Virtusa Coding Questions with Answers
Virtusa Coding Questions with Solutions
Preparing Virtusa coding questions for Virtusa Online Test can be a game changer in clearing the technical stages of the hiring process. Whether you’re aiming for the Coder or Power Coder role, understanding the type of questions asked and practicing with the right approach is essential.
In this article, we’ve compiled some of the most commonly asked Sample Virtusa coding questions, along with detailed answers and explanations to help you sharpen your problem solving skills and improve your chances of selection.
Virtusa is offering Software Developer and Software Tester job profile for 2025 batch.
Last Date to Apply: 3 October 2025
You can checkout about Virtusa Neural Hackathon 2025 below….
Virtusa Recruitment Process Details....
| Criteria | Coder | Power Coder |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Standard coding profile for general technical roles. | Advanced coding profile for top performers or specialized roles. |
| No. of Coding Questions | 4 Questions | 3 Questions |
| Difficulty Level | Moderate | Hard |
| Time Limit | 50 Minutes | 80 Minutes |
| Topics Covered | Arrays, Strings, Recursion, Sorting, Searching, etc. | Trees, Graphs, Dynamic Programming, Advanced Algorithms, etc. |
| Evaluation Criteria | Logic, Correctness an d Basic Optimization | Efficient Algorithm Design, Optimization and Edge Case Handling |
| Who Should Apply? | Freshers with good coding fundamentals | Candidates aiming for higher packages or competitive tech roles |
| Salary | Rs. 5 LPA | Rs. 6.5 LPA |
From here, you will get sample Virtusa Coding Questions with Solution to practice properly including Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Concepts…..
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Sample Virtusa Coding Questions and Answers
Problem 1. Build Pattern:
Problem Statement: Ram has been given a task by his friend to built the trapezium, but ram mocked him to give him such easy problem.
So to make problem hard , his friend apply some conditions on the problems :
- Length should be provided by the user
- Trapezium should be filled with # and –
- Trapezium should be half cut
- Last line of trapezium should be only filled with –
Input: 5
Output:
####-####
###—###
##—–##
#——-#
———
Solution:
Space Complexity: O(1)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(j < n - i - 1)
cout << "#";
else
cout << "-";
}
for(int j = 0; j < n - 1; j++) {
if(j < i)
cout << "-";
else
cout << "#";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(j < n - i - 1)
System.out.print("#");
else
System.out.print("-");
}
for(int j = 0; j < n - 1; j++) {
if(j < i)
System.out.print("-");
else
System.out.print("#");
}
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
}
}
n = int(input())
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if j < n - i - 1:
print("#", end="")
else:
print("-", end="")
for j in range(n - 1):
if j < i:
print("-", end="")
else:
print("#", end="")
print()
Problem 2: Minimum Sum Game
Problem Statement: Ram is a boy who is very interested in playing new games, so his mother took him to a puzzle game and asked him to solve it.
His mother gave some instructions to solve the puzzle game.
- Now he has to follow all the given instructions while solving the game. His mother explained the step by step rule of the game and told that first you have to take n elements, after that you have to sum the digits of that n taken numbers.
- After adding the digits of the taken number, He has to check that the sum of which digit numbers is minimum.
- Now Ram has to find the minimum sum of digits of the number which he had taken in the beginning of the game.
Write a proper algorithmic code to solve that puzzle game.
Constraints :
1<=n<= 105
Input:
4 = number of elements
21 2 30 33 elements
Output:
2
Space Complexity: O(n) for storing input value.
Run
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int digitSum(int num) {
int sum = 0;
while (num > 0) {
sum += num % 10;
num /= 10;
}
return sum;
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector vect(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cin >> vect[i];
}
int minSum = INT_MAX;
int result = vect[0];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int sum = digitSum(vect[i]);
if (sum < minSum) {
minSum = sum;
result = vect[i];
}
}
cout << result << endl;
return 0;
}
Run
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static int digitSum(int num) {
int sum = 0;
while (num > 0) {
sum += num % 10;
num /= 10;
}
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
int minSum = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int result = arr[0];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int sum = digitSum(arr[i]);
if(sum < minSum) {
minSum = sum;
result = arr[i];
}
}
System.out.println(result);
sc.close();
}
}
Run
def digit_sum(num):
return sum(int(d) for d in str(num))
n = int(input())
arr = list(map(int, input().split()))
min_sum = float('inf')
result = arr[0]
for num in arr:
s = digit_sum(num)
if s < min_sum:
min_sum = s
result = num
print(result)
Problem 3: Finding Sequence
Problem Statement: On Monday morning,the principal of a school in Noida thought that let’s do something different with the children today.
- So the principal called different students to the assembly hall and formed a group of students from different classes of his school to explain to them the task they want to do today.
- Now the principal explained to them that all the people you have gathered here are a group.
- So the task is that all you have to do is that all the people who are in this group, you have to tell your roll number.
- After collecting the roll numbers, you have to make a line according to the roll numbers in the ascending order.
And to check how many consecutive sub sequences are being formed in the line that is being formed according to these roll numbers?
- And Finally the main task is that we have to see, out of the consecutive sub-sequences that are being made according to the roll number, what is the maximum possible length of the consecutive sequence of n roll no. of students taken in the beginning ?
- Definition of consecutive sequence: Numbers that follow each other continuously in the order from smallest to largest are called consecutive numbers.
Constraints :
- 0 <= nums.length <= 10^5
- -10^9 <= nums[i] <= 10^9
Input:
- 6 = number of elements
- [100,4,200,1,3,2] = elements
Output:
4
Space Complexity: O(n) for storing extra elements
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector nums(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> nums[i];
if (n == 0) {
cout << 0;
return 0;
}
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
int maxLen = 1, count = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) continue; // skip duplicates
if (nums[i] == nums[i - 1] + 1) {
count++;
} else {
count = 1;
}
maxLen = max(maxLen, count);
}
cout << maxLen;
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] nums = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
nums[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
if (n == 0) {
System.out.println(0);
return;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
int maxLen = 1, count = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) continue;
if (nums[i] == nums[i - 1] + 1) {
count++;
} else {
count = 1;
}
maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, count);
}
System.out.println(maxLen);
}
}
n = int(input())
nums = list(map(int, input().split()))
if not nums:
print(0)
else:
nums.sort()
max_len = 1
count = 1
for i in range(1, n):
if nums[i] == nums[i - 1]:
continue
elif nums[i] == nums[i - 1] + 1:
count += 1
else:
count = 1
max_len = max(max_len, count)
print(max_len)
Problem 4: Confused String
Problem Statement: Aditya and Mohan are two friends. Aditya said to Mohan, let’s do your brain test today and check whether you get confused or not.
To test Mohan’s brain, Aditya gives him two strings, a string S1 and a string S2.
Here string S1 = coaching and string S2 = coding
While instructing Mohan, Aditya said that the letters of both the strings are in lowercase. Now Mohan’s curiosity was increasing, So he asked Aditya what he has to do with these two strings.
Aditya instructs Mohan:
- That he has to provide a solution to find the minimum number of characters that need to be appended at the end of the first string, so the second string becomes a subsequence of the first string.
- All the letters of the second string have to be compared with the first string in order to confirm/prove that first string is a subsequence of the second string.
- Now Mohan has to give the algorithmic solution to pass this brain test.
Definition of subsequence: Subsequence is a string that can be derived from another string by deleting some or no characters without changing the order of the remaining characters.
Constraints:
- 1 <= s.length <= 10^5
- String1 and string2 consist of only lowercase english letters
Input:
String 1 : coaching
String 2 : coding
Output:
4
Space Complexity: O(n)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s, t;
cin >> s >> t;
int i = 0, matched = 0;
for (char c : t) {
while (i < s.length() && s[i] != c) {
i++;
}
if (i == s.length()) break;
matched++;
i++;
}
int result = t.length() - matched;
cout << result;
return 0;
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = sc.next();
String t = sc.next();
int i = 0, matched = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < t.length(); j++) {
while (i < s.length() && s.charAt(i) != t.charAt(j)) {
i++;
}
if (i == s.length()) break;
matched++;
i++;
}
int result = t.length() - matched;
System.out.println(result);
}
}
s = input()
t = input()
i = 0
matched = 0
for c in t:
while i < len(s) and s[i] != c:
i += 1
if i == len(s):
break
matched += 1
i += 1
result = len(t) - matched
print(result)
Problem 5: Am I Panagram?
Problem Statement: Aman has given a sentence with a meaning, his task is to check whether the given sentence is panagram or not. Your task is to write an algorithmic code to help aman.
(Panagram is the sentence which complete all the english alphabet at least once)
Input:
6
abc defghu ijklmnbop qrstuvw xyy yz
Output:
True
Let L = total length of all n strings combined (i.e., res.size())
Time Complexity: O(L)
Space Complexity: O(L)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
string word, res;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> word;
res += word;
}
unordered_set letters;
for (char c : res) {
if (isalpha(c)) {
letters.insert(tolower(c));
}
}
cout << (letters.size() == 26 ? "True" : "False");
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
Set set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String s = sc.next();
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
if (Character.isLetter(c)) {
set.add(Character.toLowerCase(c));
}
}
}
System.out.println(set.size() == 26 ? "True" : "False");
}
}
n = int(input())
words = [input() for _ in range(n)]
combined = ''.join(words).lower()
letters = set()
for char in combined:
if char.isalpha():
letters.add(char)
print("True" if len(letters) == 26 else "False")
These were some Sample Virtusa Coding Questions and Answers, go through them properly and prepare effectively.
If you want to prepare questions like these for Virtusa Coding Round, do checkout our Coding Dashboard.
FAQ's related Virtusa Power Coding Challenge
Answer:
The Virtusa recruitment process mainly includes 4 rounds:
Round 1: Online Assessment (Aptitude, Logical Reasoning, Verbal, Pseudocode, CS Fundamentals and Coding)
Round 2: Technical Interview
Round 3: Group Discussion or Managerial Round
Round 4: HR Interview
Answer:
- Coder Profile: Includes 4 moderate-level coding questions to be solved in 50 minutes.
- Power Coder Profile: Includes 3 high difficulty coding questions with 80 minutes to solve. It is designed for candidates aiming for advanced roles or higher packages.
Answer:
The Virtusa assessment includes the following sections:
- Quantitative Aptitude and Logical Reasoning
- Verbal Ability
- Pseudocode and Programming Fundamentals
- Computer Science Fundamentals (OS, DBMS, Data Structures)
- Coding (for Coder/Power Coder tracks)
Answer:
No. While Virtusa hires extensively through campus placements, it also conducts off-campus drives and open hiring challenges like Talent Titan or Power Programmer Challenges through platforms like HirePro, TalentTitan, and Superset.
Answer:
To be eligible for Virtusa On campus hiring, candidates must meet the following criteria:
- Must be from the B.E./B.Tech (CSE, IT, ECE, EEE, EIE) or MCA/M.Tech background.
- Should belong to the 2025 passing out batch.
- Must have 60% or above in 10th, 12th, and graduation (or equivalent CGPA).
- Should not have more than 1 active backlog at the time of applying.
- Must not have a gap of more than 1 year in education.
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Flipkart Coding Questions and Answers
Sample Flipkart Coding Questions with Solution
Here, on Flipkart coding questions and answers page you will get sample DSA questions with solution which can be asked in Flipkart SDE 1 Coding Assessment.
Let you know that Flipkart mainly asks Data Structures and Algorithms based questions based Binary Search Tree, Graphs, Tries, Trees and Dynamic programming.
Checkout this page get all the Sample Flipkart Coding Questions with Solutions.
About Round 1 – Flipkart Coding Assessment
First stage of the Flipkart SDE-1 recruitment process is an online coding assessment, conducted on HackerRank.
This round serves as an initial screening to evaluate your problem solving and coding skills.
Duration: 90 minutes
Platform: HackerRank
Number of Questions: 3 coding problems
Difficulty Level: Medium to Hard
Topics Covered:
1. Binary Search Trees (BST)
2. Tries (Prefix Trees)
3. Tree and Graph Traversals (DFS, BFS)
4. Graph Algorithms (Cycle detection, shortest paths, connected components)
5. Dynamic Programming (Tabulation, memoization, optimization problems)
To succeed in this round, focus on writing clean, optimized code and thoroughly testing your solutions against edge cases.
After this round 2 Technical Interviews followed by Hiring Manager Round will be conducted for assessing the candidates.
You can also opt for C or C++ too.
Practice Coding Questions:
Checkout PrepInsta Prime:
Flipkart Coding Questions with Solutions
1. Program for Finding Minimum in a Rotated Sorted Array Problem
You are given a sorted array that has been rotated between 1 and n times. For example:
- If the array [1,2,3,4,5,6] is rotated 4 times, it becomes [3,4,5,6,1,2].
- If rotated 6 times, it goes back to [1,2,3,4,5,6].
Your task is to find the smallest element in this rotated array. The elements in the array are unique.
While finding the minimum in O(n) time is easy, you need to write an algorithm that works in O(logn) time.
Output: 0
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 1000
- -1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000
Solution with Binary Search Method
Use binary search to narrow down the search space by checking if the middle element lies in the rotated part, giving an O(logn) solution.
- Time complexity: O(log 1)
- Space complexity: O(1)
Code
class Solution {
public:
int findMin(vector<int> &nums) {
int res = nums[0];
int l = 0;
int r = nums.size() - 1;
while (l <= r) {
if (nums[l] < nums[r]) { res = min(res, nums[l]); break; } int m = l + (r - l) / 2; res = min(res, nums[m]); if (nums[m] >= nums[l]) {
l = m + 1;
} else {
r = m - 1;
}
}
return res;
}
};
public class Solution {
public int findMin(int[] nums) {
int l = 0;
int r = nums.length - 1;
int res = nums[0];
while (l <= r) {
if (nums[l] < nums[r]) {
res = Math.min(res, nums[l]);
break;
}
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
res = Math.min(res, nums[m]);
if (nums[m] >= nums[l]) {
l = m + 1;
} else {
r = m - 1;
}
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution:
def findMin(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
res = nums[0]
l, r = 0, len(nums) - 1
while l <= r:
if nums[l] < nums[r]:
res = min(res, nums[l])
break
m = (l + r) // 2
res = min(res, nums[m])
if nums[m] >= nums[l]:
l = m + 1
else:
r = m - 1
return res
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number}
*/
findMin(nums) {
let l = 0;
let r = nums.length - 1;
let res = nums[0];
while (l <= r) {
if (nums[l] <= nums[r]) {
res = Math.min(res, nums[l]);
break;
}
let m = l + Math.floor((r - l) / 2);
res = Math.min(res, nums[m]);
if (nums[m] >= nums[l]) {
l = m + 1;
} else {
r = m - 1;
}
}
return res;
}
}
2. Design Add and Search Words Data Structure
Design a data structure to store words and efficiently support word addition and searching, including flexible matching.
Implement the WordDictionary class with the following methods:
- addWord(word): Adds the given word to the data structure, allowing it to be stored for future searches. This is useful for building a collection of words dynamically.
- search(word): Searches for a word in the data structure. The search supports both exact matches and partial matches using the . character as a wildcard. The . can represent any letter, making the search versatile for patterns or incomplete words.
This structure is particularly useful for applications like pattern matching or word suggestions.
["WordDictionary", "addWord", "day", "addWord", "bay", "addWord", "may", "search", "say", "search", "day", "search", ".ay", "search", "b.."]
Output:
[null, null, null, null, false, true, true, true]
Explanation:
- WordDictionary wordDictionary = new WordDictionary();
- wordDictionary.addWord(“day”);
- wordDictionary.addWord(“bay”);
- wordDictionary.addWord(“may”);
- wordDictionary.search(“say”); // return false
- wordDictionary.search(“day”); // return true
- wordDictionary.search(“.ay”); // return true
- wordDictionary.search(“b..”); // return true
Constraints:
- 1 <= word.length <= 20
- word in addWord consists of lowercase English letters.
- word in search consist of ‘.’ or lowercase English letters.
Solving with Brute Force Method
Words are stored in a list, and each search checks all words by iterating through them, including handling wildcards (.) character by character. This leads to a time complexity of O(m * n), where m is the number of words and n is the word length.
- Time complexity: O(n) for addWord(), O(m∗n) for search().
- Space complexity: O(m*n)
where m is the number of words added and n is the length of the string.
Code
class WordDictionary {
public:
vector<string> store;
WordDictionary() {}
void addWord(string word) {
store.push_back(word);
}
bool search(string word) {
for (string w : store) {
if (w.length() != word.length()) continue;
int i = 0;
while (i < w.length()) {
if (w[i] == word[i] || word[i] == '.') {
i++;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (i == w.length()) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
public class WordDictionary {
private List<String> store;
public WordDictionary() {
store = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void addWord(String word) {
store.add(word);
}
public boolean search(String word) {
for (String w : store) {
if (w.length() != word.length()) continue;
int i = 0;
while (i < w.length()) {
if (w.charAt(i) == word.charAt(i) ||
word.charAt(i) == '.') {
i++;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (i == w.length()) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
class WordDictionary:
def __init__(self):
self.store = []
def addWord(self, word: str) -> None:
self.store.append(word)
def search(self, word: str) -> bool:
for w in self.store:
if len(w) != len(word):
continue
i = 0
while i < len(w):
if w[i] == word[i] or word[i] == '.':
i += 1
else:
break
if i == len(w):
return True
return False
class WordDictionary {
constructor() {
this.store = [];
}
/**
* @param {string} word
* @return {void}
*/
addWord(word) {
this.store.push(word);
}
/**
* @param {string} word
* @return {boolean}
*/
search(word) {
for (let w of this.store) {
if (w.length !== word.length) continue;
let i = 0;
while (i < w.length) {
if (w[i] === word[i] ||
word[i] === '.') {
i++;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (i === w.length) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
Flipkart Coding Questions with Solutions
3. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
You are given the root of a binary tree, and your task is to determine its depth.
Depth of a binary tree refers to the number of nodes present along the longest path starting from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
In simpler terms, it measures how deep the tree goes from the topmost node (the root) to the bottommost node (a leaf with no children). This depth represents the maximum number of steps needed to traverse the tree vertically.
Example:
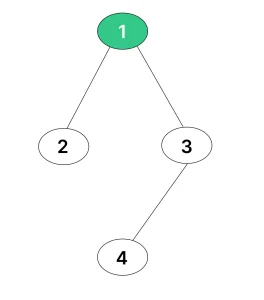
Output: 3
Constraints:
- 0 <= The number of nodes in the tree <= 100.
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Solving with Iterative DFS(Stack) Method
This method uses a stack to simulate the depth-first traversal iteratively. Each node is paired with its depth and pushed onto the stack. As you process each node, you update the maximum depth by comparing the current depth of the node with the recorded value.
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(n)
Code
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
stack> stack;
stack.push({root, 1});
int res = 0;
while (!stack.empty()) {
pair current = stack.top();
stack.pop();
TreeNode* node = current.first;
int depth = current.second;
if (node != nullptr) {
res = max(res, depth);
stack.push({node->left, depth + 1});
stack.push({node->right, depth + 1});
}
}
return res;
}
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
Stack> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(new Pair<>(root, 1));
int res = 0;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Pair current = stack.pop();
TreeNode node = current.getKey();
int depth = current.getValue();
if (node != null) {
res = Math.max(res, depth);
stack.push(new Pair<>(node.left, depth + 1));
stack.push(new Pair<>(node.right, depth + 1));
}
}
return res;
}
}
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
stack = [[root, 1]]
res = 0
while stack:
node, depth = stack.pop()
if node:
res = max(res, depth)
stack.append([node.left, depth + 1])
stack.append([node.right, depth + 1])
return res
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* constructor(val = 0, left = null, right = null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
maxDepth(root) {
const stack = [[root, 1]];
let res = 0;
while (stack.length > 0) {
const current = stack.pop();
const node = current[0];
const depth = current[1];
if (node !== null) {
res = Math.max(res, depth);
stack.push([node.left, depth + 1]);
stack.push([node.right, depth + 1]);
}
}
return res;
}
}
4. Number of Connected Components In An Undirected Graph Problem
Given an undirected graph with n nodes, an edges array is provided where edges[i] = [a, b] indicates an edge between node a and node b.
The nodes are numbered from 0 to n – 1. The task is to return the total number of connected components in the graph.
edges=[[0,1], [0,2]]
Output: 1
Constraints:
- 1 <= n <= 100
- 0 <= edges.length <= n * (n – 1) / 2
Solving with Disjoint Set Union (Rank | Size) method
DSU tracks the connected components using a union-find approach, where nodes are grouped into sets. Using union by rank or size ensures efficient merging of components, and the number of connected components is determined by the number of distinct sets.
- Time complexity: O(V+(E∗α(V)))
- Space complexity: O(V)
Where V is the number of vertices and E is the number of edges.
