+j)/2,out1);
mergeKArrays(arr,(i+j)/2+1,j,out2);
mergeArrays(out1,out2,n*(((i+j)/2)-i+1),n*(j-((i+j)/2)),output);
}
int main()
{
int arr[][n] = {{2, 6, 12, 34},{10, 19, 20, 1000},{23, 34, 90, 2000}};
int k = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int output[n*k];
mergeKArrays(arr,0,2, output);
for (int i=0; i < 12; i++)
cout << output[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
Output
2 6 10 12 19 20 23 34 34 90 1000 2000




Login/Signup to comment