C++ Program to find common elements In three sorted arrays
Common elements In three sorted arrays in C++
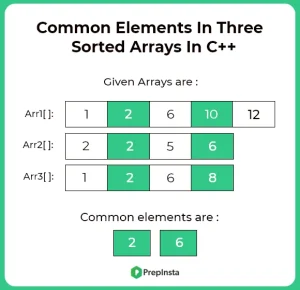
Here, in this page we will discuss the program to find the common elements in three sorted arrays in C++ programming language. We are given with three arrays sorted in non-decreasing order, and we need to print all common elements in these arrays.
Input:
- ar1[] = {1, 5, 5}
- ar2[] = {3, 4, 5, 5, 10}
- ar3[] = {5, 5, 10, 20}
Output:
- 5 5

Let’s discuss the Brute force approach to find the common elements in the given three arrays. So, to find them we iterate over one array and for every i-th element we, check whether that i-th element is present in another two arrays or not if it is present then we will print that element otherwise check for another element.
Algorithm :
- Take the size of first array and store it in variable say n1.
- Now, declare an array of n1 size and take n1 elements from the user.
- Take the size of second array and store it in variable say n2.
- Declare an array of n2 size and take n2 elements from the user.
- Now, take the size of third array from the user and store it in variable say n3. Declare an array of n3 size and take n3 elements from the user.
- Now, run a loop from i=0 to i=n1-1 and for every ar1[i] element we check if that i-th element present in second array if it is,
- Then check in third array, if element is found then print that element,
- Otherwise continue the checking for other elements.
This algorithm is not valid if elements in the particular elements are repeated.
Time and Space complexity for above Algorithm is :
- Time Complexity : O(n1*n2*n3) (Where, n1, n2 and n3 are the size of the array respectively)
- Space Complexity :O(1)
Code to find Common elements In three sorted arrays in C++
// C program to print common elements in three arrays
#include <stdio.h>
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n1;
scanf("%d", &n1);
int ar1[n1];
for(int i=0; i<n1; i++)
scanf("%d", &ar1[i]);
int n2;
scanf("%d", &n2);
int ar2[n2];
for(int i=0; i<n2; i++)
scanf("%d", &ar2[i]);
int n3;
scanf("%d", &n3);
int ar3[n3];
for(int i=0; i<n3; i++)
scanf("%d", &ar3[i]);
printf("Common Elements are ");
for(int i=0; i<n1; i++){
int flag = 0;
for(int j=0 ; j<n2; j++){
if(ar1[i]==ar2[j])
{
for(int k=0; k<n3; k++){
if(ar2[j]==ar3[k])
{
flag=1;
k++;
break;
}
}
j++;
break;
}
}
if(flag)
printf("%d ", ar1[i]);
}
return 0;
}
Efficient Algorithm :
- Take the size of first array and store it in variable say n1.
- Now, declare an array of n1 size and take n1 elements from the user.
- Take the size of second array and store it in variable say n2.
- Declare an array of n2 size and take n2 elements from the user.
- Now, take the size of third array from the user and store it in variable say n3. Declare an array of n3 size and take n3 elements from the user.
- Now, we run a loop and traverse three arrays.
Let the current element traversed in ar1[] be x, in ar2[] be y and in ar3[] be z. We can have following cases inside the loop. - If x, y and z are same, we can simply print any of them as common element and move ahead in all three arrays.
- Else If x < y, we can move ahead in ar1[] as x cannot be a common element.
- Else If x > z and y > z), we can simply move ahead in ar3[] as z cannot be a common element.
Time and Space complexity for above Algorithm is :
- Time Complexity : O(n1+n2+n3) (Where, n1, n2 and n3 are the size of the array respectively)
- Space Complexity :O(1)
Code in C++
// C++ program to print common elements in three arrays
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// This function prints common elements in ar1
void findCommon(int ar1[], int ar2[], int ar3[], int n1, int n2, int n3)
{
// Initialize starting indexes for ar1[], ar2[] and ar3[]
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
// Iterate through three arrays while all arrays have elements
while (i < n1 && j < n2 && k < n3)
{
// If x = y and y = z, print any of them and move ahead
// in all arrays
if (ar1[i] == ar2[j] && ar2[j] == ar3[k])
{ cout << ar1[i] << " "; i++; j++; k++; }
// x < y
else if (ar1[i] < ar2[j])
i++;
// y < z
else if (ar2[j] < ar3[k])
j++;
// We reach here when x > y and z < y, i.e., z is smallest
else
k++;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n1;
cin>>n1;
int ar1[n1];
for(int i=0; i<n1; i++)
cin>>ar1[i];
int n2;
cin>>n2;
int ar2[n2];
for(int i=0; i<n2; i++)
cin>>ar2[i];
int n3;
cin>>n3;
int ar3[n3];
for(int i=0; i<n3; i++)
cin>>ar3[i];
cout << "Common Elements are ";
findCommon(ar1, ar2, ar3, n1, n2, n3);
return 0;
}
Input :
3
1 5 5
5
3 4 5 5 10
4
5 5 10 20
Output
5 5
Algorithm using STL
- Declare two set, to store the elements of first array i.e, ar1[] and second array i.e, ar2[ ].
- Idea behind using the set data structure is to remove the duplicate elements from the ar1[ ] and ar2[ ].
- Now, iterate over the third array and check if it is present in first and second set both.
- If element is present in both set then print that element.
Time and Space complexity for above Algorithm is :
- Time Complexity : O(n1+n2+n3) (Where, n1, n2 and n3 are the size of the array respectively)
- Space Complexity :O(n1+n2+n3)
Code to print Common elements In three sorted arrays in C++:
// C++ program to print common elements in three arrays
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void findCommon(int a[], int b[], int c[], int n1, int n2,int n3)
{
// three sets to maintain frequency of elements
unordered_set <int> uset,uset2,uset3;
for(int i=0;i<n1;i++){
uset.insert(a[i]);
}
for(int i=0;i<n2;i++){
uset2.insert(b[i]);
}
// checking if elements of 3rd array are present in first 2 sets
for(int i=0;i<n3;i++){
if(uset.find(c[i])!=uset.end() && uset2.find(c[i])!=uset.end()){
// using a 3rd set to prevent duplicates
if(uset3.find(c[i])==uset3.end())
cout<<c[i]<<" ";
uset3.insert(c[i]);
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n1;
cin>>n1;
int ar1[n1];
for(int i=0; i<n1; i++)
cin>>ar1[i];
int n2;
cin>>n2;
int ar2[n2];
for(int i=0; i<n2; i++)
cin>>ar2[i];
int n3;
cin>>n3;
int ar3[n3];
for(int i=0; i<n3; i++)
cin>>ar3[i];
cout<<"Common Elements are ";
findCommon(ar1, ar2, ar3, n1, n2, n3);
return 0;
}
Input :
3
1 5 5
5
3 4 5 5 10
4
5 5 10 20
Output
5 5
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription



Login/Signup to comment