Code:
class DSU {
public:
vector parent;
vector rank;
DSU(int n) {
parent.resize(n);
rank.resize(n, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
int find(int node) {
int cur = node;
while (cur != parent[cur]) {
parent[cur] = parent[parent[cur]];
cur = parent[cur];
}
return cur;
}
bool unionSets(int u, int v) {
int pu = find(u);
int pv = find(v);
if (pu == pv) {
return false;
}
if (rank[pv] > rank[pu]) {
swap(pu, pv);
}
parent[pv] = pu;
rank[pu] += rank[pv];
return true;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int countComponents(int n, vector>& edges) {
DSU dsu(n);
int res = n;
for (auto& edge : edges) {
if (dsu.unionSets(edge[0], edge[1])) {
res--;
}
}
return res;
}
};
public class DSU {
int[] parent;
int[] rank;
public DSU(int n) {
parent = new int[n];
rank = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
rank[i] = 1;
}
}
public int find(int node) {
int cur = node;
while (cur != parent[cur]) {
parent[cur] = parent[parent[cur]];
cur = parent[cur];
}
return cur;
}
public boolean union(int u, int v) {
int pu = find(u);
int pv = find(v);
if (pu == pv) {
return false;
}
if (rank[pv] > rank[pu]) {
int temp = pu;
pu = pv;
pv = temp;
}
parent[pv] = pu;
rank[pu] += rank[pv];
return true;
}
}
public class Solution {
public int countComponents(int n, int[][] edges) {
DSU dsu = new DSU(n);
int res = n;
for (int[] edge : edges) {
if (dsu.union(edge[0], edge[1])) {
res--;
}
}
return res;
}
}
class DSU:
def __init__(self, n):
self.parent = list(range(n))
self.rank = [1] * n
def find(self, node):
cur = node
while cur != self.parent[cur]:
self.parent[cur] = self.parent[self.parent[cur]]
cur = self.parent[cur]
return cur
def union(self, u, v):
pu = self.find(u)
pv = self.find(v)
if pu == pv:
return False
if self.rank[pv] > self.rank[pu]:
pu, pv = pv, pu
self.parent[pv] = pu
self.rank[pu] += self.rank[pv]
return True
class Solution:
def countComponents(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> int:
dsu = DSU(n)
res = n
for u, v in edges:
if dsu.union(u, v):
res -= 1
return res
class DSU {
/**
* @param {number} n
*/
constructor(n) {
this.parent = Array.from({ length: n }, (_, i) => i);
this.rank = Array(n).fill(1);
}
/**
* @param {number} node
* @return {number}
*/
find(node) {
let cur = node;
while (cur !== this.parent[cur]) {
this.parent[cur] = this.parent[this.parent[cur]];
cur = this.parent[cur];
}
return cur;
}
/**
* @param {number} u
* @param {number} v
* @return {boolean}
*/
union(u, v) {
let pu = this.find(u);
let pv = this.find(v);
if (pu === pv) {
return false;
}
if (this.rank[pv] > this.rank[pu]) {
[pu, pv] = [pv, pu];
}
this.parent[pv] = pu;
this.rank[pu] += this.rank[pv];
return true;
}
}
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} edges
* @returns {number}
*/
countComponents(n, edges) {
const dsu = new DSU(n);
let res = n;
for (const [u, v] of edges) {
if (dsu.union(u, v)) {
res--;
}
}
return res;
}
}
Flipkart Coding Questions
5. Maximum Product Subarray Problem
Given an integer array nums, find the subarray with the maximum product and return its value.
A sub array is a continuous, non-empty portion of the array.
You can assume the result will fit within a 32-bit integer.
Output: 4
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 1000
- -10 <= nums[i] <= 10
Solving with Kadane’s Algorithm method
Modify Kadane’s algorithm to handle products by keeping track of both the maximum and minimum products at each index. This efficiently handles both positive and negative numbers.
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)
Code
class Solution {
public:
int maxProduct(vector<int>& nums) {
int res = nums[0];
int curMin = 1, curMax = 1;
for (int num : nums) {
int tmp = curMax * num;
curMax = max(max(num * curMax, num * curMin), num);
curMin = min(min(tmp, num * curMin), num);
res = max(res, curMax);
}
return res;
}
};
public class Solution {
public int maxProduct(int[] nums) {
int res = nums[0];
int curMin = 1, curMax = 1;
for (int num : nums) {
int tmp = curMax * num;
curMax = Math.max(Math.max(num * curMax, num * curMin), num);
curMin = Math.min(Math.min(tmp, num * curMin), num);
res = Math.max(res, curMax);
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution:
def maxProduct(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
res = nums[0]
curMin, curMax = 1, 1
for num in nums:
tmp = curMax * num
curMax = max(num * curMax, num * curMin, num)
curMin = min(tmp, num * curMin, num)
res = max(res, curMax)
return res
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number}
*/
maxProduct(nums) {
let res = nums[0];
let curMin = 1;
let curMax = 1;
for (const num of nums) {
const tmp = curMax * num;
curMax = Math.max(Math.max(num * curMax, num * curMin), num);
curMin = Math.min(Math.min(tmp, num * curMin), num);
res = Math.max(res, curMax);
}
return res;
}
}
6. Merging Triplets to Form a Target Triplet
The Merge Triplets to Form Target problem involves determining whether you can construct a specific triplet using a series of merging operations on given triplets.
Problem Description
Input
- triplets: A 2D list where each triplet is of the form [a, b, c].
- target: A triplet [x, y, z] that we aim to construct.
Operation
For two triplets triplets[i] = [ai, bi, ci] and triplets[j] = [aj, bj, cj], you can update triplets[j] as follows:
triplets[j]=[max(ai,aj),max(bi,bj),max(ci,cj)]
Goal
Determine whether it is possible to make target an element of triplets after performing the allowed operations.
Constraints:
- 1 <= triplets.length <= 1000
- 1 <= ai, bi, ci, x, y, z <= 100
There are mainly two approach to solve this problem –
- Greedy
- Greedy (Optimal)
Flipkart Coding Questions and Answers
1. Greedy
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)
class Solution:
def mergeTriplets(self, triplets: List[List[int]], target: List[int]) -> bool:
good = set()
for t in triplets:
if t[0] > target[0] or t[1] > target[1] or t[2] > target[2]:
continue
for i, v in enumerate(t):
if v == target[i]:
good.add(i)
return len(good) == 3class Solution {
public:
bool isNStraightHand(vector& hand, int groupSize) {
if (hand.size() % groupSize != 0) return false;
unordered_map count;
for (int num : hand) count[num]++;
sort(hand.begin(), hand.end());
for (int num : hand) {
if (count[num] > 0) {
for (int i = num; i < num + groupSize; i++) {
if (count[i] == 0) return false;
count[i]--;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}; public class Solution {
public boolean mergeTriplets(int[][] triplets, int[] target) {
Set good = new HashSet<>();
for (int[] t : triplets) {
if (t[0] > target[0] || t[1] > target[1] || t[2] > target[2]) {
continue;
}
for (int i = 0; i < t.length; i++) {
if (t[i] == target[i]) {
good.add(i);
}
}
}
return good.size() == 3;
}
} class Solution {
/**
* @param {number[][]} triplets
* @param {number[]} target
* @return {boolean}
*/
mergeTriplets(triplets, target) {
const good = new Set();
for (const t of triplets) {
if (t[0] > target[0] || t[1] > target[1] || t[2] > target[2]) {
continue;
}
for (let i = 0; i < t.length; i++) {
if (t[i] === target[i]) {
good.add(i);
}
}
}
return good.size === 3;
}
}2. Greedy (Optimal)
Time & Space Complexity
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
bool mergeTriplets(vector>& triplets, vector& target) {
bool x = false, y = false, z = false;
for (const auto& t : triplets) {
x |= (t[0] == target[0] && t[1] <= target[1] && t[2] <= target[2]);
y |= (t[0] <= target[0] && t[1] == target[1] && t[2] <= target[2]);
z |= (t[0] <= target[0] && t[1] <= target[1] && t[2] == target[2]);
if (x && y && z) return true;
}
return false;
}
}; public class Solution {
public boolean mergeTriplets(int[][] triplets, int[] target) {
boolean x = false, y = false, z = false;
for (int[] t : triplets) {
x |= (t[0] == target[0] && t[1] <= target[1] && t[2] <= target[2]);
y |= (t[0] <= target[0] && t[1] == target[1] && t[2] <= target[2]);
z |= (t[0] <= target[0] && t[1] <= target[1] && t[2] == target[2]);
if (x && y && z) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
class Solution:
def mergeTriplets(self, triplets: List[List[int]], target: List[int]) -> bool:
x = y = z = False
for t in triplets:
x |= (t[0] == target[0] and t[1] <= target[1] and t[2] <= target[2])
y |= (t[0] <= target[0] and t[1] == target[1] and t[2] <= target[2])
z |= (t[0] <= target[0] and t[1] <= target[1] and t[2] == target[2])
if x and y and z:
return True
return Falseclass Solution {
/**
* @param {number[][]} triplets
* @param {number[]} target
* @return {boolean}
*/
mergeTriplets(triplets, target) {
let x = false, y = false, z = false;
for (let t of triplets) {
x |= (t[0] === target[0] && t[1] <= target[1] && t[2] <= target[2]);
y |= (t[0] <= target[0] && t[1] === target[1] && t[2] <= target[2]);
z |= (t[0] <= target[0] && t[1] <= target[1] && t[2] === target[2]);
if (x && y && z) return true;
}
return false;
}
}If you want to practice more for Flipkart Coding Assessment, you can visit our Coding Blogs that will surely help you to prepare for Flipkart SDE 1 Coding Assessment and Flipkart Technical Interviews.
Practice Coding Questions:
Checkout PrepInsta Prime:
Faq's Related to Flipkart Coding Assessment
Answer:
The coding questions typically range from medium to hard difficulty, covering data structures, algorithms, and problem-solving logic relevant to real-world scenarios.
Answer:
Yes, Flipkart often includes problems based on Trees, Graphs, Binary Search Trees (BST), and Tries, so it’s important to have a solid grasp of these topics.
Answer:
Yes, HackerRank allows you to code in your preferred programming language, though proficiency in C++, Java, or Python is recommended due to better support and familiarity.
Uber Coding Questions and Answers
Uber Coding Questions with Solutions
Here on this page you will get Sample Uber coding questions and answers which will help you to prepare for Online Coding Assessment of Uber to hire freshers for SDE 1 Role.
Let you know that the Online Assessment will be conducted on CodeSignal Platform. After Application Process, candidates will be communicated through mail for Online Assessment on CodeSignal.

Uber SDE 1 Profile Details
Role: Software Development Engineer 1 (SDE 1)
Work:
- Develop, test, and maintain scalable software solutions.
- Collaborate with teams to build high-performance applications.
- Solve real-world engineering challenges using algorithms and data structures.
Tech Stack Required:
- Programming Languages: Python, Java, C++, Go
- Data Structures & Algorithms (DSA)
- Databases: SQL, NoSQL (MongoDB, Cassandra)
- Backend: Microservices, REST APIs
- Frontend (if required): React, Angular
- Cloud & DevOps: AWS, Kubernetes, Docker (preferred)
Checkout PrepInsta Prime:
Practice Coding Questions:
Further on this page you will get Sample Uber Coding Questions and Answers that will help you to prepare for Uber Online Coding Assessment on CodeSignal Platform.
Sample Uber Coding Questions with Solutions
Question 1: Finding Longest Repeating Character Replacement Problem
You are given a string s that contains only uppercase English letters and an integer k. Your task is to determine the length of the longest substring in s that can consist of just one distinct character after modifying the string.
You are allowed to make up to k replacements, where each replacement involves changing any character in the substring to another uppercase English letter.
The goal is to maximize the length of this uniform substring by carefully choosing which characters to replace while staying within the limit of k changes.
Output: 5
Constraints:
- 1 <= s.length <= 1000
- 0 <= k <= s.length
Solving Through Sliding Window Method
Maintain a sliding window and expand it to include more characters. If the number of characters to replace exceeds the limit, shrink the window from the left. Track the longest valid window during this process.
- Time complexity: O(m*n)
- Space complexity: O(m)
where n is the length of the string and m is the total number of unique characters in the string.
Code
class Solution {
public:
int characterReplacement(std::string s, int k) {
int res = 0;
unordered_set charSet(s.begin(), s.end());
for (char c : charSet) {
int count = 0, l = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < s.size(); r++) {
if (s[r] == c) {
count++;
}
while ((r - l + 1) - count > k) {
if (s[l] == c) {
count--;
}
l++;
}
res = std::max(res, r - l + 1);
}
}
return res;
}
};
public class Solution {
public int characterReplacement(String s, int k) {
int res = 0;
HashSet charSet = new HashSet<>();
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
charSet.add(c);
}
for (char c : charSet) {
int count = 0, l = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < s.length(); r++) {
if (s.charAt(r) == c) {
count++;
}
while ((r - l + 1) - count > k) {
if (s.charAt(l) == c) {
count--;
}
l++;
}
res = Math.max(res, r - l + 1);
}
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution:
def characterReplacement(self, s: str, k: int) -> int:
res = 0
charSet = set(s)
for c in charSet:
count = l = 0
for r in range(len(s)):
if s[r] == c:
count += 1
while (r - l + 1) - count > k:
if s[l] == c:
count -= 1
l += 1
res = max(res, r - l + 1)
return res
class Solution {
/**
* @param {string} s
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
characterReplacement(s, k) {
let res = 0;
let charSet = new Set(s);
for (let c of charSet) {
let count = 0, l = 0;
for (let r = 0; r < s.length; r++) {
if (s[r] === c) {
count++;
}
while ((r - l + 1) - count > k) {
if (s[l] === c) {
count--;
}
l++;
}
res = Math.max(res, r - l + 1);
}
}
return res;
}
}
Question 2: Serializing and Deserializing Binary Tree.
Create an algorithm to convert a binary tree into a string (serialization) and then reconstruct the same binary tree from that string (deserialization).
Serialization means converting a binary tree into a format that can be saved or sent to another system. Deserialization means converting that saved format back into the original binary tree.
Goal is to ensure that the binary tree can be serialized into a string and later deserialized back to its original structure without any loss of information. There are no specific rules for how you should implement this; the approach is up to you.
Example:
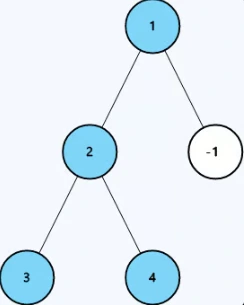
Output: []
Constraints:
- 0 <= The number of nodes in the tree <= 1000.
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solving Breadth First Search Method
In the BFS approach, the binary tree is serialized level by level using a queue to store node values. During deserialization, the data is processed sequentially to rebuild the tree by connecting child nodes level-wise.
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(n)
Code
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Codec {
public:
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
string serialize(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return "N";
string res;
queue<TreeNode*> queue;
queue.push(root);
while (!queue.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = queue.front();
queue.pop();
if (!node) {
res += "N,";
} else {
res += to_string(node->val) + ",";
queue.push(node->left);
queue.push(node->right);
}
}
return res;
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {
stringstream ss(data);
string val;
getline(ss, val, ',');
if (val == "N") return nullptr;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(stoi(val));
queue<TreeNode*> queue;
queue.push(root);
while (getline(ss, val, ',')) {
TreeNode* node = queue.front();
queue.pop();
if (val != "N") {
node->left = new TreeNode(stoi(val));
queue.push(node->left);
}
getline(ss, val, ',');
if (val != "N") {
node->right = new TreeNode(stoi(val));
queue.push(node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
};
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Codec {
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return "N";
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
Queu<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node == null) {
res.append("N,");
} else {
res.append(node.val).append(",");
queue.add(node.left);
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
return res.toString();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
String[] vals = data.split(",");
if (vals[0].equals("N")) return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[0]));
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
int index = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (!vals[index].equals("N")) {
node.left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[index]));
queue.add(node.left);
}
index++;
if (!vals[index].equals("N")) {
node.right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[index]));
queue.add(node.right);
}
index++;
}
return root;
}
}
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Codec:
# Encodes a tree to a single string.
def serialize(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> str:
if not root:
return "N"
res = []
queue = deque([root])
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
if not node:
res.append("N")
else:
res.append(str(node.val))
queue.append(node.left)
queue.append(node.right)
return ",".join(res)
# Decodes your encoded data to tree.
def deserialize(self, data: str) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
vals = data.split(",")
if vals[0] == "N":
return None
root = TreeNode(int(vals[0]))
queue = deque([root])
index = 1
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
if vals[index] != "N":
node.left = TreeNode(int(vals[index]))
queue.append(node.left)
index += 1
if vals[index] != "N":
node.right = TreeNode(int(vals[index]))
queue.append(node.right)
index += 1
return root
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* constructor(val = 0, left = null, right = null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Codec {
/**
* Encodes a tree to a single string.
*
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {string}
*/
serialize(root) {
if (!root) return "N";
const res = [];
const queue = new Queue();
queue.push(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
const node = queue.pop();
if (!node) {
res.push("N");
} else {
res.push(node.val);
queue.push(node.left);
queue.push(node.right);
}
}
return res.join(",");
}
/**
* Decodes your encoded data to tree.
*
* @param {string} data
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
deserialize(data) {
const vals = data.split(",");
if (vals[0] === "N") return null;
const root = new TreeNode(parseInt(vals[0]));
const queue = new Queue([root]);
let index = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
const node = queue.pop();
if (vals[index] !== "N") {
node.left = new TreeNode(parseInt(vals[index]));
queue.push(node.left);
}
index++;
if (vals[index] !== "N") {
node.right = new TreeNode(parseInt(vals[index]));
queue.push(node.right);
}
index++;
}
return root;
}
}
Question 3: N Queen Problem
The n-queens puzzle is about placing n queens on an n x n chessboard so that no two queens can attack each other.
Queens can attack in three ways: horizontally, vertically, and diagonally.
Your task is to find all possible ways to place the queens on the board, ensuring no two queens attack each other.
Each solution will show a unique board arrangement where ‘Q’ represents a queen and ‘.’ represents an empty square. The solutions can be returned in any order.
Example 1:
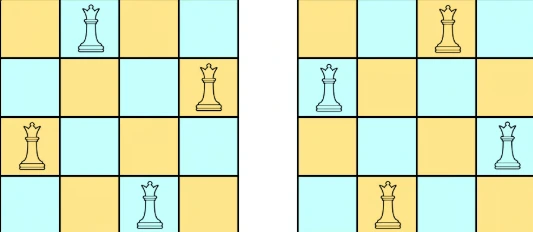
Output: [[".Q..","...Q","Q...","..Q."],
["..Q.","Q...","...Q",".Q.."]]
Explanation: There are two different solutions to the 4-queens puzzle.
Constraints:
- 1 <= n <= 8
Solving through Backtracking(Hash Set) Method
Here, we use hash sets to track the columns and diagonals already occupied by queens. These sets allow quick lookups to check if a cell is safe for placing a queen. The method reduces redundant checks and improves efficiency.
- Time complexity: O(n!)
- Space complexity: O(n^2)
Code
class Solution {
public:
unordered_set<int> col;
unordered_set<int> posDiag;
unordered_set<int> negDiag;
vector<vector<string>> res;
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {
vector<string> board(n, string(n, '.'));
backtrack(0, n, board);
return res;
}
private:
void backtrack(int r, int n, vector<string>& board) {
if (r == n) {
res.push_back(board);
return;
}
for (int c = 0; c < n; c++) {
if (col.count(c) || posDiag.count(r + c) ||
negDiag.count(r - c)) {
continue;
}
col.insert(c);
posDiag.insert(r + c);
negDiag.insert(r - c);
board[r][c] = 'Q';
backtrack(r + 1, n, board);
col.erase(c);
posDiag.erase(r + c);
negDiag.erase(r - c);
board[r][c] = '.';
}
}
};
public class Solution {
Set<Integer> col = new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> posDiag = new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> negDiag = new HashSet<>();
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
char[][] board = new char[n][n];
for (char[] row : board) {
Arrays.fill(row, '.');
}
backtrack(0, n, board);
return res;
}
private void backtrack(int r, int n, char[][] board) {
if (r == n) {
List<String> copy = new ArrayList<>();
for (char[] row : board) {
copy.add(new String(row));
}
res.add(copy);
return;
}
for (int c = 0; c < n; c++) {
if (col.contains(c) || posDiag.contains(r + c)
|| negDiag.contains(r - c)) {
continue;
}
col.add(c);
posDiag.add(r + c);
negDiag.add(r - c);
board[r][c] = 'Q';
backtrack(r + 1, n, board);
col.remove(c);
posDiag.remove(r + c);
negDiag.remove(r - c);
board[r][c] = '.';
}
}
}
class Solution:
def solveNQueens(self, n: int) -> List[List[str]]:
col = set()
posDiag = set()
negDiag = set()
res = []
board = [["."] * n for i in range(n)]
def backtrack(r):
if r == n:
copy = ["".join(row) for row in board]
res.append(copy)
return
for c in range(n):
if c in col or (r + c) in posDiag or (r - c) in negDiag:
continue
col.add(c)
posDiag.add(r + c)
negDiag.add(r - c)
board[r][c] = "Q"
backtrack(r + 1)
col.remove(c)
posDiag.remove(r + c)
negDiag.remove(r - c)
board[r][c] = "."
backtrack(0)
return res
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {string[][]}
*/
solveNQueens(n) {
const col = new Set();
const posDiag = new Set();
const negDiag = new Set();
const res = [];
const board = Array.from({ length: n },
() => Array(n).fill('.'));
/**
* @param {number} r
* @return {void}
*/
function backtrack(r) {
if (r === n) {
res.push(board.map(row => row.join('')));
return;
}
for (let c = 0; c < n; c++) {
if (col.has(c) || posDiag.has(r + c) ||
negDiag.has(r - c)) {
continue;
}
col.add(c);
posDiag.add(r + c);
negDiag.add(r - c);
board[r][c] = 'Q';
backtrack(r + 1);
col.delete(c);
posDiag.delete(r + c);
negDiag.delete(r - c);
board[r][c] = '.';
}
}
backtrack(0);
return res;
}
}
Question 4: Partition Equal Subset Sum
Given an integer array nums, return true if you can partition the array into two subsets such that the sum of the elements in both subsets is equal or false otherwise.
