0
Notifications Mark All Read
- Login
- Get Prime
JAVA Program for Insertion at the Beginning of a Doubly Linked List
Java Program for Insertion at beginning
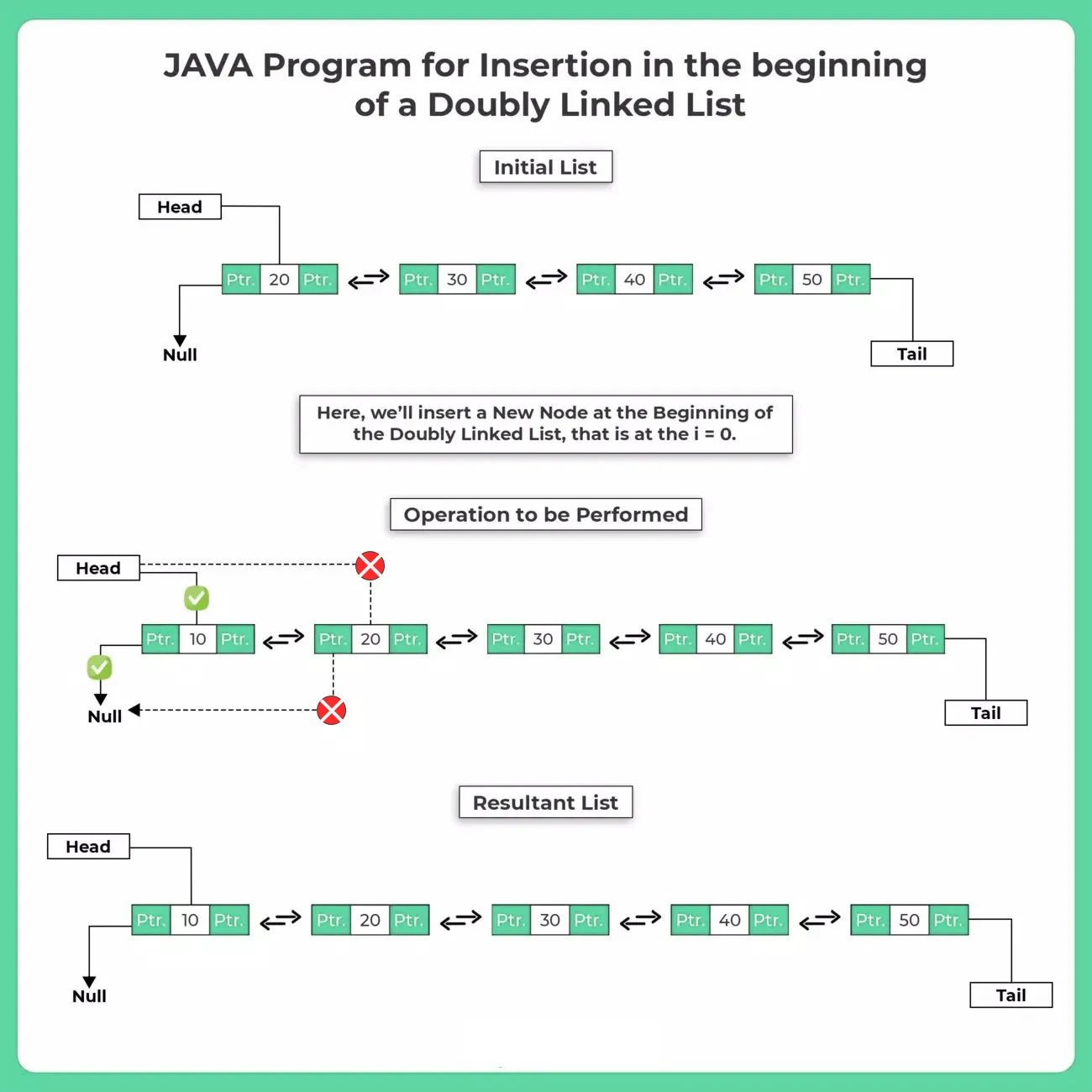
Adding or inserting a node in the beginning in doubly linked list is almost similar as the process of adding a node in singly linked list . The only difference is that we have an extra pointer (previous node) to be redirected.We will create a doubly linked list and insert every new node at the beginning of the list.

Steps to be followed while Inserting a Node at the Beginning of a Doubly Linked List
- Check for the presence of Node in the List, if there exists some Nodes, Continue.