Example 1:
- Input: nums = [1,2,3,5]
- Output: false
- Explanation: The array cannot be partitioned into equal sum subsets.
Constraints :
- 1 <= nums.length <= 200
- 1 <= nums[i] <= 100
Code:
class Solution {
public:
bool canPartition(vector< int>& nums) {
int sum = 0;
for (int num : nums)
sum += num;
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
int req = sum / 2;
int n = nums.size();
vector< bool> dp(req + 1, false);
dp[0] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = req; j >= nums[i]; j--) {
dp[j] = dp[j] || dp[j - nums[i]];
}
}
return dp[req];
}
};
class Solution {
public boolean canPartition(int[] nums) {
int sum=0;
for(int i:nums)sum+=i;
if(sum%2!=0)return false;
int req=sum/2;
int n=nums.length;
boolean[] dp=new boolean[req+1];
dp[0]=true;
for(int i=0;i=nums[i];j--){
dp[j]=dp[j] || dp[j-nums[i]];
}
}
return dp[req];
}
}
class Solution:
def canPartition(self, nums: List[int]) -> bool:
total_sum = sum(nums)
if total_sum % 2 != 0:
return False
req = total_sum // 2
n = len(nums)
dp = [False] * (req + 1)
dp[0] = True
for i in range(n):
for j in range(req, nums[i] - 1, -1):
dp[j] = dp[j] or dp[j - nums[i]]
return dp[req]
Question 5: Coin Change II: Counting Distinct Combinations
- This problem involves finding the number of distinct combinations of coins that sum up to a given target amount.
- It is a classic example of a Dynamic Programming (DP) problem, focusing on combinations rather than permutations.
Problem Description : Coin Change 2
You are given:
- An integer array coins where each element represents the denomination of a coin (e.g., 1, 5, 10, etc.).
- An integer amount representing the target sum.
Objective: Return the number of distinct combinations of coins that sum up to amount. If it’s impossible to reach the amount, return 0.
Problem Breakdown
- Input: 2D grid of non-negative integers.
- Objective: Find the length of the longest strictly increasing path.
- Movement: Can move to adjacent cells (up, down, left, right) but not diagonally.
- Constraints: Each move must go to a cell with a strictly greater value.
- Goal: Determine the longest path by efficiently exploring the grid.
Constraints:
- 1 <= coins[i] <= 1000
- 1 <= coins.length <= 100
- 0 <= amount <= 1000
Code:
class Solution:
def longestIncreasingPath(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> int:
ROWS, COLS = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
dp = {} # (r, c) -> LIP
def dfs(r, c, prevVal):
if (r < 0 or r == ROWS or c < 0 or
c == COLS or matrix[r][c] <= prevVal
):
return 0
if (r, c) in dp:
return dp[(r, c)]
res = 1
res = max(res, 1 + dfs(r + 1, c, matrix[r][c]))
res = max(res, 1 + dfs(r - 1, c, matrix[r][c]))
res = max(res, 1 + dfs(r, c + 1, matrix[r][c]))
res = max(res, 1 + dfs(r, c - 1, matrix[r][c]))
dp[(r, c)] = res
return res
for r in range(ROWS):
for c in range(COLS):
dfs(r, c, -1)
return max(dp.values())public class Solution {
public int change(int amount, int[] coins) {
Arrays.sort(coins);
int[][] memo = new int[coins.length + 1][amount + 1];
for (int[] row : memo) {
Arrays.fill(row, -1);
}
return dfs(0, amount, coins, memo);
}
private int dfs(int i, int a, int[] coins, int[][] memo) {
if (a == 0) return 1;
if (i >= coins.length) return 0;
if (memo[i][a] != -1) return memo[i][a];
int res = 0;
if (a >= coins[i]) {
res = dfs(i + 1, a, coins, memo);
res += dfs(i, a - coins[i], coins, memo);
}
memo[i][a] = res;
return res;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
int change(int amount, vector& coins) {
sort(coins.begin(), coins.end());
vector> memo(coins.size() + 1,
vector(amount + 1, -1));
return dfs(0, amount, coins, memo);
}
int dfs(int i, int a, vector& coins, vector>& memo) {
if (a == 0) return 1;
if (i >= coins.size()) return 0;
if (memo[i][a] != -1) return memo[i][a];
int res = 0;
if (a >= coins[i]) {
res = dfs(i + 1, a, coins, memo);
res += dfs(i, a - coins[i], coins, memo);
}
memo[i][a] = res;
return res;
}
}; class Solution {
/**
* @param {number} amount
* @param {number[]} coins
* @return {number}
*/
change(amount, coins) {
coins.sort((a, b) => a - b);
let memo = Array.from({ length: coins.length + 1 }, () =>
Array(amount + 1).fill(-1));
const dfs = (i, a) => {
if (a === 0) return 1;
if (i >= coins.length) return 0;
if (memo[i][a] !== -1) return memo[i][a];
let res = 0;
if (a >= coins[i]) {
res = dfs(i + 1, a);
res += dfs(i, a - coins[i]);
}
memo[i][a] = res;
return res;
};
return dfs(0, amount);
}
}These were some of most Important Uber Coding Questions and Answers. If you want to practice more you can visit our coding blogs to explore more….and also visit PrepInsta Prime Course.
Faq's Related to Uber Hiring Process
Question 1. What types of coding questions are asked in the Uber hiring process?
Answer:
Uber Coding Questions mainly includes topics like arrays, strings, dynamic programming, graphs, and recursion.
Question 2. Which programming languages are allowed for the Uber coding test?
Answer:
- Uber allows candidates to code in multiple languages, mainly including C++, Java and Python.
Question 3. How can I prepare for Uber coding round?
Answer:
To prepare effectively:
- Practice Coding Questions from our PrepInsta’s Coding Dashboard.
- Focus on Time & Space Complexity Efficient solution for the DSA Problem.
Meesho Coding Questions and Answers
Meesho Coding Questions with Solutions
Here on this page you will get Sample Meesho coding questions and answers which will help you to prepare for Online Coding Assessment of Meesho to hire freshers for SDE Role.
Let you know that the Online Assessment will be conducted on Hackerearth Platform. After Resume Shortlisting Candidates will be communicated through mail for Online Assessment on Hackerearth.
Meesho Hiring 2025 Details
Role: SDE Trainee (6-month traineeship)
Stipend: ₹1,00,000 per month
Location: Bengaluru (Hybrid, 3 days in-office)
Eligibility: B.E/B.Tech/M.E/M.Tech (CSE, IT, ECE, EEE, E&I) & MCA (2024 & 2025 batch)
Selection Process:
- Application Submission
- HackerEarth Coding Test
- Technical & Hiring Manager Interview
- Offer Letter Rollout
Full-Time Opportunity: Based on performance, FTE offer with ₹20 LPA + benefits
Key Dates:
- Apply by: 14th March 2025
- Coding Test: 22nd March 2025
- Interviews: 4th – 11th April 2025
- Offer Rollout: 12th April 2025
Note: No active backlogs allowed. Candidates who participated in Meesho hiring in the last 6 months are not eligible.
Checkout PrepInsta Prime:
Practice Coding Questions:
Further on this page you will get Sample Meesho Coding Questions and Answers that will help you to prepare for Meesho Online Coding Assessment on Hackerearth Platform.
Sample Meesho Coding Questions with Solutions
Question 1: Program to check Valid Palindrome.
Given a string s, return true if it is a palindrome, otherwise return false.
A palindrome is a string that reads the same forward and backward. It is also case-insensitive and ignores all non-alphanumeric characters.
Output: true
Explanation: After considering only alphanumerical characters we have “wasitacaroracatisaw”, which is a palindrome.
Constraints:
- 1 <= s.length <= 1000
- s is made up of only printable ASCII characters.
Solution:
Reverse String Method
This approach involves reversing the string representation of the array elements, sorting the reversed strings, and then checking for the longest consecutive sequence. However, it’s not commonly used for this problem as it focuses on string manipulation.
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(n)
Code
public class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
StringBuilder newStr = new StringBuilder();
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
if (Character.isLetterOrDigit(c)) {
newStr.append(Character.toLowerCase(c));
}
}
return newStr.toString().equals(newStr.reverse().toString());
}
}
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, s: str) -> bool:
newStr = ''
for c in s:
if c.isalnum():
newStr += c.lower()
return newStr == newStr[::-1]
class Solution {
/**
* Check if a character is alphanumeric
* @param {char} char
* @return {boolean}
*/
isAlphanumeric(char) {
return (char >= 'a' && char <= 'z') ||
(char >= 'A' && char <= 'Z') ||
(char >= '0' && char <= '9');
}
/**
* @param {string} s
* @return {boolean}
*/
isPalindrome(s) {
let newStr = '';
for (let c of s) {
if (this.isAlphanumeric(c)) {
newStr += c.toLowerCase();
}
}
return newStr === newStr.split('').reverse().join('');
}
}
Question 2: Buying and Selling Stocks Problem.
You are given an array prices, where each element prices[i] represents the price of PrepCoin on the i-th day.
Your task is to determine the maximum profit you can make by selecting one day to buy a PrepCoin and another day after it to sell.
If it’s not possible to make any profit (e.g., prices are decreasing every day), you should return 0. This means you can also choose not to make any transactions.
Output: 0
Explanation : No profitable transactions can be made, thus the max profit is 0.
Constraints:
- 1 <= prices.length <= 100
- 0 <= prices[i] <= 100
Solution:
Method 1: Two Pointers Method
Use a single pass with two variables to track the minimum price so far and the maximum profit, updating them as you traverse the array. This has a time complexity of O(n).
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)
Code
public class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int l = 0, r = 1;
int maxP = 0;
while (r < prices.length) {
if (prices[l] < prices[r]) {
int profit = prices[r] - prices[l];
maxP = Math.max(maxP, profit);
} else {
l = r;
}
r++;
}
return maxP;
}
}
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
l, r = 0, 1
maxP = 0
while r < len(prices):
if prices[l] < prices[r]:
profit = prices[r] - prices[l]
maxP = max(maxP, profit)
else:
l = r
r += 1
return maxP
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number[]} prices
* @return {number}
*/
maxProfit(prices) {
let l = 0, r = 1;
let maxP = 0;
while (r < prices.length) {
if (prices[l] < prices[r]) {
let profit = prices[r] - prices[l];
maxP = Math.max(maxP, profit);
} else {
l = r;
}
r++;
}
return maxP;
}
}
Method 2: Dynamic Programming Method
This method maintain a table or array to store intermediate results, such as the minimum price up to a given day and the maximum profit calculated so far, optimizing computation over multiple traversals. Time complexity is O(n).
- Time complexity: O(n)
- Space complexity: O(1)
Code
public class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int maxP = 0;
int minBuy = prices[0];
for (int sell : prices) {
maxP = Math.max(maxP, sell - minBuy);
minBuy = Math.min(minBuy, sell);
}
return maxP;
}
}
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
maxP = 0
minBuy = prices[0]
for sell in prices:
maxP = max(maxP, sell - minBuy)
minBuy = min(minBuy, sell)
return maxP
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number[]} prices
* @return {number}
*/
maxProfit(prices) {
let maxP = 0;
let minBuy = prices[0];
for (let sell of prices) {
maxP = Math.max(maxP, sell - minBuy);
minBuy = Math.min(minBuy, sell);
}
return maxP;
}
}
Question 3: Program for Koko Eating Bananas Problem
You are given an array piles, where each element piles[i] represents the number of bananas in the i-th pile. You also have h hours to eat all the bananas. You can choose an eating rate of k bananas per hour. In each hour, you can eat up to k bananas from one pile.
If a pile has fewer than k bananas, you finish that pile but cannot switch to another pile during the same hour.
Your task is to find the minimum value of k that allows you to eat all the bananas within h hours.
Output: 2
Explanation:
With an eating rate of 2, you can eat the bananas in 6 hours. With an eating rate of 1, you would need 10 hours to eat all the bananas (which exceeds h=9), thus the minimum eating rate is 2.
Constraints:
- 1 <= piles.length <= 1,000
- piles.length <= h <= 1,000,000
- 1 <= piles[i] <= 1,000,000,000
Solution:
Using Binary Search Method
Use binary search to find the minimum eating speed by searching between 1 and the maximum pile size, checking the feasibility of each mid-speed.
- Time complexity: O(n * log m)
- Space complexity: O(1)
where n is the length of the input array piles and m is the maximum number of bananas in a pile.
Code
public class Solution {
public int minEatingSpeed(int[] piles, int h) {
int l = 1;
int r = Arrays.stream(piles).max().getAsInt();
int res = r;
while (l <= r) {
int k = (l + r) / 2;
long totalTime = 0;
for (int p : piles) {
totalTime += Math.ceil((double) p / k);
}
if (totalTime <= h) {
res = k;
r = k - 1;
} else {
l = k + 1;
}
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution:
def minEatingSpeed(self, piles: List[int], h: int) -> int:
l, r = 1, max(piles)
res = r
while l <= r:
k = (l + r) // 2
totalTime = 0
for p in piles:
totalTime += math.ceil(float(p) / k)
if totalTime <= h:
res = k
r = k - 1
else:
l = k + 1
return res
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number[]} piles
* @param {number} h
* @return {number}
*/
minEatingSpeed(piles, h) {
let l = 1;
let r = Math.max(...piles);
let res = r;
while (l <= r) {
const k = Math.floor((l + r) / 2);
let totalTime = 0;
for (const p of piles) {
totalTime += Math.ceil(p / k);
}
if (totalTime <= h) {
res = k;
r = k - 1;
} else {
l = k + 1;
}
}
return res;
}
}
Sample Meesho Coding Questions
Question 4: Power Function (Pow(x, n))
Implement a function pow(x, n) that calculates x raised to the power n (i.e., x^n).
Constraints :
-100.0 < x < 100.0
-231 <= n <= 231-1
n is an integer.
Either x is not zero or n > 0.
-104 <= xn <= 104
Solution:
class Solution {
public double myPow(double x, long n) {
if(n < 0) {
x = 1 / x;
n = -n;
}
double result = 1;
double current_product = x;
while(n > 0) {
if(n % 2 == 1) {
result = result * current_product;
}
current_product = current_product * current_product;
n = n / 2;
}
return result;
}
}
class Solution:
def myPow(self, x: float, n: int) -> float:
if n < 0: x = 1 / x n = -n result = 1 current_product = x while n > 0:
if n % 2 == 1:
result = result * current_product
current_product = current_product * current_product
n = n // 2
return result
class Solution {
myPow(x, n) {
if (n < 0) {
x = 1 / x;
n = -n;
}
let result = 1;
let currentProduct = x;
while (n > 0) {
if (n % 2 === 1) {
result *= currentProduct;
}
currentProduct *= currentProduct;
n = Math.floor(n / 2);
}
return result;
}
}Question 5: Course Schedule Problem of Graphs.
You are given an array prerequisites, where each element prerequisites[i] = [a, b] means you must complete course b before taking course a.
For example, [0, 1] indicates that course 1 must be completed before course 0.
There are a total of numCourses, labeled from 0 to numCourses – 1. Return true if it is possible to complete all courses; otherwise, return false.
Output: true
Explanation: First take course 1 (no prerequisites) and then take course 0.
Constraints :
- 1 <= numCourses <= 1000
- 0 <= prerequisites.length <= 1000
- All prerequisite pairs are unique.
Solution:
Solving by Cycle Detection(DFS) Method
Treat the courses as a graph and use DFS to detect cycles. Maintain a visited set to track the current path during DFS. If a course is revisited in the same path, a cycle exists, making it impossible to complete all courses.
- Time complexity: O(V + E)
- Space complexity: O(V + E)
where V is the number of courses and E is the number of prerequisites.
Code
public class Solution {
// Map each course to its prerequisites
private Map<Integer, List<Integer>> preMap = new HashMap<>();
// Store all courses along the current DFS path
private Set<Integer> visiting = new HashSet<>();
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
preMap.put(i, new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int[] prereq : prerequisites) {
preMap.get(prereq[0]).add(prereq[1]);
}
for (int c = 0; c < numCourses; c++) {
if (!dfs(c)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean dfs(int crs) {
if (visiting.contains(crs)) {
// Cycle detected
return false;
}
if (preMap.get(crs).isEmpty()) {
return true;
}
visiting.add(crs);
for (int pre : preMap.get(crs)) {
if (!dfs(pre)) {
return false;
}
}
visiting.remove(crs);
preMap.put(crs, new ArrayList<>());
return true;
}
}
class Solution:
def canFinish(self, numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
# Map each course to its prerequisites
preMap = {i: [] for i in range(numCourses)}
for crs, pre in prerequisites:
preMap[crs].append(pre)
# Store all courses along the current DFS path
visiting = set()
def dfs(crs):
if crs in visiting:
# Cycle detected
return False
if preMap[crs] == []:
return True
visiting.add(crs)
for pre in preMap[crs]:
if not dfs(pre):
return False
visiting.remove(crs)
preMap[crs] = []
return True
for c in range(numCourses):
if not dfs(c):
return False
return True
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number} numCourses
* @param {number[][]} prerequisites
* @return {boolean}
*/
canFinish(numCourses, prerequisites) {
const preMap = new Map();
for (let i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) { preMap.set(i, []); } for (let [crs, pre] of prerequisites) { preMap.get(crs).push(pre); } // Store all courses along the current DFS path const visiting = new Set(); const dfs = (crs) => {
if (visiting.has(crs)) {
// Cycle detected
return false;
}
if (preMap.get(crs).length === 0) {
return true;
}
visiting.add(crs);
for (let pre of preMap.get(crs)) {
if (!dfs(pre)) {
return false;
}
}
visiting.delete(crs);
preMap.set(crs, []);
return true;
}
for (let c = 0; c < numCourses; c++) {
if (!dfs(c)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
Question 6: Counting the Number of 1’s in Binary Representations of Numbers in a Range
Understanding binary numbers and efficiently processing them is a critical skill.
Common problem involves counting how many 1 bits are present in the binary representation of numbers within a given range.In this article, we will explore a solution to count the number of 1 bits in every number from 0 to n.
We need to count the number of 1 bits in the binary representations of numbers from 0 to 4. Let’s convert these numbers to binary:
0in binary:0→ Number of1bits:01in binary:1→ Number of1bits:12in binary:10→ Number of1bits:13in binary:11→ Number of1bits:24in binary:100→ Number of1bits:1
Solution:
Method 1. Bit Mask – I
Time & Space Complexity
- Time complexity: O(1)O(1)
- Space complexity: O(1)O(1)
class Solution:
def hammingWeight(self, n: int) -> int:
res = 0
for i in range(32):
if (1 << i) & n:
res += 1
return res
public class Solution {
public int hammingWeight(int n) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {
if ((1 << i & n) != 0) {
res++;
}
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number} n - a positive integer
* @return {number}
*/
hammingWeight(n) {
let res = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < 32; i++) {
if ((1 << i) & n) {
res++;
}
}
return res;
}
}
Method 2. Built-In Function
Time & Space Complexity
- Time complexity: O(1)O(1)
- Space complexity: O(1)O(1)
Code
public class Solution {
public int hammingWeight(int n) {
return Integer.bitCount(n);
}
}
class Solution:
def hammingWeight(self, n: int) -> int:
return bin(n).count('1')
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number} n - a positive integer
* @return {number}
*/
hammingWeight(n) {
return n.toString(2).split('0').join('').length;
}
}
Meesho Coding Questions and Answers
Question 7: Print all combinations of balanced parentheses problem
You are given a positive integer n, representing the number of pairs of parentheses. Your task is to generate and return all possible combinations of well-formed (valid) parentheses strings that can be created using exactly n pairs.
A well-formed parentheses string maintains the correct order, meaning every opening parenthesis ( has a corresponding closing parenthesis ) that appears after it.
Output: ["((()))","(()())","(())()","()(())","()()()"]
Explanation: You may return the answer in any order.
Constraints:
- 1 <= n <= 7
Solution:
Using Dynamic Programming Method
Construct valid combinations using previously computed solutions for smaller values of n, combining them in different ways to form well-balanced parentheses for the current n.