- Now, to insert a node in the beginning of the Doubly Linked List, we’ll have to store and redirect various links of the Linked List.
- First of all the Head will now store the address of the space where the data of the New Node is stored.
- Now Since the New Node is going to be the first Node of the Linked List. So, the Previous Pointer of the New Node will point to Null.
- Then the Next Pointer of the New Node will now point to the Previously First Node of the List.
- Now, at last the Previous Pointer of the Previously First node of the list will be directed towards the New Node that is being Inserted.
Example :
If we have doubly linked listed like, (1–>2–>3–>4) and we have to add 5 at the beginning of the list then after adding linked list would look like (5–>1–>2–>3–>4 ) .
Algorithm to write a function to add a Node in the Beginning of a Linked List
- AppendStart(int data)
- Node newNode = new Node(data)
- IF HEAD == NULL
- newNode HEAD = TAIL = newNode
- HEAD.previous = NULL
- TAIL.next = NULL
- ELSE
- HEAD.previous = newNode
- newNode.next = HEAD
- newNode.previous = NULL
- HEAD = newNode
JAVA Program to Insert a Node at the Beginning of a Linked List
import java.lang.*;
class DoublyLinkedList
{
Node head;
// not using parameterized constructor would by default
// force head instance to become null
// Node head = null; // can also do this, but not required
// Node Class
class Node
{
int data;
Node next, prev;
Node (int x) // parameterized constructor
{
data = x;
next = null;
prev = null;
}
}
public void insertBeginning (int data)
{
// Creating newNode memory & assigning data value
Node freshNode = new Node (data);
freshNode.next = head;
freshNode.prev = null;
// if DLL had already >=1 nodes
if (head != null)
head.prev = freshNode;
// changing head to this
head = freshNode;
}
public void printList ()
{
Node node = head;
Node end = null;
//as linked list will end when Node reaches Null
System.out.print ("\nIn forward: ");
while (node != null)
{
System.out.print (node.data + " ");
end = node;
node = node.next;
}
System.out.print ("\nIn backward: ");
while (end != null)
{
System.out.print (end.data + " ");
end = end.prev;
}
System.out.println ();
}
}
class Main
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
DoublyLinkedList doublylist = new DoublyLinkedList ();
doublylist.insertBeginning (3);
doublylist.insertBeginning (2);
doublylist.insertBeginning (1);
doublylist.insertBeginning (4);
doublylist.insertBeginning (5);
doublylist.printList ();
}
}
Output
In forward: 5 4 1 2 3 In backward: 3 2 1 4 5
import java.lang.*;
// Node Class
class Node
{
int data;
Node next, prev;
Node (int x) // parameterized constructor
{
data = x;
next = null;
prev = null;
}
}
class Main
{
static Node insertBeginning (Node head, int data)
{
// Creating newNode memory & assigning data value
Node newNode = new Node (data);
newNode.next = head;
newNode.prev = null;
// if DLL had already >=1 nodes
if (head != null)
head.prev = newNode;
// changing head to this
head = newNode;
return head;
}
static void printList (Node temp)
{
Node end = null;
//as linked list will end when Node reaches Null
System.out.print ("\nIn forward: ");
while (temp != null)
{
System.out.print (temp.data + " ");
end = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.print ("\nIn backward: ");
while (end != null)
{
System.out.print (end.data + " ");
end = end.prev;
}
System.out.println ();
}
// required for insertAfterPosition() method
static int getLength (Node node)
{
int size = 0;
// traverse to the last node each time incrementing the size
while (node != null)
{
node = node.next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
Node head = null;
head = insertBeginning (head, 3);
head = insertBeginning (head, 2);
head = insertBeginning (head, 1);
head = insertBeginning (head, 4);
head = insertBeginning (head, 5);
printList (head);
}
}
Output
In forward: 5 4 1 2 3 In backward: 3 2 1 4 5
Prime Course Trailer
Related Banners
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
Click Here - Doubly Linked List in –
- Insertion in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at beginning in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at end in doubly linked list –
- Insertion at nth node in doubly linked list –
- Deletion in doubly linked list –
- Deletion from beginning in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from nth in doubly linked list :
- Deletion from end in doubly linked list :
- Insertion and Deletion in a doubly linked list :
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list :
Doubly Linked List
- Introduction to Doubly Linked list in Data Structure
- Doubly Linked List in – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion and Deletion in doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java
- Insertion in the middle in a doubly linked list – C | C++ | Java

 0
0