- Time complexity: O(4^n/(n)^1/2)
- Space complexity: O(n)
Code
public class Solution {
public List generateParenthesis(int n) {
List> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
res.get(0).add("");
for (int k = 0; k <= n; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
for (String left : res.get(i)) {
for (String right : res.get(k - i - 1)) {
res.get(k).add("(" + left + ")" + right);
}
}
}
}
return res.get(n);
}
}
class Solution:
def generateParenthesis(self, n):
res = [[] for _ in range(n+1)]
res[0] = [""]
for k in range(n + 1):
for i in range(k):
for left in res[i]:
for right in res[k-i-1]:
res[k].append("(" + left + ")" + right)
return res[-1]
class Solution {
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {string[]}
*/
generateParenthesis(n) {
const res = Array.from({ length: n + 1 }, () => []);
res[0] = [""];
for (let k = 0; k <= n; k++) {
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
for (const left of res[i]) {
for (const right of res[k - i - 1]) {
res[k].push("(" + left + ")" + right);
}
}
}
}
return res[n];
}
}
Question 8: LRU Cache Leetcode Problem
Design a data structure that follows the constraints of a Least Recently Used (LRU) cache.
Implement the LRUCache class:
- LRUCache(int capacity) Initialize the LRU cache with positive size capacity.
- int get(int key) Return the value of the key if the key exists, otherwise return -1.
- void put(int key, int value) Update the value of the key if the key exists. Otherwise, add the key-value pair to the cache.
- If the number of keys exceeds the capacity from this operation, evict the least recently used key.
- The functions get and put must each run in O(1) average time complexity.
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
Constraints :
- 1 <= capacity <= 3000
- 0 <= key <= 104
- 0 <= value <= 105
- At most 2 * 105 calls will be made to get and put.
Solution:
class LRUCache {
class Node {
int key;
int val;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node(int key, int val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
Node head = new Node(-1, -1);
Node tail = new Node(-1, -1);
int cap;
HashMap< Integer, Node> m = new HashMap<>();
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
cap = capacity;
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
private void addNode(Node newnode) {
Node temp = head.next;
newnode.next = temp;
newnode.prev = head;
head.next = newnode;
temp.prev = newnode;
}
private void deleteNode(Node delnode) {
Node prevv = delnode.prev;
Node nextt = delnode.next;
prevv.next = nextt;
nextt.prev = prevv;
}
public int get(int key) {
if (m.containsKey(key)) {
Node resNode = m.get(key);
int ans = resNode.val;
m.remove(key);
deleteNode(resNode);
addNode(resNode);
m.put(key, head.next);
return ans;
}
return -1;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if (m.containsKey(key)) {
Node curr = m.get(key);
m.remove(key);
deleteNode(curr);
}
if (m.size() == cap) {
m.remove(tail.prev.key);
deleteNode(tail.prev);
}
addNode(new Node(key, value));
m.put(key, head.next);
}
}
class LRUCache:
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, val):
self.key = key
self.val = val
self.prev = None
self.next = None
def __init__(self, capacity: int):
self.cap = capacity
self.head = self.Node(-1, -1)
self.tail = self.Node(-1, -1)
self.head.next = self.tail
self.tail.prev = self.head
self.m = {}
def addNode(self, newnode):
temp = self.head.next
newnode.next = temp
newnode.prev = self.head
self.head.next = newnode
temp.prev = newnode
def deleteNode(self, delnode):
prevv = delnode.prev
nextt = delnode.next
prevv.next = nextt
nextt.prev = prevv
def get(self, key: int) -> int:
if key in self.m:
resNode = self.m[key]
ans = resNode.val
del self.m[key]
self.deleteNode(resNode)
self.addNode(resNode)
self.m[key] = self.head.next
return ans
return -1
def put(self, key: int, value: int) -> None:
if key in self.m:
curr = self.m[key]
del self.m[key]
self.deleteNode(curr)
if len(self.m) == self.cap:
del self.m[self.tail.prev.key]
self.deleteNode(self.tail.prev)
self.addNode(self.Node(key, value))
self.m[key] = self.head.nextclass LRUCache {
constructor(capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.map = new Map();
// Create dummy head and tail nodes
this.head = new Node(-1, -1);
this.tail = new Node(-1, -1);
this.head.next = this.tail;
this.tail.prev = this.head;
}
addNode(node) {
let temp = this.head.next;
node.next = temp;
node.prev = this.head;
this.head.next = node;
temp.prev = node;
}
deleteNode(node) {
let prev = node.prev;
let next = node.next;
prev.next = next;
next.prev = prev;
}
get(key) {
if (this.map.has(key)) {
let resNode = this.map.get(key);
let value = resNode.val;
this.map.delete(key);
this.deleteNode(resNode);
this.addNode(resNode);
this.map.set(key, this.head.next);
return value;
}
return -1;
}
put(key, value) {
if (this.map.has(key)) {
let curr = this.map.get(key);
this.map.delete(key);
this.deleteNode(curr);
}
if (this.map.size === this.capacity) {
this.map.delete(this.tail.prev.key);
this.deleteNode(this.tail.prev);
}
let newNode = new Node(key, value);
this.addNode(newNode);
this.map.set(key, this.head.next);
}
}
class Node {
constructor(key, val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
}Question 9: Encode and Decode Strings Problem
Design an algorithm to encode a list of strings to a single string. The encoded string is then decoded back to the original list of strings. Please implement encode and decode.
Output: ["we","say",":","yes"]
Constraints:
- 0 <= strs.length < 100
- 0 <= strs[i].length < 200
- strs[i] contains only UTF-8 characters.
Solution:
Solving Encoding and Decoding Method
This method use a delimiter (like a special character or length-prefix) to encode strings, and split the encoded string using the same delimiter to decode. Simple but may face issues with delimiter conflicts.
- Time complexity: O(m) for encode() and decode().
- Space complexity: O(n) for encode() and decode().
where m is the sum of lengths of all the strings and n is the number of strings.
Code
public class Solution {
public String encode(List strs) {
if (strs.isEmpty()) return "";
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
List sizes = new ArrayList<>();
for (String str : strs) {
sizes.add(str.length());
}
for (int size : sizes) {
res.append(size).append(',');
}
res.append('#');
for (String str : strs) {
res.append(str);
}
return res.toString();
}
public List decode(String str) {
if (str.length() == 0) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List res = new ArrayList<>();
List sizes = new ArrayList<>();
int i = 0;
while (str.charAt(i) != '#') {
StringBuilder cur = new StringBuilder();
while (str.charAt(i) != ',') {
cur.append(str.charAt(i));
i++;
}
sizes.add(Integer.parseInt(cur.toString()));
i++;
}
i++;
for (int sz : sizes) {
res.add(str.substring(i, i + sz));
i += sz;
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution:
def encode(self, strs: List[str]) -> str:
if not strs:
return ""
sizes, res = [], ""
for s in strs:
sizes.append(len(s))
for sz in sizes:
res += str(sz)
res += ','
res += '#'
for s in strs:
res += s
return res
def decode(self, s: str) -> List[str]:
if not s:
return []
sizes, res, i = [], [], 0
while s[i] != '#':
cur = ""
while s[i] != ',':
cur += s[i]
i += 1
sizes.append(int(cur))
i += 1
i += 1
for sz in sizes:
res.append(s[i:i + sz])
i += sz
return res
class Solution {
/**
* @param {string[]} strs
* @returns {string}
*/
encode(strs) {
if (strs.length === 0) return "";
let sizes = [], res = "";
for (let s of strs) {
sizes.push(s.length);
}
for (let sz of sizes) {
res += sz + ',';
}
res += '#';
for (let s of strs) {
res += s;
}
return res;
}
/**
* @param {string} str
* @returns {string[]}
*/
decode(str) {
if (str.length === 0) return [];
let sizes = [], res = [], i = 0;
while (str[i] !== '#') {
let cur = "";
while (str[i] !== ',') {
cur += str[i];
i++;
}
sizes.push(parseInt(cur));
i++;
}
i++;
for (let sz of sizes) {
res.push(str.substr(i, sz));
i += sz;
}
return res;
}
}
Sample Meesho Coding Questions and Answers
Question 10: Kth Largest Element in an Array
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return the kth largest element in the array.
Note that it is the kth largest element in the sorted order, not the kth distinct element.
Can you solve it without sorting?
Constraints :
- 1 <= k <= nums.length <= 10^5
- -10^4 <= nums[i] <= 10^4
class Solution {
findKthLargest(nums, k) {
// Create a max heap using a priority queue
let maxHeap = new MaxHeap(nums);
// Remove the top element (largest) k-1 times
for (let i = 0; i < k - 1; i++) {
maxHeap.pop();
}
// The k-th largest element will be at the top now
return maxHeap.top();
}
}
// Max Heap implementation using a Priority Queue
class MaxHeap {
constructor(arr) {
this.heap = [...arr];
this.buildHeap();
}
buildHeap() {
this.heap.sort((a, b) => b - a); // Sort in descending order (Max Heap)
}
pop() {
return this.heap.shift(); // Remove and return the largest element
}
top() {
return this.heap[0]; // Return the largest element
}
}
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
quickSelect(nums, 0, nums.length - 1, k - 1);
return nums[k - 1];
}
Random r = new Random();
private int[] pivot(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
int idx = start + r.nextInt(end - start + 1);
int pivoted = nums[idx];
int i = start, j = start, k = end;
while (j <= k) {
if (nums[j] > pivoted) {
swap(nums, i, j);
i++;
j++;
} else if (nums[j] == pivoted) {
j++;
} else {
swap(nums, j, k);
k--;
}
}
return new int[]{i, j};
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
return;
}
private void quickSelect(int[] nums, int start, int end, int k) {
if (start > end) {
return;
}
int[] pivotRes = pivot(nums, start, end);
if (k >= pivotRes[0] && k < pivotRes[1]) {
return;
}
if (k < pivotRes[0]) {
quickSelect(nums, start, pivotRes[0] - 1, k);
} else {
quickSelect(nums, pivotRes[1], end, k);
}
}
}
class Solution:
def findKthLargest(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> int:
pivot=random.choice(nums)
left=[x for x in nums if x>pivot]
mid=[x for x in nums if x==pivot]
right=[x for x in nums if x< pivot]
n=len(left)
m=len(mid)
if k<=n:
return self.findKthLargest(left,k)
elif k>(n+m):
return self.findKthLargest(right,k-(n+m))
else:
return mid[0] These were some of most Important Meesho Coding Questions and Answers. If you want to practice more you can visit our coding blogs to explore more….and also visit PrepInsta Prime Course.
FAQ's related to Meesho Coding Assessment
Question 1. What types of coding questions are asked in the Meesho hiring process?
Answer:
Meesho Coding Questions mainly includes topics like arrays, strings, dynamic programming, graphs, and recursion.
Problems can range from easy to hard, depending on the role you are applying for.
Question 2. Which programming languages are allowed for the meesho coding test?
Answer:
- Meesho allows candidates to code in multiple languages, including Java, Python and JavaScript.
It is best to use one of these three languages that you are comfortable with and has built-in support for efficient data structures.
Question 3. How can I prepare for Meesho coding round?
Answer:
To prepare effectively:
- Practice Coding Questions from our PrepInsta’s Coding Dashboard.
- Focus on Time & Space Complexity of solutions.
- Revise important algorithms like Binary Search, Two Pointers, and Graph Traversal.
Wipro Turbo Coding Questions
Wipro Turbo Coding Questions Asked
The Wipro Turbo hiring process is known for its rigorous assessment of candidates technical and problem-solving abilities. The Wipro Turbo Coding Questions, in particular, is designed to evaluate proficiency in various programming languages, including C, C++, Java, and Python.
Unlike the Wipro Elite NTH coding questions, which may focus on fundamental programming concepts, the Wipro Turbo coding assessments often present more complex and challenging problems.

| Total number of questions | 2 questions |
| Total Time Duration | 60 minutes |
| Type of Test | Non-Adaptive |
| Mode Conducted | Online/Written |
| Negative Marking | No |
WIPRO TURBO Coding Questions and PROGRAMMING MODEL QUESTIONS
In this page you will find coding questions asked during the off-campus placement of students, Wipro previous year questions:
- Wipro Turbo C Programming Questions for Off Campus
- Wipro Turbo Java Programming Questions for Off Campus
- Wipro Turbo C++ Programming Questions for Off Campus
Wipro Turbo programming practice questions and coding paper
Wipro Turbo Coding Questions 2025
Free Material
- Program to calculate the GCD of two numbers –
- Program to calculate the GCD of three numbers –
- Program to check if the given number is Prime or not –
- Program to Display the distinct elements of an array –
- Program to Sort first half in ascending order and second half in descending order in an array –
- Program for Matrix multiplication –
- Program to Remove vowels from an input string –
- Program to Print Sum of all Odd Numbers present in a larger number –
- Program to Print the Transpose of a matrix –
- Program to Display the largest element in each row in a 2-D Array –
- Program to Check the balance of Parenthesis –
Some Coding Questions for Practice
Note – These are some practice questions which are asked in Wipro on campus as well as Wipro off camous, so go through each questions and prepare well.
Question 1
Wipro’s client eBay wants to run a campaign on their website, which will have the following parameters, eBay wants that on certain x products, they want to calculate the final price, for each product on eBay there will be a stock unit parameter, this parameter will denote, how many items are their in their fulfillment center
Now, while these numbers if are positive means product x is available in the fulfillment center and if not than the product is not available and cannot be shipped to the customer
Now the price on for each product varies based on the distance of the customer from the fulfillment center. Now, each product is in different fulfillment zone. Now, these values are 00’s kms for each centurion km. The price available would further increase by factor distance.
You’ve to find the maximum discount price for each product if the product can be shipped.
Following are the input/output parameters :
Input
- The first line of the input will contain number of products.
- The second line will contain price for each of these products.
- The third line contains shipping distance in 00’s kms
- The fourth line contains SKU’s
Output
- It will contain the final price for each deliverable item in SKU’s
Example :
Input:
- 6
- 87 103 229 41 8 86
- 3 1 9 2 1 2
- 7 -21 30 0 -4 -3
Output
- 261 2061
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int noOfProducts; scanf("%d",&noOfProducts); int price[noOfProducts], distance[noOfProducts], sku[noOfProducts]; for(int i=0;i<noOfProducts;i++) { scanf("%d",&price[i]); } for(int i=0;i<noOfProducts;i++) { scanf("%d",&distance[i]); } for(int i=0;i<noOfProducts;i++) { scanf("%d",&sku[i]); } int final_Price[noOfProducts]; int count =0; for(int i=0;i<noOfProducts;i++) { if(sku[i]>0) { final_Price[count]= price[i] * distance[i]; count++; } } for(int i=0;i<count;i++) { printf("%d ", final_Price[i]); } return 0; }
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int noOfProducts=sc.nextInt();
int price[]=new int[noOfProducts];
int distance[]=new int[noOfProducts];
int sku[]=new int[noOfProducts];
for(int i=0;i<noOfProducts;i++)
price[i]=sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<noOfProducts;i++)
distance[i]=sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<noOfProducts;i++)
sku[i]=sc.nextInt();
int finalPrice[]=new int[noOfProducts];
int count =0;
for(int i=0;i<noOfProducts;i++)
{
if(sku[i]>0)
{
finalPrice[count]= price[i] * distance[i];
count++;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<count;i++)
{
System.out.print(finalPrice[i]+" ");
}
}
}
number_of_products = int(input()) list_price = list(input().split(" ")) list_distance = list(input().split(" ")) list_sku = list(input().split(" ")) list_final=[] for item in range (0, number_of_products): if int(list_sku[item]) >0 : temp_val = int(list_price[item]) * int(list_distance[item]) list_final.append(temp_val) for item in range(0, len(list_final)): print(list_final[item], sep=" ",end=" ")
Question : 2
(asked in Wipro On Campus, Sastra University, Aug, 2020)
Problem: in this first line you are required to take the value of m and n as the number of rows and columns of matrix, then you are required to take the input elements of array.
As an output you are required to print the sum of each row then the row having the maximum sum.
Test Case :
Input : 3 3
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
Output :
Row 1 : 6
Row 2 : 15
Row 3 : 24
Row 3 is having the maximum sum : 24
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int row, colm, i, j, temp, max = 1; int mat[100][100]; int sum[100]; printf("enter the number of rows : "); scanf("%d",&row); printf("enter the number of columms : "); scanf("%d",&colm); for(i=0; i<row; i++) { for(j=0; j<colm; j++) { printf("enter [%d %d] element : ",i+1,j+1); scanf("%d",&mat[i][j]); } } for(i=0; i<row; i++) { sum[i] = 0; for(j=0; j<colm; j++) { sum[i] = sum[i] + mat[i][j]; } printf("\n"); } for(i=0; i<row; i++) { printf("Row %d : %d\n",i+1,sum[i]); } for(i=0; i<row; i++) { if(sum[0]<sum[i+1]) { temp = sum[0]; sum [0] = sum[i+1]; sum[i+1] = temp; max = max+1; } } printf("\nRow %d is having the maximum sum : %d",max,sum[0]); return 0; }
#include <iostream>
int main() {
int row, colm, i, j, temp, max = 1;
int mat[100][100];
int sum[100];
std::cout << "Enter the number of rows: "; std::cin >> row;
std::cout << "Enter the number of columns: "; std::cin >> colm;
for(i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < colm; j++) {
std::cout << "Enter [" << i + 1 << "][" << j + 1 << "] element: "; std::cin >> mat[i][j];
}
}
for(i = 0; i < row; i++) {
sum[i] = 0;
for(j = 0; j < colm; j++) {
sum[i] += mat[i][j];
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
for(i = 0; i < row; i++) {
std::cout << "Row " << i + 1 << ": " << sum[i] << std::endl;
}
for(i = 0; i < row; i++) {
if(sum[0] < sum[i + 1]) {
temp = sum[0];
sum[0] = sum[i + 1];
sum[i + 1] = temp;
max = max + 1;
}
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "Row " << max << " is having the maximum sum: " << sum[0] << std::endl;
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in);
int m = sc.nextInt ();
int n = sc.nextInt ();
int arr[][] = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
arr[i][j] = sc.nextInt ();
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { sum = sum + arr[i][j]; } System.out.println ("Row " + (i + 1) + " : " + sum); if (sum > max)
{
max = sum;
index = i + 1;
}
}
System.out.println ("Row " + index + " is having the maximum sum : " +
max);
}
}
Question : 3
(asked in Wipro On Campus, PESIT Bangalore, Oct, 2019)
Problem: You are required to count the number of words in a sentence.
You are required to pass all the test cases
Test Cases :
Test Case : 1
Input : welcome to the world
Output : 4
Test Case : 2
Input : [space] say hello
Output : 2
Test Case : 3
Input : To get pass you need to study hard [space] [space]
Output : 8
#include <stdio.h> #include int main() { char a[100]; int i=0,count; printf("Enter the string : "); scanf("%[^\n]s",a); if(a[0]==' ') { count = 0; } else { count = 1; } while(a[i]!='\0') { if(a[i]==' ' && a[i+1]!=' ' && a[i+1]!='\0') { count = count + 1; } i++; } printf("%d",count); }
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
int main() {
std::string str;
std::getline(std::cin, str);
str = str.substr(0, str.find_last_not_of(" \t") + 1);
std::stringstream ss(str);
std::string word;
int count = 0;
while (ss >> word) {
count++;
}
std::cout << count << std::endl;
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String str=sc.nextLine();
str=str.trim();
String arr[]=str.split(" ");
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) { arr[i]=arr[i].trim(); if(arr[i].length()>0)
count++;
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
str = input()
str = str.strip()
arr = str.split()
count = 0
for word in arr:
word = word.strip()
if len(word) > 0:
count += 1
print(count)
Question : 4
(asked in Wipro On Campus, VIT University, Aug, 2019)
Problem: First of all you need to input a whole sentence in the string, then you need to enter the target
word.
As an output you need to find the number of times that particular target word is repeated in the
sentence.
Test Cases :
Test Case : 1
Input : welcome world to the new world
world
Output : 2
Test Case : 2
Input : working hard and working smart both are different ways of working
working
Output : 3
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int main() { char str[100]; char toSearch[100]; int count; int i, j, found; int stringLen, searchLen; scanf("%[^\n]s",str); scanf("%s",toSearch); stringLen = strlen(str); searchLen = strlen(toSearch); count = 0; for(i=0; i <= stringLen-searchLen; i++) { found = 1; for(j=0; j<searchLen; j++) { if(str[i + j] != toSearch[j]) { found = 0; break; } } if(found == 1) { count++; } } printf("%d",count); return 0; }
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
int main() {
char str[100];
char toSearch[100];
int count;
int i, j, found;
int stringLen, searchLen;
std::cin.getline(str, 100);
std::cin >> toSearch;
stringLen = strlen(str);
searchLen = strlen(toSearch);
count = 0;
for (i = 0; i <= stringLen - searchLen; i++) {
found = 1;
for (j = 0; j < searchLen; j++) {
if (str[i + j] != toSearch[j]) {
found = 0;
break;
}
}
if (found == 1) {
count++;
}
}
std::cout << count;
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String str=sc.nextLine();
String target=sc.next();
str=str.trim();
String arr[]=str.split(" ");
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++)
{
arr[i]=arr[i].trim();
if(arr[i].equals(target))
count++;
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
str = input()
toSearch = input()
stringLen = len(str)
searchLen = len(toSearch)
count = 0
for i in range(stringLen - searchLen + 1):
found = True
for j in range(searchLen):
if str[i + j] != toSearch[j]:
found = False
break
if found:
count += 1
print(count)
Question : 5
(asked in Wipro On Campus, MIET Meerut, Aug, 2019)
Problem Statement
You are required to implement the following function:
Int SumNumberDivisible(int m, int n);
The function accepts 2 positive integer ‘m’ and ‘n’ as its arguments.
You are required to calculate the sum of numbers divisible both by 3 and 5, between ‘m’ and ‘n’ both inclusive and return the same.
Note
0 < m <= n
Example
Input:
m : 12
n : 50
Output 90
Explanation:
The numbers divisible by both 3 and 5, between 12 and 50 both inclusive are
{15, 30, 45} and their sum is 90.
Sample Input
m : 100
n : 160
Sample Output
510
/* Programming Question */ #include <stdio.h> int Calculate(int, int); int main() { int m, n, result; // Getting Input printf("Enter the value of m : "); scanf("%d",&m); printf("Enter the value of n : "); scanf("%d",&n); result = Calculate(n,m); // Getting Output printf("%d",result); return 0; } /* Write your code below . . . */ int Calculate(int n, int m) { // Write your code here int i, sum = 0; for(i=m;i<=n;i++) { if((i%3==0)&&(i%5==0)) { sum = sum + i; } } return sum; }
#include <iostream
#include <cstring>
int main() {
char str[100];
char toSearch[100];
int count;
int i, j, found;
int stringLen, searchLen;
std::cin.getline(str, 100);
std::cin >> toSearch;
stringLen = strlen(str);
searchLen = strlen(toSearch);
count = 0;
for (i = 0; i <= stringLen - searchLen; i++) {
found = 1;
for (j = 0; j < searchLen; j++) {
if (str[i + j] != toSearch[j]) {
found = 0;
break;
}
}
if (found == 1) {
count++;
}
}
std::cout << count;
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static int sumNumberDivisible(int m,int n)
{
int sum=0;
for(int i=m;i<=n;i++)
{
if((i%3==0)&&(i%5==0))
{
sum=sum+i;
}
}
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int m=sc.nextInt();
int n=sc.nextInt();
int res=sumNumberDivisible(m,n);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
str = input()
toSearch = input()
stringLen = len(str)
searchLen = len(toSearch)
count = 0
for i in range(stringLen - searchLen + 1):
found = True
for j in range(searchLen):
if str[i + j] != toSearch[j]:
found = False
break
if found:
count += 1
print(count)
Question : 6
(asked in Wipro Off Campus)
Input
The first line of input consists of three space separated integers. Num, start and end representing the size of list [N], the starting value of the range and the ending value of the range respectively.
The second line of input consists N space separated integers representing the distances of the employee from the company.
Output
Print space separated integers representing the ID’s of the employee whose distance liew within the given range else return -1.
Example
Input
6 30 50
29 38 12 48 39 55
Output
1 3 4
Explanation :
There are 3 employees with id 1, 3, 4 whose distance from the office lies within the given range.
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int start, end, a[50], num, i, flag; scanf("%d %d %d",&num,&start,&end); for(i=0; i<num; i++) { scanf("%d",&a[i]); } for(i=0;i<num;i++) { if(a[i]>start && a[i]<end) { flag = 1; } else { flag = -1; } if(flag == 1) { printf("%d ",i); } } return 0; }
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int num=sc.nextInt();
int start=sc.nextInt();
int end=sc.nextInt();
int list[]=new int[num];
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
list[i]=sc.nextInt();
boolean flag=false;
for(int i=0;i<num;i++) { if(list[i]>start && list[i]<end)
{
flag=true;
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
if(flag==false)
System.out.println("-1");
}
}
Question : 7
(asked in Wipro On Campus, IIIT Hyderabad, Aug, 2019)
Write a code for the following functions
Function 1 : sortArray
It’s function is to sort the passed array with a particular length, there are 2 parameters passed into it first is the length of array and next is the elements of list.
Function 2 : findMaxElement
It’s function is to get the 2 array with their own particular elements and length, and find the maximum element from both the array and print it.
Input
12
2 5 1 3 9 8 4 6 5 2 3 11
11
11 13 2 4 15 17 67 44 2 100 23
Output
100
#include <stdio.h> int* sortArray(int len, int* arr) { int i=0, j=0, temp = 0; for(i=0; i<len; i++) { for(j=i+1; j<len; j++) { if(arr[i]>arr[j]) { temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; } } } return arr; } int findMaxElement(int len1, int* arr1, int len2, int* arr2) { sortArray(len1, arr1); sortArray(len2, arr2); if(arr1[len1-1]>arr2[len2-1]) return arr1[len1-1]; else return arr2[len2-1]; } int main() { int len1, len2, arr1[20], arr2[20], i; int ans; scanf("%d",&len1); for(i=0; i<len1; i++) { scanf("%d",&arr1[i]); } scanf("%d",&len2); for(i=0; i<len2; i++) { scanf("%d",&arr2[i]); } ans = findMaxElement(len1, arr1, len2, arr2); printf("%d",ans); return 0; }
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void sortArray(int len,int arr[])
{
int i=0,j=0,temp=0;
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
{
int countOfSwap=0;
for(j=0;j<len-1-i;j++) { if(arr[j]>arr[j+1])
{
temp=arr[j];
arr[j]=arr[j+1];
arr[j+1]=temp;
countOfSwap++;
}
}
if(countOfSwap==0)
break;
}
}
public static int findMaxElement(int len1, int arr1[],int len2,int arr2[])
{
sortArray(len1,arr1);
sortArray(len2,arr2);
if(arr1[len1-1]>arr2[len2-1])
return arr1[len1-1];
else
return arr2[len2-1];
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int len1=sc.nextInt();
int arr1[]=new int[len1];
for(int i=0;i<len1;i++)
arr1[i]=sc.nextInt();
int len2=sc.nextInt();
int arr2[]=new int[len2];
for(int i=0;i<len2;i++)
arr2[i]=sc.nextInt();
int ans=findMaxElement(len1,arr1,len2,arr2);
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
Question 8
(asked in Wipro On Campus, HBTI Kanpur, Sep, 2019)
Problem: you are given a number, and you have to extract the key by finding the difference between the sum of the even and odd numbers of the input.
Test Case :
Input : 24319587
Output : 11
Explanation : odd terms : 3 + 1 + 9 + 5 + 7 = 25
even terms : 2 + 4 + 8 = 14
output : 11 (25-14)
/* Program to find key */ #include <stdio.h> int main() { int n; int r, odd=0, even=0, key; scanf("%d",&n); while(n!=0) { r = n%10; if(r%2==0) { even = even + r; } else { odd = odd + r; } n = n/10; } if(odd>even) { key = odd - even; } else { key = even - odd; } printf("%d",key); }
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int num=sc.nextInt();
int odd=0,even=0;
while(num>0)
{
int rem=num%10;
if(rem%2==0)
even=even+rem;
else
odd=odd+rem;
num=num/10;
}
System.out.println(Math.abs(even-odd));
}
}
Question 9
(asked in Wipro NLTH 2019)
Problem: in this first line you are required to take the value of m and n as the number of rows and columns of matrix, then you are required to take the input elements of array.
As an output you are required to print the sum of each row then the row having the maximum sum.
Test Case :
Input : 3 3
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
Output :
Row 1 : 6
Row 2 : 15
Row 3 : 24
Row 3 is having the maximum sum : 24
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int m, n, i, j, temp, max = 1; int mat[100][100]; int sum[100]; scanf("%d %d",&m, &n); for(i=0; i<m; i++) { for(j=0; j<n; j++) { scanf("%d",&mat[i][j]); } } for(i=0; i<m; i++) { sum[i] = 0; for(j=0; j<n; j++) { sum[i] = sum[i] + mat[i][j]; } printf("\n"); } for(i=0; i<m; i++) { printf("Row %d : %d\n",i+1,sum[i]); } for(i=0; i<m; i++) { if(sum[0]<sum[i+1]) { temp = sum[0]; sum [0] = sum[i+1]; sum[i+1] = temp; max = max+1; } } printf("\nRow %d is having the maximum sum : %d",max,sum[0]); return 0; }
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int m=sc.nextInt();
int n=sc.nextInt();
int arr[][]=new int[m][n];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
arr[i][j]=sc.nextInt();
int max=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int index=-1;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
int sum=0;
for(int j=0;j<n;j++) { sum=sum+arr[i][j]; } System.out.println("Row "+(i+1)+" : "+sum); if(sum>max)
{
max=sum;
index=i+1;
}
}
System.out.println("Row "+index+" is having the maximum sum : "+max);
}
}
Wipro Turbo Coding Questions
Question 10
(asked in Wipro NLTH 2019)
Problem: in this first line you are required to take the input that set the number of elements to be inserted, the next line takes the elements as input.
You are required to print the sum of maximum and minimum element of the list
Test Case :
Input : 6
55 87 46 21 34 79
Output :
108
Explanation :
21 + 87 = 108
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int a[100]; int n, sum, temp; int i, j; scanf("%d",&n); for(i=0; i<n; i++) { scanf("%d",&a[i]); } for(i=0; i<n; i++) { for(j=i+1; j<n; j++) { if(a[i]>a[j]) { temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; } } } sum = a[0]+a[n-1]; printf("%d",sum); return 0; }
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
int arr[]=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
int max=Integer.MIN_VALUE,min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
min=Math.min(min,arr[i]);
max=Math.max(max,arr[i]);
}
System.out.println(max+min);
}
}
Question 11
(asked in Wipro NLTH 2019)
Problem: in this first line you are required to take the input of an integer number, and in the second line you are required to input the target element
You are required to print the number of time target element occured in the integer
Test Case :
Input : 734139
3
Output :
2
Explanation :
3 occured 2 times in the integer.
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int num, target, count = 0, r; scanf("%d",&num); scanf("%d",&target); while(num!=0) { r = num%10; if(r==target) { count = count + 1; } num = num/10; } printf("%d",count); }
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int num=sc.nextInt();
int target=sc.nextInt();
int count=0;
while(num>0)
{
int rem=num%10;
if(rem==target)
count++;
num=num/10;
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
Some more Wipro Turbo Coding Questions for practice
Deloitte NLA Coding Questions and Answers
Deloitte NLA Coding Questions with Solutions
On the Deloitte NLA Coding Questions and Answers page, you will find out all the details related to the Hiring process of Deloitte including Coding Questions asked in NLA ( National Level Assessment ) and Technical Interview, Job Profile, Salary, Job Location, and other related details.

About Deloitte
Deloitte, formally known as Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited is a leading global services provider company. They provide services in consulting, financial advisory, tax management, risk management, audit, and assurance.
Deloitte is also having a Subsidiary, Deloitte US – India Consulting, which works under the Deloitte US Organization providing the same services as Deloitte US Organization gives.
About Deloitte NLA Recruitment Process
This Hiring process of Deloiite National Level Assessment consists of following steps :
- Online Assessment [ Aptitude, Verbal and Technical Based ]
- Technical and HR Interview
Note – We have a dedicated page for Deloitte NLA Coding Questions and Answers, but if you want exact “What type of questions asked in Deloitte NLA Coding Round”, scroll down and fulfill your dream 🙂
We have mentioned further details of Deloitte NLA Recruitment Process in following Tabular Form for a particular Job Profile
| Points | Related Informations |
|---|---|
| Position : | Analyst Trainee |
| Course : |
|
| Eligibility Criteria / Academic Qualification Required : | Minimum 60% or equivalent CGPA of 6.5 and above |
| Cost to Company (CTC) | Rs 4,00,000 /- P.A |
| Selection Process : |
|
Pattern of Deloitte NLA Recruitment Exam :
Deloitte National Level Assessment has a 90-minute time limit and is divided into 4 sections, which are mentioned below :
| Topics | Number of Questions | |
|---|---|---|
| Language Skills (English) | 10 MCQs + 3 FUBs | |
General Aptitude | 12 Reasoning + 10 Quants | |
| Technical MCQs | 30 Questions | |
| Coding Questions | 2 Questions |
Deloitte NLA Coding Questions and Answers
Question 1
Problem Statement –
A chocolate factory is packing chocolates into the packets. The chocolate packets here represent an array of N number of integer values. The task is to find the empty packets(0) of chocolate and push it to the end of the conveyor belt(array).
Example 1 :
N=8 and arr = [4,5,0,1,9,0,5,0].
There are 3 empty packets in the given set. These 3 empty packets represented as O should be pushed towards the end of the array
Input :
8 – Value of N
[4,5,0,1,9,0,5,0] – Element of arr[O] to arr[N-1],While input each element is separated by newline
Output:
4 5 1 9 5 0 0 0
Example 2:
Input:
6 — Value of N.
[6,0,1,8,0,2] – Element of arr[0] to arr[N-1], While input each element is separated by newline
Output:
6 1 8 2 0 0
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n, j = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
int a[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[j]);
if (a[j] != 0)
{
j++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int n, j = 0;
cin >> n;
int a[n] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a[j];
if (a[j] != 0)
{
j++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
int arr[]=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i< n;i++)
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i< n;i++)
if(arr[i]!=0)
arr[count++]=arr[i];
for(int i=count;i < n;i++)
arr[i]=0;
for(int i=0;i< n;i++)
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
n = int(input()) # Read the size of the list
L = list(map(int, input().split())) # Read the list of integers
j = 0
i=0
# Move non-zero elements to the front
for i in range(n):
if L[i] != 0:
L[j] = L[i]
j += 1
# Fill remaining positions with zeros
for i in range(j, n):
L[i] = 0
# Print the list with non-zero elements followed by zeros
print(*L)
Question 2
Problem Statement –
Joseph is learning digital logic subject which will be for his next semester. He usually tries to solve unit assignment problems before the lecture. Today he got one tricky question. The problem statement is “A positive integer has been given as an input. Convert decimal value to binary representation. Toggle all bits of it after the most significant bit including the most significant bit. Print the positive integer value after toggling all bits”.
Constraints-
1<=N<=100
Example 1:
Input :
10 -> Integer
Output :
5 -> result- Integer
Explanation:
Binary representation of 10 is 1010. After toggling the bits(1010), will get 0101 which represents “5”. Hence output will print “5”.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int N;
cin >> N;
// Convert to binary and toggle bits
int result = ~N & ((1 << (int(log2(N)) + 1)) - 1);
cout << result << endl;
return 0;
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
// Find the number of bits required to represent N
int bitLength = (int) (Math.log(N) / Math.log(2)) + 1;
// Toggle the bits and mask out the higher bits
int result = (~N) & ((1 << bitLength) - 1);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
def main():
N = int(input())
# Find the number of bits required to represent N
bit_length = N.bit_length()
# Toggle the bits and mask out the higher bits
result = ~N & ((1 << bit_length) - 1)
print(result)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Question 3
You are given a function,
int findCount(int arr[], int length, int num, int diff);
The function accepts an integer array ‘arr’, its length and two integer variables ‘num’ and ‘diff’. Implement this function to find and return the number of elements of ‘arr’ having an absolute difference of less than or equal to ‘diff’ with ‘num’.
Note: In case there is no element in ‘arr’ whose absolute difference with ‘num’ is less than or equal to ‘diff’, return -1.
Example:
Input:
- arr: 12 3 14 56 77 13
- num: 13
- diff: 2
Output:
3
Explanation:
Elements of ‘arr’ having absolute difference of less than or equal to ‘diff’ i.e. 2 with ‘num’ i.e. 13 are 12, 13 and 14.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int findCount (int n, int arr[], int num, int diff)
{
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
if (abs (arr[i] - num) <= diff)
{
count++;
}
}
return count > 0 ? count : -1;
}
int main ()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int arr[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
cin >> arr[i];
}
int num;
cin >> num;
int diff;
cin >> diff;
cout << findCount (n, arr, num, diff);
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int findCount (int n, int arr[], int num, int diff)
{
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
if (abs (arr[i] - num) <= diff)
{
count++;
}
}
return count > 0 ? count : -1;
}
int main ()
{
int n;
scanf ("%d", &n);
int arr[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
scanf ("%d", &arr[i]);
}
int num;
scanf ("%d", &num);
int diff;
scanf ("%d", &diff);
printf ("%d\n", findCount (n, arr, num, diff));
return 0;
}
def findCount(n, arr, num, diff):
count=0
for i in range(n):
if(abs(arr[i]-num)<=diff):
count+=1
if count:
return count
return 0
n=int(input())
arr=list(map(int,input().split()))
num=int(input())
diff=int(input())
print(findCount(n, arr, num, diff))
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static int findCount (int arr[], int length, int num, int diff)
{
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
if (Math.abs (num - arr[i]) <= diff)
count++;
}
return count > 0 ? count : -1;
}
public static void main (String[]args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt ();
int arr[] = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = sc.nextInt ();
int num = sc.nextInt ();
int diff = sc.nextInt ();
System.out.println (findCount (arr, n, num, diff));
}
}
Question 4
Implement the following Function
def differenceofSum(n. m)
The function accepts two integers n, m as arguments Find the sum of all numbers in range from 1 to m(both inclusive) that are not divisible by n. Return difference between sum of integers not divisible by n with sum of numbers divisible by n.
Assumption:
- n>0 and m>0
- Sum lies between integral range
Example
Input
n:4
m:20
Output
90
Explanation
- Sum of numbers divisible by 4 are 4 + 8 + 12 + 16 + 20 = 60
- Sum of numbers not divisible by 4 are 1 +2 + 3 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 9 + 10 + 11 + 13 + 14 + 15 + 17 + 18 + 19 = 150
- Difference 150 – 60 = 90
Sample Input
n:3
m:10
Sample Output
19
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int differenceofSum (int n, int m)
{
int i, sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++) { if (i % n == 0) { sum1 = sum1 + i; } else { sum2 = sum2 + i; } } if (sum2 > sum1)
return sum2 - sum1;
else
return sum1 - sum2;
}
int main ()
{
int n, m;
int result;
cin >> n;
cin >> m;
result = differenceofSum (n, m);
cout << result;
return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
int differenceofSum (int n, int m)
{
int i, sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
if (i % n == 0)
{
sum1 = sum1 + i;
}
else
{
sum2 = sum2 + i;
}
}
if (sum2 > sum1)
return sum2 - sum1;
else
return sum1 - sum2;
}
int main ()
{
int n, m;
int result;
scanf ("%d", &n);
scanf ("%d", &m);
result = differenceofSum (n, m);
printf ("%d", result);
return 0;
}
n = int(input())
m = int(input())
sum1 = 0
sum2 = 0
for i in range(1,m+1):
if i % n == 0:
sum1+=i
else:
sum2+=i
print(abs(sum2-sum1))
import java.util.*;
class Solution
{
public static int differenceOfSum (int m, int n)
{
int sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
if (i % n == 0)
sum1 = sum1 + i;
else
sum2 = sum2 + i;
}
return Math.abs (sum1 - sum2);
}
public static void main (String[]args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt ();
int m = sc.nextInt ();
System.out.println (differenceOfSum (m, n));
}
}
Question 5
Airport security officials have confiscated several item of the passengers at the security check point. All the items have been dumped into a huge box (array). Each item possesses a certain amount of risk[0,1,2]. Here, the risk severity of the items represent an array[] of N number of integer values. The task here is to sort the items based on their levels of risk in the array. The risk values range from 0 to 2.
Example :
Input :
7 -> Value of N
[1,0,2,0,1,0,2]-> Element of arr[0] to arr[N-1], while input each element is separated by new line.
Output :
0 0 0 1 1 2 2 -> Element after sorting based on risk severity
Example 2:
input : 10 -> Value of N
[2,1,0,2,1,0,0,1,2,0] -> Element of arr[0] to arr[N-1], while input each element is separated by a new line.
Output :
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 2 2 2 ->Elements after sorting based on risk severity.
Explanation:
In the above example, the input is an array of size N consisting of only 0’s, 1’s and 2s. The output is a sorted array from 0 to 2 based on risk severity.
#include<stdio.h>
void swap(int* a, int* b) {
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
void sortArray(int arr[], int size) {
int low = 0, mid = 0, high = size - 1;
while (mid <= high) {
if (arr[mid] == 0) {
swap(&arr[low], &arr[mid]);
low++;
mid++;
} else if (arr[mid] == 1) {
mid++;
} else {
swap(&arr[mid], &arr[high]);
high--;
}
}
}
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
int a[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
sortArray(a, n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n; cin>>n;
int a[n];
for(int i=0;i< n;i++) cin>>a[i];
int l=0,m=0,h=n-1;
while(m<=h)
{
if(a[m]==0) swap(a[l++],a[m++]);
else if(a[m]==1) m++;
else swap(a[m],a[h--]);
}
for(int i=0;i< n;i++) cout<< a[i]<<" ";
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
int arr[]=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i< n;i++)
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
int countZero=0,countOne=0,countTwo=0;
for(int i=0;i< n;i++) { if(arr[i]==0) countZero++; else if(arr[i]==1) countOne++; else if(arr[i]==2) countTwo++; } int j =0; while(countZero >0)
{
arr[j++]=0;
countZero--;
}
while(countOne >0)
{
arr[j++]=1;
countOne--;
}
while(countTwo >0)
{
arr[j++]=2;
countTwo--;
}
for(int i=0;i < n;i++)
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
n = int(input())
arr = []
for i in range(n):
arr.append(int(input()))
for i in sorted(arr):
print(i, end=" ")
FAQs related to Deloitte NLA Coding Questions
Question 1: What kind of roles are available at Deloitte in India?
Deloitte offers a variety of roles across different domains like Audit, Consulting, Financial Advisory, Risk advisory, Tax and related services.
Question 2: Does Deloitte asks coding questions in there Recruitment Process?
Yes, Deloitte asks coding questions in there National Level Assessment and Technical Interview.
Question 3: Is Registration Process is still going on?
Yes, The registration process is still going on, You can apply directly via Deloitte Registration Page.
TCS NQT Coding Questions and Answers 2025
TCS NQT Coding Questions with Answers for Freshers

TCS NQT Coding Questions are asked in TCS NQT Advanced Coding Round. This round will be of high difficulty. Below you will find questions based on the current updated pattern on TCS NQT 2025. You must prepare for the upcoming TCS NQT Advanced Coding Round from this page in order to ace your exam.
- C / C++
- Java
- Python
- Perl
Details regarding TCS NQT Coding Round
| Details | Coding Round |
|---|---|
| Number of Questions | 3 questions |
| Time Limit | 90 mins |
TCS NQT Coding Question – September Day 1 – Slot 1
Problem Statement –
A chocolate factory is packing chocolates into the packets. The chocolate packets here represent an array of N number of integer values. The task is to find the empty packets(0) of chocolate and push it to the end of the conveyor belt(array).
Example 1 :
N=8 and arr = [4,5,0,1,9,0,5,0].
There are 3 empty packets in the given set. These 3 empty packets represented as O should be pushed towards the end of the array
Input :
8 – Value of N
[4,5,0,1,9,0,5,0] – Element of arr[O] to arr[N-1],While input each element is separated by newline
Output:
4 5 1 9 5 0 0 0
Example 2:
Input:
6 — Value of N.
[6,0,1,8,0,2] – Element of arr[0] to arr[N-1], While input each element is separated by newline
Output:
6 1 8 2 0 0
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
int L[n];
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a != 0) {
L[j] = a;
j++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i < j) {
printf("%d ", L[i]);
}
else {
printf("0");
}
}
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int n, j = 0;
cin >> n;
int a[n] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a[j];
if (a[j] != 0)
{
j++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
int arr[]=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i< n;i++)
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i< n;i++)
if(arr[i]!=0)
arr[count++]=arr[i];
for(int i=count;i < n;i++)
arr[i]=0;
for(int i=0;i< n;i++)
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
n=int(input())
j=0
L=[0 for i in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
a=int(input())
if a!=0:
L[j]=a
j+=1
for i in L:
print(i,end=" ")TCS NQT Coding Question – September Day 1 – Slot 1
Problem Statement –
Joseph is learning digital logic subject which will be for his next semester. He usually tries to solve unit assignment problems before the lecture. Today he got one tricky question. The problem statement is “A positive integer has been given as an input. Convert decimal value to binary representation. Toggle all bits of it after the most significant bit including the most significant bit. Print the positive integer value after toggling all bits”.
Constrains-
1<=N<=100
Example 1:
Input :
10 -> Integer
Output :
5 -> result- Integer
Explanation:
Binary representation of 10 is 1010. After toggling the bits(1010), will get 0101 which represents “5”. Hence output will print “5”.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
int k = (1 << (int)(log2(n) + 1)) - 1;
printf("%d", n ^ k);
return 0;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int k = (1 << (int) floor (log2 (n)) + 1) - 1;
cout << (n ^ k);
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int no=sc.nextInt();
String bin="";
while(no!=0)
{
bin=(no&1)+bin;
no=no>>1;
}
bin=bin.replaceAll("1","2");
bin=bin.replaceAll("0","1");
bin=bin.replaceAll("2","0");
int res=Integer.parseInt(bin,2);
System.out.println(res);
}
}
import math n=int(input()) k=(1<< int(math.log2(n))+1)-1 print(n^k)
TCS NQT Coding Question Day 1 Slot 2 – Question 1
Jack is always excited about sunday. It is favourite day, when he gets to play all day. And goes to cycling with his friends.
So every time when the months starts he counts the number of sundays he will get to enjoy. Considering the month can start with any day, be it Sunday, Monday…. Or so on.
Count the number of Sunday jack will get within n number of days.
Example 1:
Input
mon-> input String denoting the start of the month.
13 -> input integer denoting the number of days from the start of the month.
Output :
2 -> number of days within 13 days.
Explanation:
The month start with mon(Monday). So the upcoming sunday will arrive in next 6 days. And then next Sunday in next 7 days and so on.
Now total number of days are 13. It means 6 days to first sunday and then remaining 7 days will end up in another sunday. Total 2 sundays may fall within 13 days.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#define MAX_LENGTH 4
int main()
{
char s[MAX_LENGTH];
scanf("%s", s);
int a, ans = 0;
scanf("%d", &a);
// Map weekdays to their corresponding values
char weekdays[][MAX_LENGTH] = {
"mon", "tue", "wed", "thu", "fri", "sat", "sun"
};
int values[] = {6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0};
// Find the corresponding value for the input weekday
int mapSize = sizeof(weekdays) / sizeof(weekdays[0]);
int m = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < mapSize; i++) {
if (strcmp(s, weekdays[i]) == 0) {
m = values[i]; break; }
} if (m != -1) { // Calculate the answer
if (a - m >= 1) {
ans = 1 + (a - m) / 7;
}
}
printf("%d", ans);
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s; cin>>s;
int a,ans=0;
cin>>a;
unordered_map< string,int > m;
m["mon"]=6;m["tue"]=5;m["wed"]=4;
m["thu"]=3;m["fri"]=2;m["sat"]=1;
m["sun"]=0;
if(a-m[s.substr(0,3)] >=1) ans=1+(a-m[s.substr(0,3)])/7;
cout<< ans;
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String str=sc.next();
int n=sc.nextInt();
String arr[]={"mon","tue,","wed","thu","fri","sat","sun"};
int i=0;
for(i=0;i< arr.length;i++)
if(arr[i].equals(str)) break;
int res=1;
int rem=6-i;
n=n-rem;
if(n >0)
res+=n/7;
System.out.println(res);
}
}def main():
s = input()
a = int(input())
m = {
"mon": 6, "tue": 5, "wed": 4,
"thu": 3, "fri": 2, "sat": 1,
"sun": 0
}
ans = 0
if a - m[s[:3]] >= 1:
ans = 1 + (a - m[s[:3]]) // 7
print(ans)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
TCS NQT Coding Question Day 1 Slot 2 – Question 2
Airport security officials have confiscated several item of the passengers at the security check point. All the items have been dumped into a huge box (array). Each item possesses a certain amount of risk[0,1,2]. Here, the risk severity of the items represent an array[] of N number of integer values. The task here is to sort the items based on their levels of risk in the array. The risk values range from 0 to 2.
Example :
Input :
7 -> Value of N
[1,0,2,0,1,0,2]-> Element of arr[0] to arr[N-1], while input each element is separated by new line.
Output :
0 0 0 1 1 2 2 -> Element after sorting based on risk severity
Example 2:
input : 10 -> Value of N
[2,1,0,2,1,0,0,1,2,0] -> Element of arr[0] to arr[N-1], while input each element is separated by a new line.
Output :
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 2 2 2 ->Elements after sorting based on risk severity.
Explanation:
In the above example, the input is an array of size N consisting of only 0’s, 1’s and 2s. The output is a sorted array from 0 to 2 based on risk severity.
#include<stdio.h>
void swap(int* a, int* b) {
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
void sortArray(int arr[], int size) {
int low = 0, mid = 0, high = size - 1;
while (mid <= high) {
if (arr[mid] == 0) {
swap(&arr[low], &arr[mid]);
low++;
mid++;
} else if (arr[mid] == 1) {
mid++;
} else {
swap(&arr[mid], &arr[high]);
high--;
}
}
}
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
int a[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
sortArray(a, n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n; cin>>n;
int a[n];
for(int i=0;i< n;i++) cin>>a[i];
int l=0,m=0,h=n-1;
while(m<=h)
{
if(a[m]==0) swap(a[l++],a[m++]);
else if(a[m]==1) m++;
else swap(a[m],a[h--]);
}
for(int i=0;i< n;i++) cout<< a[i]<<" ";
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
int arr[]=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i< n;i++)
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
int countZero=0,countOne=0,countTwo=0;
for(int i=0;i< n;i++) {
if(arr[i]==0) countZero++;
else if(arr[i]==1) countOne++;
else if(arr[i]==2) countTwo++;
}
int j =0;
while(countZero >0)
{
arr[j++]=0;
countZero--;
}
while(countOne >0)
{
arr[j++]=1;
countOne--;
}
while(countTwo >0)
{
arr[j++]=2;
countTwo--;
}
for(int i=0;i < n;i++)
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
n = int(input())
arr = []
for i in range(n):
arr.append(int(input()))
for i in sorted(arr):
print(i, end=" ")
TCS NQT Coding Question Day 2 Slot 1 – Question 1
Given an integer array Arr of size N the task is to find the count of elements whose value is greater than all of its prior elements.
Note : 1st element of the array should be considered in the count of the result.
For example,
Arr[]={7,4,8,2,9}
As 7 is the first element, it will consider in the result.
8 and 9 are also the elements that are greater than all of its previous elements.
Since total of 3 elements is present in the array that meets the condition.
Hence the output = 3.
Example 1:
Input
5 -> Value of N, represents size of Arr
7-> Value of Arr[0]
4 -> Value of Arr[1]
8-> Value of Arr[2]
2-> Value of Arr[3]
9-> Value of Arr[4]
Output :
3
Example 2:
5 -> Value of N, represents size of Arr
3 -> Value of Arr[0]
4 -> Value of Arr[1]
5 -> Value of Arr[2]
8 -> Value of Arr[3]
9 -> Value of Arr[4]
Output :
5
Constraints
1<=N<=20
1<=Arr[i]<=10000
#include<stdio.h>
#include<limits.h>
int main() {
int n, c = 0, a, m = INT_MIN;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n--) {
scanf("%d", &a);
if (a >= m) {
m = a;
c++;
}
}
printf("%d", c);
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,c=0,a,m=INT_MIN;
cin>>n;
while(n--)
{
cin>>a;
if(a>m)
{
m=a;
c++;
}
}
cout << c;
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
int arr[]=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i< n;i++)
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
int max=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i< n;i++) { if(arr[i]>max)
{
max=arr[i];
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
import sys
n=int(input())
c=0
m=-sys.maxsize-1
while n:
n-=1
a=int(input())
if a>m:
m=a
c+=1
print(c)
TCS NQT Coding Question Day 2 Slot 1 – Question 2
A supermarket maintains a pricing format for all its products. A value N is printed on each product. When the scanner reads the value N on the item, the product of all the digits in the value N is the price of the item. The task here is to design the software such that given the code of any item N the product (multiplication) of all the digits of value should be computed(price).
Example 1:
Input :
5244 -> Value of N
Output :
160 -> Price
Explanation:
From the input above
Product of the digits 5,2,4,4
5*2*4*4= 160
Hence, output is 160.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<limits.h>
int main() {
char s[100];
scanf("%s", s);
int p = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(s); i++) {
p *= (s[i] - '0');
}
printf("%d", p);
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
cin>>s;
int p=1;
for(auto i:s)
p*=(i-'0');
cout<< p;
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
int res=1;
while(n>0)
{
res=res*(n%10);
n=n/10;
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
n=input()
p=1
for i in n:
p*=int(i)
print(p)
TCS NQT Coding Question Day 3 Slot 2 – Question 1
A furnishing company is manufacturing a new collection of curtains. The curtains are of two colors aqua(a) and black (b). The curtains color is represented as a string(str) consisting of a’s and b’s of length N. Then, they are packed (substring) into L number of curtains in each box. The box with the maximum number of ‘aqua’ (a) color curtains is labeled. The task here is to find the number of ‘aqua’ color curtains in the labeled box.
Note :
If ‘L’ is not a multiple of N, the remaining number of curtains should be considered as a substring too. In simple words, after dividing the curtains in sets of ‘L’, any curtains left will be another set(refer example 1)
Example 1:
Input :
bbbaaababa -> Value of str
3 -> Value of L
Output:
3 -> Maximum number of a’s
Explanation:
From the input given above.
Dividing the string into sets of 3 characters each
Set 1: {b,b,b}
Set 2: {a,a,a}
Set 3: {b,a,b}
Set 4: {a} -> leftover characters also as taken as another set
Among all the sets, Set 2 has more number of a’s. The number of a’s in set 2 is 3.
Hence, the output is 3.
Example 2:
Input :
abbbaabbb -> Value of str
5 -> Value of L
Output:
2 -> Maximum number of a’s
Explanation:
From the input given above,
Dividing the string into sets of 5 characters each.
Set 1: {a,b,b,b,b}
Set 2: {a,a,b,b,b}
Among both the sets, set 2 has more number of a’s. The number of a’s in set 2 is 2.
Hence, the output is 2.
Constraints:
1<=L<=10
1<=N<=50
The input format for testing
The candidate has to write the code to accept two inputs separated by a new line.
First input- Accept string that contains character a and b only
Second input- Accept value for N(Positive integer number)
The output format for testing
The output should be a positive integer number of print the message(if any) given in the problem statement.(Check the output in Example 1, Example 2).
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main() {
char str[100];
scanf("%s", str);
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
int max = 0, count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(str); i++) {
if (i % n == 0) {
if (count > max)
max = count;
count = 0;
}
if (str[i] == 'a')
count++;
}
if (count > max)
max = count;
printf("%d\n", max);
return 0;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string str;
cin >> str;
int n;
cin >> n;
int max = 0, count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
if (i % n == 0) {
max = std::max(count, max);
count = 0;
}
if (str[i] == 'a')
count++;
}
max = std::max(count, max);
cout << max << endl;
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String str=sc.next();
int n=sc.nextInt();
int max=0,count=0;
for(int i=0;i< str.length();i++)
{
if(i%n==0)
{
max=Math.max(count,max);
count=0;
}
if(str.charAt(i)=='a')
count++;
}
max=Math.max(count,max);
System.out.println(max);
}
}
str = input()
n = int(input())
max_val = 0
count = 0
for i in range(len(str)):
if i % n == 0:
max_val = max(count, max_val)
count = 0
if str[i] == 'a':
count += 1
if count > max_val:
max_val = count
print(max_val)
TCS NQT Coding Question Day 3 Slot 2 – Question 2
An international round table conference will be held in india. Presidents from all over the world representing their respective countries will be attending the conference. The task is to find the possible number of ways(P) to make the N members sit around the circular table such that.
The president and prime minister of India will always sit next to each other.
Example 1:
Input :
4 -> Value of N(No. of members)
Output :
12 -> Possible ways of seating the members
Explanation:
2 members should always be next to each other.
So, 2 members can be in 2!ways
Rest of the members can be arranged in (4-1)! ways.(1 is subtracted because the previously selected two members will be considered as single members now).
So total possible ways 4 members can be seated around the circular table 2*6= 12.
Hence, output is 12.
Example 2:
Input:
10 -> Value of N(No. of members)
Output :
725760 -> Possible ways of seating the members
Explanation:
2 members should always be next to each other.
So, 2 members can be in 2! ways
Rest of the members can be arranged in (10-1)! Ways. (1 is subtracted because the previously selected two members will be considered as a single member now).
So, total possible ways 10 members can be seated around a round table is
2*362880 = 725760 ways.
Hence, output is 725760.
The input format for testing
The candidate has to write the code to accept one input
First input – Accept value of number of N(Positive integer number)
The output format for testing
The output should be a positive integer number or print the message(if any) given in the problem statement(Check the output in example 1, example2)
Constraints :
2<=N<=50
#include<stdio.h>
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
int fact[n + 1];
fact[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i;
}
printf("%d\n", fact[n - 1] * 2);
return 0;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector fact(n + 1, 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i;
}
cout << fact[n - 1] * 2 << endl;
return 0;
}
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static BigInteger fact(int number)
{
BigInteger res= BigInteger.ONE;
for (int i = number; i > 0; i--)
res = res.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(i));
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
BigInteger res=fact(n-1);
System.out.println(res.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(2)));
}
}
n = int(input())
fact = [0] * (n + 1)
fact[0] = 1
for i in range(1, n + 1):
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i
print(fact[n - 1] * 2)
TCS NQT Coding Question Day 4 Slot 1 – Question 1
Problem Statement
An intelligence agency has received reports about some threats. The reports consist of numbers in a mysterious method. There is a number “N” and another number “R”. Those numbers are studied thoroughly and it is concluded that all digits of the number ‘N’ are summed up and this action is performed ‘R’ number of times. The resultant is also a single digit that is yet to be deciphered. The task here is to find the single-digit sum of the given number ‘N’ by repeating the action ‘R’ number of times.
If the value of ‘R’ is 0, print the output as ‘0’.
Example 1:
Input :
99 -> Value of N
3 -> Value of R
Output :
9 -> Possible ways to fill the cistern.
Explanation:
Here, the number N=99
- Sum of the digits N: 9+9 = 18
- Repeat step 2 ‘R’ times i.e. 3 tims (9+9)+(9+9)+(9+9) = 18+18+18 =54
- Add digits of 54 as we need a single digit 5+4
Hence , the output is 9.
Example 2:
Input :
1234 -> Value of N
2 -> Value of R
Output :
2 -> Possible ways to fill the cistern
Explanation:
Here, the number N=1234
- Sum of the digits of N: 1+2+3+4 =10
- Repeat step 2 ‘R’ times i.e. 2 times (1+2+3+4)+(1+2+3+4)= 10+10=20
- Add digits of 20 as we need a single digit. 2+0=2
Hence, the output is 2.
Constraints:
0<N<=1000
0<=R<=50
The Input format for testing
The candidate has to write the code to accept 2 input(s)
First input- Accept value for N (positive integer number)
Second input: Accept value for R(Positive integer number)
The output format for testing
The output should be a positive integer number or print the message (if any) given in the problem statement. (Check the output in Example 1, Example 2).
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main() {
char s[100];
scanf("%s", s);
int n, sum = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(s); i++) {
sum += (s[i] - '0');
}
sum *= n;
sprintf(s, "%d", sum);
while (strlen(s) > 1) {
sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(s); i++) {
sum += (s[i] - '0');
}
sprintf(s, "%d", sum);
}
printf("%s", s);
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s; cin>>s;
int n,sum=0; cin>>n;
for(auto i:s) sum+=(i-'0');
sum*=n;
s=to_string(sum);
while(s.length()>1)
{
sum=0;
for(auto i:s) sum+=(i-'0');
s=to_string(sum);
}
cout<< s;
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static int sumOfDigits(int n)
{
int sum=0;
while(n>0)
{
sum+=n%10;
n=n/10;
}
return sum;
}
public static void main(String []args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=sc.nextInt();
int r=sc.nextInt();
if(r==0)
System.out.println("0");
else
{
int res=sumOfDigits(n)*r;
int sum=0;
while(true)
{
while(res>0)
{
sum=sum+res%10;
res=res/10;
}
if((sum/10)==0)
break;
else
res=sum;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
} }
s=input()
n=int(input())
sum=0
for i in s:
sum+=int(i)
sum*=n
s=str(sum)
while len(s)>1:
sum=0
for i in s:
sum+=int(i)
s=str(sum)
print(s)
TCS NQT Coding Question Day 4 Slot 1 – Question 2
Problem Statement
Particulate matters are the biggest contributors to Delhi pollution. The main reason behind the increase in the concentration of PMs include vehicle emission by applying Odd Even concept for all types of vehicles. The vehicles with the odd last digit in the registration number will be allowed on roads on odd dates and those with even last digit will on even dates.
Given an integer array a[], contains the last digit of the registration number of N vehicles traveling on date D(a positive integer). The task is to calculate the total fine collected by the traffic police department from the vehicles violating the rules.
Note : For violating the rule, vehicles would be fined as X Rs.
Example 1:
Input :
4 -> Value of N
{5,2,3,7} -> a[], Elements a[0] to a[N-1], during input each element is separated by a new line
12 -> Value of D, i.e. date
200 -> Value of x i.e. fine
Output :
600 -> total fine collected
Explanation:
Date D=12 means , only an even number of vehicles are allowed.
Find will be collected from 5,3 and 7 with an amount of 200 each.
Hence, the output = 600.
Example 2:
Input :
5 -> Value of N
{2,5,1,6,8} -> a[], elements a[0] to a[N-1], during input each element is separated by new line
3 -> Value of D i.e. date
300 -> Value of X i.e. fine
Output :
900 -> total fine collected
Explanation:
Date D=3 means only odd number vehicles with are allowed.
Find will be collected from 2,6 and 8 with an amount of 300 each.
Hence, the output = 900
Constraints:
- 0<N<=100
- 1<=a[i]<=9
- 1<=D <=30
- 100<=x<=5000
The input format for testing
The candidate has to write the code to accept 4 input(s).
First input – Accept for N(Positive integer) values (a[]), where each value is separated by a new line.
Third input – Accept value for D(Positive integer)
Fourth input – Accept value for X(Positive integer )
The output format for testing
The output should be a positive integer number (Check the output in Example 1, Example e) if no fine is collected then print ”0”.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
int arr[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
int d, x;
scanf("%d %d", &d, &x);
int countEven = 0, countOdd = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] % 2 == 0)
countEven++;
else
countOdd++;
}
if (d % 2 != 0) {
if (countEven == 0)
printf("0\n");
else
printf("%d\n", countEven * x);
} else {
if (countOdd == 0)
printf("0\n");
else
printf("%d\n", countOdd * x);
}
return 0;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> arr(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> arr[i];
int d, x;
cin >> d >> x;
int countEven = 0, countOdd = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i] % 2 == 0)
countEven++;
else
countOdd++;
}
if (d % 2 != 0) {
if (countEven == 0)
cout << "0" << endl;
else
cout << countEven * x << endl;
} else {
if (countOdd == 0)
cout << "0" << endl;
else
cout << countOdd * x << endl;
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt ();
int arr[] = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = sc.nextInt ();
int d = sc.nextInt ();
int x = sc.nextInt ();
int countEven = 0, countOdd = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (arr[i] % 2 == 0)
countEven++;
else
countOdd++;
}
if (d % 2 != 0)
{
if (countEven == 0)
System.out.println ("0");
else
System.out.println (countEven * x);
}
else
{
if (countOdd == 0)
System.out.println ("0");
else
System.out.println (countOdd * x);
}
}
}
n = int(input())
arr = list(map(int, input().split()))
d, x = map(int, input().split())
countEven = 0
countOdd = 0
for i in range(n):
if arr[i] % 2 == 0:
countEven += 1
else:
countOdd += 1
if d % 2 != 0:
if countEven == 0:
print("0")
else:
print(countEven * x)
else:
if countOdd == 0:
print("0")
else:
print(countOdd * x)HCL Coding Questions and Answers
HCL Practice Coding Questions
As coding turns out to be the most crucial section of HCL recruitment examination, we believe that having a mindset for HCL Coding Questions & Answers is important. As the number of questions is only 2 but the time allotted is only 20 mins so it becomes very hard to pass all the test cases. Hence, this makes it obvious to understand the pattern of questions asked in HCL Placement Paper. This page will help you to know the solution of some coding questions.

About HCL Exam Pattern 2025
| Topics | Number of Questions | Time | Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Numerical Ability | 15 | 15 mins | Medium |
| Verbal Ability | 15 | 15 mins | Medium |
| Reasoning Ability | 15 | 15 mins | Medium |
| Computer Programming | 30 | 30 mins | High |
| Coding | 2 | 20 mins | High |
HCL Coding Questions : Detailed Analysis
Find the complete analysis for HCL Coding Section below in the tabular format for better understanding.
| HCL Section | No. of questions | Total Time |
|---|---|---|
| MCQ | 30 | 30 mins |
| Coding Challenge | 2 | 20 mins |
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Some facts about Eligibility Criteria:-
| HCL | Requirements |
|---|---|
| Qualification | B.Tech |
| Eligible stream | (CSE,IT,ECE,EN,EI, ME) |
| Percentage Criteria | 75% throughout academics (10th, 12th / Diploma & UG) |
| Backlog | No Active Backlog |
| Service Agreement | Probation period for selected SE/GET will be of 12 Months. |
Practice Coding Question for HCL
Question 1 :
PrepInsta Name : Move Hash to Front
Problem Statement : You have write a function that accepts, a string which length is “len”, the string has some “#”, in it you have to move all the hashes to the front of the string and return the whole string back and
print it.
char* moveHash(char str[],int n);
Example :
Sample Test Case
- Input:
Move#Hash#to#Front - Output:
###MoveHashtoFront
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
char *moveHash(char str[],int n)
{
char str1[100],str2[100];
int i,j=0,k=0;
for(i=0;str[i];i++)
{
if(str[i]=='#')
str1[j++]=str[i];
else
str2[k++]=str[i];
}
strcat(str1,str2);
printf("%s",str1);
}
int main()
{
char a[100], len;
scanf("%[^\n]s",a);
len = strlen(a);
moveHash(a, len);
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string moveHash(string s)
{
string ans="";
for(auto i:s)
if(i=='#') ans='#'+ans;
else ans+=i;
return ans;
}
int main()
{
string s;
getline(cin,s);
cout<< moveHash(s);
}
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void moveHash(String str ,int n)
{
String str1= new String("");
String str2= new String("");
int i=0;
for(i=0;i < n;i++)
{
if(str.charAt(i)=='#')
str1=str1 + str.charAt(i);
else
str2 = str2 + str.charAt(i);
}
String result = str1.concat(str2);
System.out.println(result);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String a = sc.nextLine();
int len= a.length();
moveHash(a, len);
}
}
def moveHash(s):
x=s.count("#")
s=s.replace("#","")
return ("#"*x+s)
s=input()
print(moveHash(s))Question 2 :
PrepInsta Name : Borrow Number
Problem statement : You have two numbers number1 and number2, your job is to check the number of borrow operations needed for subtraction of number1 from number2. If the subtraction is not possible
then return the string not possible.
Example :
- 754
658 - Answer :
2
654
666 - Answer:
Not possible
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
int number1,number2,count=0;
scanf("%d%d",&number1,&number2);
if(number1< number2)
printf("Not possible");
else
{
int flag=0;
int temp1,temp2;
while(number1!=0 && number2!=0)
{
temp1=0;
temp2=number2%10;
if(flag==1)
temp1=number1%10-1;
else
temp1=number1%10;
if(temp1< temp2)
{
count+=1;
flag=1;
}
else
flag=0;
number1=number1/10;
number2=number2/10;
}
printf("%d",count);
}
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1,s2;
int c=0,f=0;
cin>>s1>>s2;
if(stoi(s1)< stoi(s2)) {cout<<"Impossible";}
reverse(s1.begin(),s1.end());
reverse(s2.begin(),s2.end());
for(int i=0;i< s1.length();i++)
if(s1[i]< s2[i]) {f=1;c++;}
else if(s1[i]==s2[i])
{
if(f==1) {c++;}
f=0;
}
else f=0;
cout<< c;
}
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int number1=sc.nextInt();
int number2=sc.nextInt();
int count=0;
if(number1< number2)
{
System.out.println("Not possible");
}
else
{
boolean flag=false;
while(number1!=0 && number2!=0)
{
int temp1=0;
int temp2=number2%10;
if(flag)
temp1=number1%10-1;
else
temp1=number1%10;
if(temp1< temp2)
{
count++;
flag=true;
}
else
flag=false;
number1=number1/10;
number2=number2/10;
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
}
number1=int(input())
number2=int(input())
count=0
if(number1< number2):
print("Not possible")
else:
flag=0
while(number1!=0 and number2!=0):
temp1=0
temp2=number2%10
if(flag):
temp1=number1%10-1
else:
temp1=number1%10
if(temp1< temp2):
count+=1
flag=1
else:
flag=0
number1=number1//10
number2=number2//10
print(count)
Question 3 :
PrepInsta Name : Capitalize/Decapitalize
Problem statement : You’re given a function that accepts the following, a string1, its length and a character c. Your job is to replace all the occurrences of character c in string1 and capitalize it or decapitalize it based on the character c.
Input :
hello world
l
Output :
heLLo worLd
Input :
prepinsta
p
Output :
PrePinsta
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void changeCharacter (char str[], char chr, int len)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
if (chr == str[i])
{
if (str[i] >= 64 && str[i] <= 92)
str[i] += 32;
else if (str[i] >= 90 && str[i] <= 122)
str[i] -= 32;
}
printf ("%s", str);
}
int main ()
{
char str[1000], chr;
int len;
scanf ("%[^\n]s", str);
len = strlen (str);
scanf (" %c", &chr);
changeCharacter (str, chr, len);
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
getline(cin,s);
char k; cin>>k;
for(auto i:s)
if(i==k)
{
if(i>95)cout<<char(i-32);
else cout<<char(i+32);
}
else cout<<i;
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main
{
public static void change(String str, char c, int len)
{
char[] ch = str.toCharArray();
for(int i=0; i<ch.length; i++)
{
if( c == ch[i] )
{
if(Character.isUpperCase(ch[i]))
{
ch[i]= Character.toLowerCase(ch[i]);
}
else if(Character.isLowerCase(ch[i]))
{
ch[i]= Character.toUpperCase(ch[i]);
}
}
}
System.out.print(new String(ch) );
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.nextLine();
char c = sc.next().charAt(0);
int len = str.length();
change(str, c, len);
}
}
s=input()
k=input()
if(k.isupper()):
s=s.replace(k,chr(ord(k)+32))
else:
s=s.replace(k,chr(ord(k)-32))
print(s)
Question 4 :
Problem statement : You’re given a string where multiple characters are repeated consecutively. You’re supposed to reduce the size of this string using mathematical logic given as in the example below :
Input :
abbccccc
Output:
ab2c5
Input :
aabbbbeeeeffggg
Output:
a2b4e4f2g3
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char str[100];
scanf("%[^\n]s",str);
int i, j, k=0, count = 0;
char str1[100];
for(i=0; str[i]!='\0'; i++)
{
count = 0;
for(j=0; j<=i; j++)
{
if(str[i]==str[j])
{
count++;
}
}
if(count==1)
{
str1[k] = str[i];
k++;
}
}
for(i=0; i< k; i++)
{
count = 0;
for(j=0; str[j]!='\0'; j++)
{
if(str1[i]==str[j])
{
count++;
}
}
if(count==1)
{
printf("%c",str1[i]);
}
else
{
printf("%c%d",str1[i],count);
}
}
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
getline(cin,s);
map< char,int > m;
for(auto i:s) m[i]++;
for(auto i:m)cout<< i.first<< i.second;
}
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.nextLine();
int i, j, k = 0, count = 0;
String uni = new String("");
for(i=0; i<str.length(); i++)
{
count = 0;
for(j=0; j<=i; j++)
{
if(str.charAt(i)==str.charAt(j))
{
count++;
}
}
if(count==1)
{
uni = uni + str.charAt(i);
}
}
for(i=0; i <uni.length(); i++)
{
count = 0;
for(j=0; j<str.length(); j++)
{
if(uni.charAt(i)==str.charAt(j))
{
count++;
}
}
if(count==1)
{
System.out.printf("%c",uni.charAt(i));
}
else
{
System.out.printf("%c%d",uni.charAt(i),count);
}
}
}
}
s=input()
i=1
c=1
while i<len(s):
if s[i]==s[i-1]:
c+=1
else:
print(s[i-1],end="")
print(c,end="")
c=1
i+=1
print(s[i-1],end="")
print(c)
Question 5 :
PrepInsta Name : Spiral Matrix
Problem statement : You will be given a 2d matrix. Write the code to traverse the matrix in a spiral format. Check the input and output for better understanding.
Example :
Input :
5 4
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
17 18 19 20
Output :
1 2 3 4 8 12 16 20 19 18 17 13 9 5 6 7 11 15 12 14 10
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int a[5][4] = {{1,2,3,4},{5,6,7,8},{9,10,11,12},{13,14,15,16},{17,18,19,20}};
int rs = 0, re = 5, cs = 0, ce = 4;
int i, j, k=0;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<4;j++)
{
printf("%d ",a[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
while(rs< re && cs< ce)
{
for(i=cs;i< ce;i++)
{
printf("%d ",a[rs][i]);
}
rs++;
for(i=rs;i< re;i++)
{
printf("%d ",a[i][ce-1]);
}
ce--;
if(rs< re) { for(i=ce-1; i>=cs; --i)
{
printf("%d ", a[re - 1][i]);
}
re--;
}
if(cs< ce) { for(i=re-1; i>=rs; --i)
{
printf("%d ", a[i][cs]);
}
cs++;
}
}
return 0;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void Spiral (vector < vector < int >>a)
{
if (a.size () == 0)
return;
int m = a.size (), n = a[0].size ();
int i, k = 0, l = 0;
while (k < m && l < n)
{
for (i = l; i < n; ++i)
cout << a[k][i] << " ";
k++;
for (i = k; i < m; ++i)
cout << a[i][n - 1] << " ";
n--;
if (k < m)
{
for (i = n - 1; i >= l; --i)
cout << a[m - 1][i] << " ";
m--;
}
if (l < n)
{
for (i = m - 1; i >= k; --i)
cout << a[i][l] << " ";
l++;
}
}
}
int main ()
{
int r, c;
cin >> r >> c;
vector < vector < int >>mat (r, vector < int >(c));
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < c; j++)
{
cin >> mat[i][j];
}
}
Spiral (mat);
}
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static List< Integer> solve(int [][]matrix,int row,int col)
{
List< Integer> res=new ArrayList< Integer>();
boolean[][] temp=new boolean[row][col];
int []arr1={0,1,0,-1};
int []arr2={1,0,-1,0};
int di=0,r=0,c=0;
for(int i=0;i< row*col;i++)
{
res.add(matrix[r][c]);
temp[r][c]=true;
int count1=r+arr1[di];
int count2=c+arr2[di];
if(count1 >=0 && row >count1 && count2 >=0 && col >count2 && !temp[count1][count2]){
r=count1;
c=count2;
}
else
{
di=(di+1)%4;
r+=arr1[di];
c+=arr2[di];
}
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int m=sc.nextInt();
int n=sc.nextInt();
int matrix[][]=new int[m][n];
for(int i=0;i < m;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j < n;j++)
matrix[i][j]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println(solve(matrix,m,n));
}
}
def spiralOrder(arr):
ans=[]
while arr:
ans+=arr.pop(0)
arr= (list(zip(*arr)))[::-1]
return ans
arr=[]
n,m=map(int,input().split())
for i in range(n):
arr.append(list(map(int,input().split())))
print(*spiralOrder(arr))
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Amazon Coding Questions
Amazon Coding Questions and Answers
On this page, the 2024 Amazon Coding Questions and Answers are discussed. One of the most crucial rounds for landing a job at Amazon is the coding round.
You can use this section to analyse the level of complexity of the Amazon problem. Understanding the level of complexity and question format for the coding phase is made easier by practising Amazon code questions and answers.
The Amazon Coding Round questions and their solutions in different languages can be found below. For a good grade, you must be prepared for the Amazon code problems.

Coding Test Format
The Amazon coding round is an important step in the interview process.
It assesses a candidate’s problem-solving skills and ability to apply algorithms and data structures to solve coding problems.
- Coding round contains 3 questions that will have to be attended in 3 hours.
- Each questions have different difficulty level.
- There is one Easy problem based on Algorithm , Aptitude and Data structures.
- One of the problem is of Medium level and that problem is based on Greedy Algorithm.
- One is of Hard difficulty level, and usually based on Dynamic Programming.
| No Of Questions | Marks per question |
|---|---|
| Question 1 | 20 |
| Question 2 | 30 |
| Question 3 | 50 |
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Question 1
Problem Statement: Check if strings are rotations of each other or not
Given two strings s1 and s2. The task is to check if s2 is a rotated version of the string s1. The characters in the strings are in lowercase.
Test Case 1:
Input:
mightandmagic
andmagicmigth
Output:
0
Explanation:
Here with any amount of rotation s2 can’t be obtained by s1.
Your Task:
The task is to complete the function areRotations() which checks if the two strings are rotations of each other. The function returns true if string 1 can be obtained by rotating string 2, else it returns false.
- Expected Time Complexity: O(N).
- Expected Space Complexity: O(N).
- Note: N = |s1|.
Constraints:
- 1 <= |s1|, |s2| <= 107
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner (System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt ();
int price[] = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i diff = new Vector <> ();
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
diff.add (price[i + 1] - price[i]);}
int ans = solve (diff); if (ans < 0)
{
System.out.println (0);}
else
{
System.out.println (ans);}
}
private static int solve (Vector v)
{
int n = v.size (); if (n == 0)
{
return 0;}
int mx = v.get (0); for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
mx = Math.max (mx, v.get (i));}
if (mx <= 0)
{
return 0;}
int mxSum = 0, csum = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
csum += v.get (i);
if (csum < 0) csum = 0; mxSum = Math.max (csum, mxSum);}
return mxSum;}
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Main
{
public:
bool Rotation(string s1,string s2)
{
int a = s1.size() - 1;
int b = s2.size() - 1;
if (a != b) {
return false;
}
string temp = s1 + s1;
if(temp.find(s2) <= a+b) { } return false; } }; int main() { int t; cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
string s1;
string s2;
cin>>s1>>s2;
Solution obj;
cout<<obj.Rotation(s1,s2)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int areRotations (char *s1, char *s2)
{
int len1 = strlen (s1);
int len2 = strlen (s2);
if (len1 != len2)
{
return 0;
}
char temp[200];
strcpy (temp, s1);
strcat (temp, s1);
if (strstr (temp, s2) != 0)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int main ()
{
char s1[100], s2[100];
printf ("Enter string 1: ");
scanf ("%s", s1);
printf ("Enter string 2: ");
scanf ("%s", s2);
int result = areRotations (s1, s2);
if (result)
{
printf ("1\n");
}
else
{
printf ("0\n");
}
return 0;
}
Question 2
Problem Statement:
Jarvis is weak in computing palindromes for Alphanumeric characters.While Ironman is busy fighting Thanos, he needs to activate sonic punch but Jarvis is stuck in computing palindromes.You are given a string S containing alphanumeric characters. Find out whether the string is a palindrome or not. If you are unable to solve it then it may result in the death of Iron Man.
Test Case 1:-
Input:
S = “I am :IronnorI Ma, i”
Output:
YES
Explanation:
Ignore all the symbols and whitespaces S = “IamIronnorIMai”. Now, Check for palindrome ignoring uppercase and lowercase English letter.
Test Case 2:-
Input:
S = Ab?/Ba
Output:
YES
Explanation:
Here with any amount of rotation s2 can’t be obtained by s1.
Your Task:
This is a function problem. The input is already taken care of by the driver code. You only need to complete the function saveIronman() that takes an string (ch), and return the true if the string is a palindrome and false if the string is not a palindrome. The driver code takes care of the printing.
- Expected Time Complexity: O(N).
- Expected Space Complexity: O(1).
Note: N = |s1|.
Constraints:
- 1 ≤ |S| ≤ 100000
Note: Consider alphabets and numbers only for palindrome check. Ignore symbols and whitespaces.
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main
{
public static void main (String[]args) throws Exception
{
BufferedReader br =
new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader (System.in));
String s = br.readLine ();
s = s.toLowerCase ();
s = s.replaceAll (" [,?/:;!]", "");
char ch[] = s.toCharArray ();
int i = 0;
int j = s.length () - 1;
boolean check = true;
while (i < j)
{
if (check (ch[i]) == false)
{
i++;
continue;
}
if (check (ch[j]) == false)
{
j--;
continue;
}
if ((ch[i] != ch[j]))
{
check = false;
break;
}
i++;
j--;
}
if (check)
System.out.println ("YES");
else
System.out.println ("NO");
}
public static boolean check (char c)
{
boolean f = false;
byte b = (byte) c;
if (b >= 97 && b <= 122)
{
return true;
}
else
{
if (c == '1' || c == '2' || c == '3' || c == '4' || c == '5'
|| c == '6' || c == '7' || c == '8' || c == '9' || c == '0')
return true;
}
return f;
}
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cctype>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
bool isPalindrome(const string& str) {
int i = 0, j = str.length() - 1;
while (i < j) {
// Skip symbols and whitespaces
while (!isalnum(str[i]) && i < j)
i++;
while (!isalnum(str[j]) && i < j)
j--;
// Convert characters to lowercase for comparison
char left = tolower(str[i]);
char right = tolower(str[j]);
if (left != right)
return false;
i++;
j--;
}
return true;
}
int main() {
string str;
getline(cin, str); // Read input string with spaces
if (isPalindrome(str))
cout << "YES\n";
else
cout << "NO\n";
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
bool isPalindrome(char ch[], int len) {
int i = 0, j = len - 1;
while (i < j) {
// Skip symbols and whitespaces
while (!isalnum(ch[i]) && i < j)
i++;
while (!isalnum(ch[j]) && i < j)
j--;
// Convert characters to lowercase for comparison
char left = tolower(ch[i]);
char right = tolower(ch[j]);
if (left != right)
return false;
i++;
j--;
}
return true;
}
int main() {
char ch[100001];
scanf(" %[^\n]s", ch); // Read input string with spaces
int len = 0;
for (int i = 0; ch[i] != '\0'; i++)
len++;
if (isPalindrome(ch, len))
printf("YES\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
return 0;
}
Question 3
Problem Statement:
Given a binary tree, print the bottom view from left to right.
A node is included in bottom view if it can be seen when we look at the tree from bottom.
20
/ \
8 22
/ \ \
5 3 25
/ \
10 14
For the above tree, the bottom view is 5 10 3 14 25.
If there are multiple bottom-most nodes for a horizontal distance from root, then print the later one in level traversal. For example, in the below diagram, 3 and 4 are both the bottommost nodes at horizontal distance 0, we need to print 4.
20
/ \
8 22
/ \ / \
5 3 4 25
/ \
10 14
For the above tree the output should be 5 10 4 14 25.
Example 1:
Input:
1
/ \
3 2
Output: 3 1 2
Explanation:
First case represents a tree with 3 nodes and 2 edges where root is 1, left child of 1 is 3 and right child of 1 is 2.
Example 2:
Input:
10
/ \
20 30
/ \
40 60
Output: 40 20 60 30
Your Task:
This is a functional problem, you don’t need to care about input, just complete the function bottomView() which takes the root node of the tree as input and returns an array containing the bottom view of the given tree.
- Expected Time Complexity: O(N).
- Expected Auxiliary Space: O(N).
Constraints:
- 1 <= Number of nodes <= 105
- 1 <= Data of a node <= 105
// C++ Program to print Bottom View of Binary Tree
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Tree node class
struct Node
{
int data; //data of the node
int hd; //horizontal distance of the node
Node *left, *right; //left and right references
// Constructor of tree node
Node(int key)
{
data = key;
hd = INT_MAX;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
// Method that prints the bottom view.
void bottomView(Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Initialize a variable 'hd' with 0
// for the root element.
int hd = 0;
// TreeMap which stores key value pair
// sorted on key value
map m;
// Queue to store tree nodes in level
// order traversal
queue q;
// Assign initialized horizontal distance
// value to root node and add it to the queue.
root->hd = hd;
q.push(root); // In STL, push() is used enqueue an item
// Loop until the queue is empty (standard
// level order loop)
while (!q.empty())
{
Node *temp = q.front();
q.pop(); // In STL, pop() is used dequeue an item
// Extract the horizontal distance value
// from the dequeued tree node.
hd = temp->hd;
// Put the dequeued tree node to TreeMap
// having key as horizontal distance. Every
// time we find a node having same horizontal
// distance we need to replace the data in
// the map.
m[hd] = temp->data;
// If the dequeued node has a left child, add
// it to the queue with a horizontal distance hd-1.
if (temp->left != NULL)
{
temp->left->hd = hd-1;
q.push(temp->left);
}
// If the dequeued node has a right child, add
// it to the queue with a horizontal distance
// hd+1.
if (temp->right != NULL)
{
temp->right->hd = hd+1;
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
// Traverse the map elements using the iterator.
for (auto i = m.begin(); i != m.end(); ++i)
cout << i->second << " ";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node *root = new Node(20);
root->left = new Node(8);
root->right = new Node(22);
root->left->left = new Node(5);
root->left->right = new Node(3);
root->right->left = new Node(4);
root->right->right = new Node(25);
root->left->right->left = new Node(10);
root->left->right->right = new Node(14);
cout << "Bottom view of the given binary tree :\n";
bottomView(root);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
// Tree node structure
typedef struct Node
{
int data; // Data of the node
int hd; // Horizontal distance of the node
struct Node *left, *right; // Left and right references
} Node;
// Constructor of tree node
Node *createNode (int key)
{
Node *newNode = (Node *) malloc (sizeof (Node));
newNode->data = key;
newNode->hd = INT_MAX;
newNode->left = newNode->right = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// Linked list to store tree nodes in level order traversal
typedef struct QueueNode
{
Node *node;
struct QueueNode *next;
} QueueNode;
// Balanced Binary Search Tree to store key value pair
typedef struct MapNode
{
int key;
int value;
struct MapNode *left;
struct MapNode *right;
} MapNode;
// Create a new MapNode and initialize its values
MapNode *createMapNode (int key, int value)
{
MapNode *newMapNode = (MapNode *) malloc (sizeof (MapNode));
newMapNode->key = key;
newMapNode->value = value;
newMapNode->left = newMapNode->right = NULL;
return newMapNode;
}
// Insert a new MapNode into the balanced BST
MapNode *insertMapNode (MapNode * node, int key, int value)
{
if (node == NULL)
return createMapNode (key, value);
if (key < node->key)
node->left = insertMapNode (node->left, key, value);
else if (key > node->key)
node->right = insertMapNode (node->right, key, value);
else
{
// Update the value for nodes with the same horizontal distance
node->value = value;
}
return node;
}
// Enqueue a tree node to the queue
void enqueue (QueueNode ** front, QueueNode ** rear, Node * node)
{
QueueNode *newQueueNode = (QueueNode *) malloc (sizeof (QueueNode));
newQueueNode->node = node;
newQueueNode->next = NULL;
if (*rear == NULL)
{
*front = *rear = newQueueNode;
return;
}
(*rear)->next = newQueueNode;
*rear = newQueueNode;
}
// Dequeue a tree node from the queue
Node * dequeue (QueueNode ** front, QueueNode ** rear)
{
if (*front == NULL)
return NULL;
QueueNode *temp = *front;
Node *node = temp->node;
*front = (*front)->next;
if (*front == NULL)
*rear = NULL;
free (temp);
return node;
}
// Method that prints the bottom view.
void bottomView (Node * root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
// Initialize a variable 'hd' with 0 for the root element.
int hd = 0;
QueueNode *front = NULL;
QueueNode *rear = NULL;
MapNode *rootMap = NULL;
// Assign initialized horizontal distance value to root node and add it to the queue.
root->hd = hd;
enqueue (&front, &rear, root);
// Loop until the queue is empty (standard level order loop)
while (front != NULL)
{
Node *temp = dequeue (&front, &rear);
// Extract the horizontal distance value from the dequeued tree node.
hd = temp->hd;
// Put the dequeued tree node to the balanced BST having key as horizontal distance.
// Every time we find a node having the same horizontal distance, we need to replace the data in the BST.
rootMap = insertMapNode (rootMap, hd, temp->data);
// If the dequeued node has a left child, add it to the queue with a horizontal distance hd-1.
if (temp->left != NULL)
{
temp->left->hd = hd - 1;
enqueue (&front, &rear, temp->left);
}
// If the dequeued node has a right child, add it to the queue with a horizontal distance hd+1.
if (temp->right != NULL)
{
temp->right->hd = hd + 1;
enqueue (&front, &rear, temp->right);
}
}
// Traverse the map elements in order and print the values
MapNode *currentNode = rootMap;
while (currentNode != NULL)
{
printf ("%d ", currentNode->value);
currentNode = currentNode->right;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main ()
{
Node *root = createNode (20);
root->left = createNode (8);
root->right = createNode (22);
root->left->left = createNode (5);
root->left->right = createNode (3);
root->right->left = createNode (4);
root->right->right = createNode (25);
root->left->right->left = createNode (10);
root->left->right->right = createNode (14);
printf ("Bottom view of the given binary tree:\n");
bottomView (root);
return 0;
}
Question 4
An expression is called the postfix expression if the operator appears in the expression after the operands.
Example :
Infix expression: A + B * C – D
Postfix expression: A B + C D – *
Given a postfix expression, the task is to evaluate the expression. The answer could be very large, output your answer modulo (10^9+7). Also, use modular division when required.
Note:
- Operators will only include the basic arithmetic operators like ‘*’, ‘/’, ‘+’, and ‘-‘.
- The operand can contain multiple digits.
- The operators and operands will have space as a separator between them.
- There won’t be any brackets in the postfix expression.
Input Format:
- The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases.
- The next ‘T’ lines represent the ‘T’ test cases.
- The first and only line of each test case contains a postfix expression.
Output Format:
- The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ denoting the number of test cases.
- For each test case, print an integer obtained by evaluating the given postfix expression.
Note:
You are not required to print the expected output; it has already been taken care of, Just implement the function.
Constraints
- 1 <= T <= 100
- 1 <= N <= 10^3
- 1 <= NUM <= 100
Where ‘N’ denotes the length of postfix expression and ‘NUM’ denotes the operand.
Time Limit: 1 sec
Sample input 1
2
2 3 1 * + 9 –
1 2 3 + * 8 –
Explanation of sample input 1:
Sample output 1
-4
-3
Test case 1:
2 3 1 * + 9 –
– : ( ) – ( )
9 : ( ) – (9)
+ : ( ( ) + ( ) ) – (9)
‘*’: ( ( ) + ( ( ) * ( ) ) ) – (9)
1 : ( ( ) + ( ( ) * (1) ) ) – (9)
3 : ( ( ) + ( (3) * (1) ) ) – (9)
2 : ( (2) + ( (3) * (1) ) ) – (9)
Result = (2 + 3) – 9 = 5 – 9 = -4
Test case 2:
1 2 3 + * 8 –
– : ( ) – ( )
8 : ( ) – (8)
* : ( ( ) * ( ) ) – (8)
+ : ( ( ) * ( ( ) + ( ) ) ) – (8)
3 : ( ( ) * ( ( ) + (3) ) ) – (8)
2 : ( ( ) * ( (2) + (3) ) ) – (8)
1 : ( (1) * ( (2) + (3) ) ) – (8)
Result = (1 * 5) – 8 = 5 – 8 = -3
Sample input 2
1
100 200 + 2 / 5 * 7 +
Explanation of sample input 2:
100 + 200 = 300
300 / 2 = 150
150 * 5 = 750
750 + 7 = 757
Sample output 2
757
// C++ program to evaluate value of a postfix expression
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// The main function that returns value
// of a given postfix expression
int evaluatePostfix (string exp)
{
// Create a stack of capacity equal to expression size
stack < int >st;
// Scan all characters one by one
for (int i = 0; i < exp.size (); ++i)
{
// If the scanned character is an operand
// (number here), push it to the stack.
if (isdigit (exp[i]))
st.push (exp[i] - '0');
// If the scanned character is an operator,
// pop two elements from stack apply the operator
else
{
int val1 = st.top ();
st.pop ();
int val2 = st.top ();
st.pop ();
switch (exp[i])
{
case '+':
st.push (val2 + val1);
break;
case '-':
st.push (val2 - val1);
break;
case '*':
st.push (val2 * val1);
break;
case '/':
st.push (val2 / val1);
break;
}
}
}
return st.top ();
}
// Driver code
int main ()
{
int t;
scanf ("%d", &t);
getchar ();
vector < string > expressions (t);
for (int i = 0; i < t; ++i)
{
char expression[1005];
fgets (expression, sizeof (expression), stdin);
expression[strcspn (expression, "\n")] = '\0';
expressions[i] = expression;
}
vector < long long >results (t);
for (int i = 0; i < t; ++i)
{
results[i] = evaluatePostfix (expressions[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < t; ++i)
{
printf ("%lld\n", results[i]);
}
return 0;
}
// C program to evaluate value of a postfix
// expression having multiple digit operands
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// Stack type
struct Stack
{
int top;
unsigned capacity;
int *array;
};
// Stack Operations
struct Stack *createStack (unsigned capacity)
{
struct Stack *stack = (struct Stack *) malloc (sizeof (struct Stack));
if (!stack)
return NULL;
stack->top = -1;
stack->capacity = capacity;
stack->array = (int *) malloc (stack->capacity * sizeof (int));
if (!stack->array)
return NULL;
return stack;
}
int isEmpty (struct Stack *stack)
{
return stack->top == -1;
}
int peek (struct Stack *stack)
{
return stack->array[stack->top];
}
int pop (struct Stack *stack)
{
if (!isEmpty (stack))
return stack->array[stack->top--];
return '$';
}
void push (struct Stack *stack, int op)
{
stack->array[++stack->top] = op;
}
// The main function that returns value
// of a given postfix expression
int evaluatePostfix (char *exp)
{
// Create a stack of capacity equal to expression size
struct Stack *stack = createStack (strlen (exp));
int i;
// See if stack was created successfully
if (!stack)
return -1;
// Scan all characters one by one
for (i = 0; exp[i]; ++i)
{
// if the character is blank space then continue
if (exp[i] == ' ')
continue;
// If the scanned character is an
// operand (number here),extract the full number
// Push it to the stack.
else if (isdigit (exp[i]))
{
int num = 0;
// extract full number
while (isdigit (exp[i]))
{
num = num * 10 + (int) (exp[i] - '0');
i++;
}
i--;
// push the element in the stack
push (stack, num);
}
// If the scanned character is an operator, pop two
// elements from stack apply the operator
else
{
int val1 = pop (stack);
int val2 = pop (stack);
switch (exp[i])
{
case '+':
push (stack, val2 + val1);
break;
case '-':
push (stack, val2 - val1);
break;
case '*':
push (stack, val2 * val1);
break;
case '/':
push (stack, val2 / val1);
break;
}
}
}
return pop (stack);
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main ()
{
char exp[] = "100 200 + 2 / 5 * 7 +";
// Function call
printf ("%d", evaluatePostfix (exp));
return 0;
}
Question 5
Asked in Infosys Placment Paper – Feb 2022
Problem Statement :
You are given a binary tree, the task is to find out the length of the longest path which contains nodes with the exact same value. It is not necessary for the path to pass through the root of the binary tree.Between two nodes, the length of the path can be defined as the number of edges contained between them.
For example, consider the following binary tree:
7
/ \
7 7
/ \ \
8 3 7
For the above tree, the length of the longest path where each node in the path has the same value is 3 and path is 7 -> 7 -> 7 -> 7
Input format:
- The first line of input contains an integer ‘T’ representing the number of test cases. Then the test cases follow.
- The only line of each test case contains elements in the level order form. The line consists of values of nodes separated by a single space. In case a node is null, we take -1 on its place.
- For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image would be:
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation:
- Level 1:
- The root node of the tree is 1
- Level 2:
- Left child of 1 = 2
- Right child of 1 = 3
- Level 3:
- Left child of 2 = 4
- Right child of 2 = null (-1)
- Left child of 3 = 5
- Right child of 3 = 6
- Level 4:
- Left child of 4 = null (-1)
- Right child of 4 = 7
- Left child of 5 = null (-1)
- Right child of 5 = null (-1)
- Left child of 6 = null (-1)
- Right child of 6 = null (-1)
- Level 5:
- Left child of 7 = null (-1)
- Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node(of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null(-1).
Note:
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree. The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Output Format:
For each test case, a single integer denoting the length of the longest path where each node in the path has the same value is printed. The output for each test case is to be printed on a separate line.
Note:
You do not need to print anything; it has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Constraints:
- 1 <= T <= 100
- 1 <= N <= 3000
- -10^9 <= data <= 10^9 and data != -1
Where ‘T’ is the number of test cases, ‘N’ is the total number of nodes in the binary tree, and “data” is the value of the binary tree node.
Time Limit: 1sec
Sample Input 1:
2
7 7 7 1 1 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
10 3 4 3 3 -1 5 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 1:
3
2
Sample Input 2:
2
1 4 5 4 4 -1 5 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
5 4 5 1 1 -1 5 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
Sample Output 2:
2
2
Explanation of Sample Input 1:
7
/ \
7 7
/ \ \
1 1 7
For the first test case, the length of the longest path where each node in the path has the same value is 3 and path is 7 -> 7 -> 7 -> 7.
10
/ \
3 4
/ \ \
3 3 5
For the second test case, the length of the longest path where each node in the path has the same value is 2 and path is 3 -> 3 -> 3.
class Main {
static class Node{
int val;
Node left, right;
};
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.val = data;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Node root = null;
root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(4);
root.right = newNode(5);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(4);
root.right.right = newNode(5);
System.out.print(longestSamevaluePath(root));
}
static int res = 0;
public static int longestSamevaluePath(Node root){
if(root == null) return 0;
solve(root);
return res;
}
public static int solve(Node root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int lHeight = solve(root.left);
int rHeight = solve(root.right);
int lchk = 0;
int rchk = 0;
if(root.left != null && root.left.val == root.val){
lchk = lHeight + 1;
}
if(root.right != null && root.right.val == root.val){
rchk = rHeight + 1;
}
res = Math.max(res, lchk + rchk);
return Math.max(lchk, rchk);
}
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
};
Node *newNode (int data)
{
Node *temp = new Node ();
temp->val = data;
temp->left = temp->right = nullptr;
return temp;
}
int res = 0;
int solve (Node * root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
int lHeight = solve (root->left);
int rHeight = solve (root->right);
int lchk = 0;
int rchk = 0;
if (root->left != nullptr && root->left->val == root->val)
{
lchk = lHeight + 1;
}
if (root->right != nullptr && root->right->val == root->val)
{
rchk = rHeight + 1;
}
res = max (res, lchk + rchk);
return max (lchk, rchk);
}
int longestSamevaluePath (Node * root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
solve (root);
return res;
}
int main ()
{
Node *root = nullptr;
root = newNode (1);
root->left = newNode (4);
root->right = newNode (5);
root->left->left = newNode (4);
root->left->right = newNode (4);
root->right->right = newNode (5);
cout << longestSamevaluePath (root) << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int val;
struct Node *left;
struct Node *right;
};
struct Node *newNode (int data)
{
struct Node *temp = (struct Node *) malloc (sizeof (struct Node));
temp->val = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
int res = 0;
int solve (struct Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int lHeight = solve (root->left);
int rHeight = solve (root->right);
int lchk = 0;
int rchk = 0;
if (root->left != NULL && root->left->val == root->val)
{
lchk = lHeight + 1;
}
if (root->right != NULL && root->right->val == root->val)
{
rchk = rHeight + 1;
}
res = (res > lchk + rchk) ? res : lchk + rchk;
return (lchk > rchk) ? lchk : rchk;
}
int longestSamevaluePath (struct Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
solve (root);
return res;
}
int main ()
{
struct Node *root = NULL;
root = newNode (1);
root->left = newNode (4);
root->right = newNode (5);
root->left->left = newNode (4);
root->left->right = newNode (4);
root->right->right = newNode (5);
printf ("%d\n", longestSamevaluePath (root));
return 0;
}
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others










import java.util.*;
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int t=0;
int n=sc.nextInt();
int arr[]=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
int c=1;
int d=sc.nextInt();
int f=sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(d%2==0){
if(arr[i]%2!=0){
t=f*c;
c++;
}
}
else{
if(arr[i]%2==0){
t=f*c;
c++;
}
}
}System.out.println(t);
}
}
n=int(input())
ar=list(map(int,input().split()))
date=int(input())
fine=int(input())
e,o=0,0
for i in range(n):
if ar[i]%2==0:
e=e+1
else:
o=o+1
if date%2==0:
if o==0:
print(“0”)
else:
print(o*fine)
else:
if e==0:
print(“0”)
else:
print(e*fine)
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println(“ENter how many people cross road”);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int arr[]=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("Enter date");
int date= sc .nextInt();
System.out.println("Enter fine amount");
int fine= sc.nextInt();
int totalfine=0;
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
if((date%2==0 && arr[i]%2!=0) ||(date%2!=0 && arr[i]%2==0)) {
totalfine +=fine;
}
}
System.out.println(totalfine);
}
TCS NQT Coding Question Day 4 Slot 1 – Question 2
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TotalFine {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int arr[] = new int[n];
for(int i=0; i<arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
int d = sc.nextInt();
int f = sc.nextInt();
sc.close();
boolean isEvenDate = d%2 == 0;
int totalFine = 0;
for(int x:arr) {
if(x%2 != 0 && isEvenDate || x%2 == 0 && !isEvenDate) {
totalFine += f;
}
}
System.out.println(totalFine);
}
}
def count_sundays(start_day, n):
# Mapping of days to their respective indices
day_map = {
‘sun’: 0,
‘mon’: 1,
‘tue’: 2,
‘wed’: 3,
‘thu’: 4,
‘fri’: 5,
‘sat’: 6
}
startindex=day_map[start_day]
first_sunday=7-startindex
if first_sunday>n:
return 0
else:
rem=n-first_sunday
return (1+(rem//7))
start_day = ‘sat’ # Starting day of the month
n_days = 30 # Number of days from the start of the month
result = count_sundays(start_day, n_days)
print(result)
n = int(input())
reg_num = []
for _ in range(n):
reg_num.append(int(input()))
d = int(input())
s = int(input())
total = 0
for num in reg_num:
if (d % 2 == 0 and num % 2 != 0) or (d % 2 != 0 and num % 2 == 0):
total += s
if total != 0 :
print(total)
else:
print(“0”)
import java.util.*;
public class main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s= new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(“enter the number of arrays: “);
int n= s.nextInt();
int []arr=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
arr[i]=s.nextInt();
} int x=300;
int d=3;
int count=0;
if(d%2!=0){
for(int j=0;j<arr.length;j++){
if(j%2==0){
count++;
}
}
}else{
for(int j=0;j<arr.length;j++){
if(j%2!=0){
count++;
}
}
}
System.out.print(count*x);
}
}
TCS NQT Coding Question Day 4 Slot 1 – Question 2
Initial=list(map(int,input().split()))
Date=int(input(“Enter the date:”))
fine1=int(input(“Enter the Fine Amount:”))
fine=0
if Date%2==0:
for i in Initial:
if i==1:
fine+=0
elif i%2!=0 :
fine+=fine1
else:
for i in Initial:
if i==1:
fine+=0
elif i%2==0 :
fine+=fine1
print(“The Total Fine amount will be:”,fine)
Day 2 slot 1-Question 2
n=int(input(“Enter number”))
a=[]
for i in range(n):
a.append(int(input()))
d=int(input(“Enter date”))
fine=int(input(“Enter fine”))
count=0
if d%2==0:
temp=1
else:
temp=0
for i in a:
if temp==1:
if i%2!=0:
count+=fine
else:
if i%2==0:
count+=fine
print(count)
Kindly refer to our discord community for all your technical doubts.
Day 4 slot 1 question 1
N = int(input())
R = int(input())
def sum_of_digits(num):
sum_of_digits = 0
for i in str(num):
sum_of_digits += int(i)
return sum_of_digits
num_sum = sum_of_digits(N)
result = num_sum * R
result_sum = sum_of_digits(result)
final_result = result_sum if R!=0 else 0
print(final_result)